Health
Unraveling the Mystery: What Causes Stomach Flu in the Body?

Last Updated on July 20, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
Unraveling the Mystery: What Causes Stomach Flu in the Body?
Stomach flu is a condition that impacts countless people across the globe annually, leading to substantial discomfort, distress, and disruption of daily activities.
Understanding the causes, mechanisms, and potential preventative measures surrounding this illness is key to safeguarding our health.
This comprehensive exploration of the causes of stomach flu in the body will offer an in-depth perspective on the condition, leaving no stone unturned.
Understanding Stomach Flu
Also known as viral gastroenteritis, stomach flu is an inflammation of the stomach and intestines typically caused by certain viruses.
Contrary to what its name suggests, it’s not related to the influenza virus which primarily affects the respiratory system. Stomach flu is incredibly common and can affect individuals of all ages.
Causes of Stomach Flu
The main culprits behind stomach flu are various infectious agents including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. These pathogens can enter the body through contaminated food, water, or surfaces, and direct contact with an infected person.
Viral Causes of Stomach Flu
Among viral agents, the most notorious ones include the Norovirus, Rotavirus, Adenovirus, and Astrovirus. Norovirus, often linked with contaminated food or water, is the most common cause of stomach flu in adults.
Rotavirus was once the most frequent cause of severe diarrhea among children, but the widespread use of the rotavirus vaccine has significantly reduced these cases.
Adenoviruses and Astroviruses also frequently cause stomach flu, especially in young children.
Bacterial Causes of Stomach Flu
Stomach flu can also stem from bacterial infections caused by bacteria such as Salmonella, Shigella, Campylobacter, E. coli, and Clostridium difficile.
Parasitic Causes of Stomach Flu
Parasitic infections leading to stomach flu are less common but can occur, particularly in individuals who travel frequently. Giardia and Cryptosporidium are among the most common parasitic culprits.
The Role of the Immune System
The immune system plays a vital role in managing and mitigating the effects of stomach flu. Once the pathogens infiltrate the body, they trigger an immune response. The body tries to flush out the infectious agents by causing symptoms like vomiting and diarrhea.
Symptoms and Complications
The most common symptoms include abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle aches, headache, and low-grade fever.
Complications may arise in severe cases, leading to dehydration due to excessive loss of fluids and electrolytes.
Diagnostic Techniques
Stool tests are often used to diagnose stomach flu, especially when symptoms are severe and persistent, or when an outbreak occurs in a group setting.
Treatment Options and Prevention Measures
There’s no specific cure for stomach flu. Treatment usually involves managing symptoms, rest, and hydration. Good hygiene practices and careful food handling can help prevent the disease.
Stomach Flu Vs. Food Poisoning
Stomach flu and food poisoning share similar symptoms, but they are caused by different agents and have different onsets and durations.
Stomach Flu’s Impact on Various Age Groups
Understanding the effects of stomach flu across different age demographics can offer greater insight into its impact on public health.
Stomach Flu in Children
Stomach flu is especially common in children, particularly those who attend daycare or school, given the close proximity and frequent interaction with others. Young children, in particular, are more susceptible due to their still-developing immune systems.
Symptoms can be severe, and in some cases, lead to dehydration, making it essential for parents or caregivers to ensure the child is adequately hydrated and receives appropriate medical attention when necessary.
Stomach Flu in AdultsIn adults, stomach flu can result in uncomfortable symptoms but is generally less severe than in children.
However, certain populations, such as the elderly or individuals with weakened immune systems, may experience more significant symptoms and are at higher risk of complications like dehydration4.
Navigating Through Stomach Flu Season
“Stomach flu season” typically occurs during the colder months, particularly in the fall and winter, coinciding with an increased incidence of stomach flu cases .
Understanding this seasonal pattern can help with prevention efforts, especially in high-risk environments like schools, nursing homes, and family households.
Dietary Considerations During Stomach Flu
Nutrition plays an essential role in managing stomach flu symptoms and promoting recovery. Consuming clear liquids and bland, easy-to-digest foods can help manage symptoms and prevent dehydration6. Gradually reintroducing normal foods as symptoms improve is also important.
Unresolved Myths About Stomach Flu
Despite significant advancements in understanding stomach flu, various misconceptions persist. For instance, the term “stomach flu” can be misleading as it implies a connection to the influenza virus, which is not the case.
