Child Health
How to Protect Your Child from Measles: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
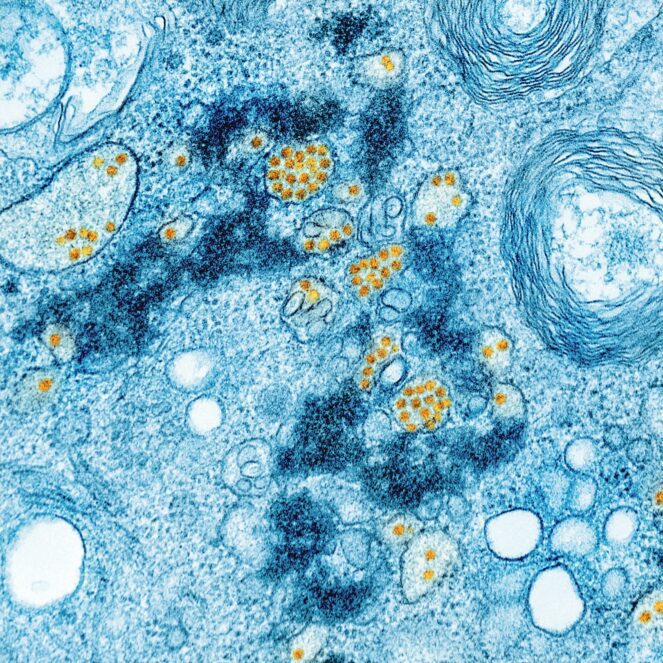
Measles, a highly contagious viral infection, can pose a significant risk to children’s health. As a parent, it is crucial to take proactive measures to protect your child from this potentially dangerous disease. In this comprehensive guide, we will discuss various strategies and precautions you can take to safeguard your child’s well-being.
Understanding Measles
Before diving into preventive measures, it is essential to understand what measles is and how it spreads. Measles is caused by the measles virus and primarily affects the respiratory system. It spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. The virus can survive in the air and on surfaces for several hours, making it highly contagious.
Vaccination: The Best Defense
The most effective way to protect your child from measles is through vaccination. The measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) vaccine is safe, highly effective, and recommended by healthcare professionals worldwide. It provides long-term immunity against measles and significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Ensure that your child receives the MMR vaccine according to the recommended schedule. The first dose is typically administered around 12-15 months of age, followed by a second dose between 4-6 years. Vaccination not only protects your child but also contributes to overall community immunity, preventing the spread of the disease.
Healthy Hygiene Practices
In addition to vaccination, practicing good hygiene habits can help minimize the risk of measles transmission. Encourage your child to:
- Wash their hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoid touching their face, especially their eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Cover their mouth and nose with a tissue or their elbow when coughing or sneezing.
- Dispose of used tissues properly and wash their hands afterward.
Avoiding Exposure
Measles is highly contagious, and exposure to infected individuals increases the risk of transmission. Take the following precautions to minimize your child’s exposure:
- Avoid close contact with individuals showing symptoms of measles, such as coughing, sneezing, and fever.
- Avoid crowded places, especially during outbreaks.
- If traveling to areas with known measles outbreaks, ensure that your child is adequately vaccinated beforehand.
Recognizing Measles Symptoms
Being able to identify the early signs of measles is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- High fever
- Cough
- Runny nose
- Red, watery eyes
- Rash that starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body
If your child exhibits these symptoms, contact their healthcare provider immediately for guidance and avoid exposing others to the infection.
Conclusion
Protecting your child from measles requires a combination of vaccination, healthy hygiene practices, and avoiding exposure to infected individuals. By taking proactive measures and staying informed, you can significantly reduce the risk of your child contracting this potentially serious disease. Remember, prevention is key when it comes to safeguarding your child’s health.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can measles be deadly?
While most individuals recover from measles without complications, it can lead to severe complications, especially in young children and individuals with weakened immune systems.
2. Is the MMR vaccine safe?
Yes, the MMR vaccine is considered safe and has undergone extensive testing to ensure its safety and efficacy.
3. Can my child still get measles if they have been vaccinated?
While the MMR vaccine is highly effective, there is a small chance of breakthrough infection. However, vaccinated individuals usually experience milder symptoms and a lower risk of complications.
4. Are there any side effects of the MMR vaccine?
Most children experience no side effects from the MMR vaccine. Mild side effects, such as fever or rash, may occur but are generally short-lived.
5. Can adults get measles?
Yes, adults who have not been vaccinated or previously infected with measles can still contract the virus. It is important for adults to ensure they are up to date with their vaccinations.
6. How long does immunity from the MMR vaccine last?
The MMR vaccine provides long-term immunity, and most individuals remain protected for life after receiving the recommended doses.
7. Are there any specific travel recommendations for measles prevention?
If traveling to areas with known measles outbreaks, it is crucial to ensure that both children and adults are adequately vaccinated before departure. Consult with your healthcare provider for specific recommendations.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and recommendations.
Child Health
Understanding the 5 Causes of Diarrhoea in Children

Understanding the 5 Causes of Diarrhoea in Children
Diarrhoea is a common health issue that affects children worldwide. It can be caused by various factors, and understanding these causes is crucial for prevention and effective management. In this article, we will explore the five main causes of diarrhoea in children and provide valuable insights into each.
1. Viral Infections
One of the leading causes of diarrhoea in children is viral infections. Viruses such as rotavirus and norovirus can easily spread through contaminated food, water, or close contact with infected individuals. These infections often result in watery stools, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
2. Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Escherichia coli (E. coli), Salmonella, or Campylobacter, can also lead to diarrhoea in children. These bacteria are commonly found in contaminated food, water, or poor hygiene practices. Symptoms may include bloody stools, fever, and severe abdominal cramps.
3. Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections, like giardiasis or cryptosporidiosis, can cause diarrhoea in children. These parasites are often found in contaminated water sources or unsanitary environments. Symptoms may include persistent diarrhoea, weight loss, and fatigue.
4. Food Intolerance
Food intolerance, especially to lactose or gluten, can trigger diarrhoea in children. Lactose intolerance occurs when the body lacks the enzyme needed to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products. Gluten intolerance, known as celiac disease, occurs when the body reacts negatively to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye.
5. Medications and Antibiotics
Some medications and antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut, leading to diarrhoea in children. This condition, known as antibiotic-associated diarrhoea, can occur during or after antibiotic treatment. It is essential to follow proper dosage guidelines and consult a healthcare professional when administering medications to children.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How can I prevent viral infections in children?