Additionally, while some believe that you can only contract stomach flu once and then become immune, this isn’t accurate as there are multiple viruses, bacteria, and parasites that can cause the condition7.
Stomach Flu’s Impact on Various Age Groups
Understanding the effects of stomach flu across different age demographics can offer greater insight into its impact on public health.
Stomach Flu in Adults
In adults, stomach flu can result in uncomfortable symptoms but is generally less severe than in children3. However, certain populations, such as the elderly or individuals with weakened immune systems, may experience more significant symptoms and are at higher risk of complications like dehydration
Unresolved Myths About Stomach Flu
Despite significant advancements in understanding stomach flu, various misconceptions persist. For instance, the term “stomach flu” can be misleading as it implies a connection to the influenza virus, which is not the case.
Additionally, while some believe that you can only contract stomach flu once and then become immune, this isn’t accurate as there are multiple viruses, bacteria, and parasites that can cause the condition7.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary cause of stomach flu?
Stomach flu, or viral gastroenteritis, is primarily caused by viruses such as Norovirus and Rotavirus, but it can also result from certain bacteria or parasites.
Can stomach flu be prevented?
Good hygiene practices like hand washing, using clean utensils, drinking safe water, and proper food handling can significantly reduce the risk of stomach flu.
How is stomach flu diagnosed?
Stomach flu is often diagnosed based on symptoms, but stool tests may be used in severe or persistent cases.
What are the potential complications of stomach flu?
The most common complication of stomach flu is dehydration due to excessive vomiting and diarrhea. It is especially concerning in children and older adults.
Is there a cure for stomach flu?
There is no specific cure for stomach flu. The treatment usually involves managing symptoms, such as replacing lost fluids and electrolytes to prevent dehydration.
Can adults get Rotavirus?
While Rotavirus primarily affects infants and young children, adults can also get infected, though the symptoms are usually milder.
Can I catch stomach flu from someone else?
Yes, stomach flu is highly contagious. It can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by consuming contaminated food or water.
Is there a vaccine for stomach flu?
There’s no single vaccine for all causes of stomach flu. However, there are vaccines available for Rotavirus which is a common cause of stomach flu in children.
How long does stomach flu last?
Most cases of stomach flu last about 1 to 3 days. However, symptoms can sometimes persist for up to a week.
Is stomach flu the same as food poisoning?
Although the symptoms can be similar, stomach flu and food poisoning are not the same. Food poisoning is caused by consuming food or drink contaminated with bacteria, viruses, or parasites, whereas stomach flu is often caused by direct infection with these agents.
How often can you get stomach flu?
There is no set frequency for stomach flu as it’s caused by a variety of viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Therefore, it’s possible to experience it multiple times.
What foods should I eat if I have stomach flu?
It’s generally recommended to eat bland, easy-to-digest foods like rice, crackers, bananas, and chicken soup. Drinking plenty of fluids is also crucial to prevent dehydration.
Are there any long-term effects of stomach flu?
Stomach flu is typically a short-term illness and doesn’t usually lead to long-term effects. However, in cases of severe dehydration or persistent symptoms, it’s best to seek medical attention.
Why is stomach flu more common in winter?
The exact reason isn’t clear, but it could be due to people spending more time indoors in close contact with others, promoting the spread of the viruses that cause stomach flu.
Can I take antibiotics for stomach flu?
Antibiotics are not effective against viruses, which are the most common cause of stomach flu. They may be used if your stomach flu is caused by certain bacteria or parasites.
Can I become immune to stomach flu?
Because stomach flu can be caused by many different viruses, bacteria, and parasites, it’s not possible to become immune to all of them.
Is stomach flu dangerous for pregnant women?
Stomach flu itself isn’t usually dangerous for pregnant women, but dehydration, a possible complication, can be. Therefore, it’s essential to stay well-hydrated.
What’s the difference between a stomach bug and food poisoning?
A stomach bug, or stomach flu, refers to gastroenteritis caused by an infection with certain viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Food poisoning, on the other hand, results from consuming food or drink contaminated with these pathogens.
Can stress cause stomach flu?
While stress doesn’t directly cause stomach flu, it can weaken the immune system, making one more susceptible to infections, including those that cause stomach flu.
How do I clean my house after stomach flu?
It’s essential to clean and disinfect high-touch surfaces like doorknobs, bathroom fixtures, and kitchen utensils. Washing bedding, clothing, and other fabrics that the sick person has touched can also help prevent the spread of the illness.
Conclusion
While stomach flu can be unpleasant, understanding its causes and preventive measures can help mitigate its impact. The condition is often self-limiting, and with proper care and hydration, most individuals recover fully.
Health
Protein-Infused Diet Coke: The Viral ‘Dirty Soda’ Trend Taking TikTok by Storm
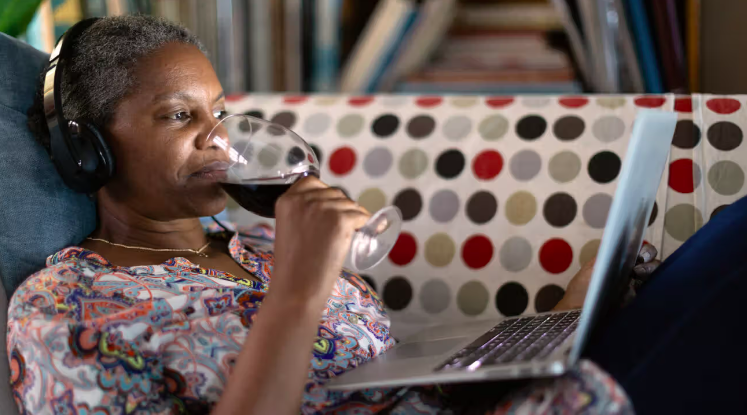

Protein-Infused Diet Coke: The Viral ‘Dirty Soda’ Trend Taking TikTok by Storm
The rise of quirky, unconventional food and drink trends is a staple of social media, but one concoction that’s recently captured TikTok’s imagination is “Protein Diet Coke,” fondly referred to as a “dirty soda.”
Combining the classic fizz of Diet Coke with creamy protein shakes, this bizarre yet fascinating combination has gained traction for its unique taste, nutritional benefits, and shareable aesthetic appeal.
But is it more than just a passing fad? Let’s dive into why this drink has taken the internet by storm, the health implications, and how you can make your own.
What Is Protein Diet Coke?
Protein Diet Coke is a mashup of two popular beverages: Diet Coke, known for its zero-calorie allure, and protein shakes, a go-to choice for fitness enthusiasts.
By blending these seemingly unrelated drinks, you get a fizzy, creamy concoction that surprises the palate and offers a protein-packed twist.
This beverage has become a TikTok sensation, with videos showcasing creative ways to personalize the drink by experimenting with flavors, toppings, and presentation.
How Did Protein Diet Coke Become a Trend?
The trend began with users sharing videos of themselves trying the drink and reacting to its surprising taste.
The hashtag #ProteinDietCoke amassed millions of views as influencers and everyday users alike showcased their custom recipes. Social media thrives on novelty, and the odd pairing of soda and protein shake fits the bill perfectly.
Moreover, this trend reflects a broader shift toward incorporating fun into fitness and healthy eating. As people explore unique ways to stay healthy, Protein Diet Coke offers a mix of indulgence and nutrition.
Health Benefits of Protein Diet Coke
1. Boosts Protein Intake:
Protein is essential for muscle repair, weight management, and overall body function. By mixing Diet Coke with a protein shake, you create a delicious way to meet your daily protein goals.
2. Low-Calorie Alternative:
For those watching their calorie intake, using Diet Coke and low-sugar protein shakes keeps the drink guilt-free while satisfying cravings for something sweet and fizzy.
3. A Fun Recovery Drink:
The combination of carbonation and protein makes this drink a potential post-workout recovery option. While traditional recovery drinks are effective, Protein Diet Coke brings a fun twist to replenishing nutrients.
Possible Drawbacks of Protein Diet Coke
While this beverage has many enthusiasts, it’s not without its critics.
1. Artificial Sweeteners:
Diet Coke contains artificial sweeteners like aspartame, which some people prefer to avoid due to potential health concerns.
2. Unusual Flavor:
Not everyone loves the combination of cola and creamy textures. For some, it’s an acquired taste.
3. Limited Nutritional Value from Soda:
Though protein shakes provide nutrients, the soda itself doesn’t offer significant health benefits. Consuming it in moderation is key.
How to Make Protein Diet Coke at Home
Ingredients:
- 1 can of Diet Coke (12 oz)
- 1 scoop or 8 oz of your favorite protein shake (vanilla or caramel flavors work best)
- Ice cubes
- Optional: toppings like whipped cream, syrups, or fruit
Instructions:
- Fill a glass with ice cubes.
- Pour the Diet Coke into the glass, leaving some space for the protein shake.
- Slowly add the protein shake to the Diet Coke. Stir gently to combine.
- Customize with toppings or syrups if desired.
- Enjoy immediately!
Why Do People Love It?
The allure of Protein Diet Coke lies in its unexpected combination and social media appeal.
The drink’s unique flavor profile intrigues people, while its aesthetic presentation makes it Instagram-worthy.
Additionally, it’s a fun way to consume protein without feeling like you’re drinking a traditional shake.
Creative Variations of Protein Diet Coke
1. Mocha Protein Soda:
Add a chocolate-flavored protein shake for a mocha-inspired treat.
2. Tropical Twist:
Use coconut-flavored protein powder and garnish with pineapple slices.
3. Spicy Cola Blend:
Mix in a dash of cinnamon or chili powder for a bold kick.
4. Vanilla Caramel Float:
Top with a dollop of whipped cream and caramel drizzle for an indulgent dessert-like drink.
Is Protein Diet Coke Here to Stay?
Trends often fade as quickly as they emerge, but Protein Diet Coke might have staying power due to its flexibility and nutritional appeal. As long as social media continues to celebrate creativity in the kitchen, this quirky beverage is likely to remain a go-to option for adventurous foodies.
Conclusion
Protein Diet Coke is more than just a viral sensation; it’s a testament to how creativity can turn everyday ingredients into something extraordinary.
While it may not replace traditional sources of protein or be everyone’s cup of tea (or soda), it has undeniably carved out a niche in the world of health-conscious indulgence.
Whether you’re in it for the taste, the health benefits, or the TikTok-worthy moments, this “dirty soda” trend is worth a try.
FAQs
1. Can I use regular Coke instead of Diet Coke?
Yes, but keep in mind that regular Coke has significantly more sugar and calories, which might defeat the purpose of a low-calorie drink.
2. What type of protein shake works best?
Vanilla and caramel protein shakes are popular choices because they complement the flavor of cola. However, feel free to experiment with other flavors.
3. Is Protein Diet Coke suitable for kids?
While it’s not inherently harmful, the caffeine content in Diet Coke might not be suitable for children. Opt for caffeine-free soda if making this for kids.
4. Can I make a vegan version?
Absolutely! Use plant-based protein shakes and ensure the soda is vegan-friendly.
5. How often can I drink Protein Diet Coke?
Like any treat, moderation is key. Consuming it occasionally as part of a balanced diet is perfectly fine.
References
Health
STI Epidemic: Decline in New Syphilis and Gonorrhea Cases in the US, CDC Reports
Health
Dave Coulier Opens Up About His Battle with Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
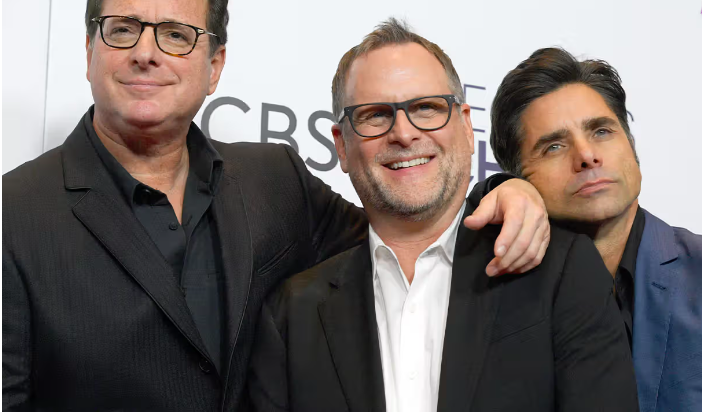

Dave Coulier Opens Up About His Battle with Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
A Beloved Star Faces a Serious Diagnosis
Dave Coulier, best known for his role as Joey Gladstone on the iconic sitcom Full House, has revealed a deeply personal health challenge.
The comedian and actor recently announced his diagnosis of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, sparking widespread concern and support from fans worldwide.
Coulier’s bravery in sharing his journey sheds light on this complex form of cancer, its symptoms, treatment options, and the importance of early detection.
What is Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
Understanding the Disease
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL) is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, which is an integral part of the body’s immune defense.
This form of lymphoma is distinct from Hodgkin’s lymphoma due to differences in the cancerous cells’ appearance and behavior.
- Lymphatic System’s Role: It helps fight infections and regulates fluid balance in the body.
- Lymphoma’s Impact: NHL occurs when lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors.
Dave Coulier’s Journey: From Diagnosis to Awareness
The Diagnosis
Coulier disclosed that he had been feeling fatigued and unwell for several months before seeking medical advice.
A series of diagnostic tests, including a biopsy and imaging scans, confirmed the presence of Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.
How He Shared the News
In a heartfelt video shared with his fans, Coulier discussed his diagnosis candidly. The star emphasized the importance of listening to one’s body and seeking medical help when something feels off.
“I’ve always tried to make people laugh, but now, I want to use my voice to educate and inspire,” he said.
Symptoms of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Recognizing the symptoms early can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes.
Some common symptoms include:
- Swollen lymph nodes, often painless
- Persistent fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fever and night sweats
- Abdominal pain or swelling
- Chest pain, coughing, or trouble breathing
Why Early Detection Matters
Coulier’s journey highlights the importance of not ignoring persistent symptoms. Timely diagnosis can improve treatment effectiveness and overall prognosis.
Stages of Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
NHL is categorized into four stages based on its spread:
- Stage 1: Cancer is localized to one lymph node region.
- Stage 2: Two or more lymph node regions on the same side of the diaphragm are affected.
- Stage 3: Cancer involves lymph nodes on both sides of the diaphragm.
- Stage 4: The disease has spread beyond the lymphatic system to other organs.
Coulier’s diagnosis at Stage 3 underscores the critical need for awareness and early intervention.
Treatment Options for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Tailored Treatment Plans
The treatment for NHL varies depending on the stage and specific subtype.
Common approaches include:
- Chemotherapy: Often the first line of defense to target rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- Radiation Therapy: Used to shrink tumors in localized areas.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system’s ability to fight cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Dave Coulier’s Treatment Regimen
While Coulier hasn’t shared detailed specifics about his treatment, he expressed gratitude for his medical team and the support of loved ones.
Living with Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Physical and Emotional Challenges
Coping with cancer involves more than just physical treatments. Patients often face emotional struggles, including anxiety, fear, and uncertainty.
Coulier’s Positive Outlook
Despite his diagnosis, Coulier remains optimistic, often sharing moments of humor and gratitude. His resilience inspires others battling similar challenges.
Raising Awareness for Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
The Power of Advocacy
Coulier is using his platform to spread awareness about NHL. His message encourages individuals to prioritize their health and support ongoing cancer research.
Supporting Research and Treatment Advances
Progress in lymphoma treatment, such as CAR T-cell therapy and advancements in immunotherapy, offers hope for patients worldwide.
How Fans Can Show Their Support
Messages of Encouragement
Fans have flooded social media with messages of love and encouragement for Coulier. Sharing personal stories of resilience and hope strengthens the community of those affected by lymphoma.
Donating to Lymphoma Research
Supporting organizations focused on lymphoma research and patient advocacy can make a significant impact.
Conclusion:
Dave Coulier’s openness about his battle with Stage 3 Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma reminds us of the importance of health awareness and community support. As he navigates this challenging chapter, his strength and advocacy serve as a beacon of hope for others facing similar battles.
FAQs
1. Can Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma be cured?
Yes, many cases of NHL can be treated effectively, especially when diagnosed early. Advanced treatments have improved survival rates significantly.
2. How does Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma differ from Hodgkin’s Lymphoma?
The primary difference lies in the specific type of cancerous cells. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma involves Reed-Sternberg cells, which are absent in NHL.
3. Are there lifestyle factors that increase the risk of NHL?
While the exact cause is unknown, factors like a weakened immune system, certain infections, and exposure to specific chemicals can increase risk.
4. What support resources are available for NHL patients?
Numerous organizations, such as the Lymphoma Research Foundation, offer resources, support groups, and financial assistance for patients and their families.
5. How can I reduce my risk of developing lymphoma?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, avoiding exposure to harmful chemicals, and addressing infections promptly can help lower your risk.
References:
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health8 months ago
Health8 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know






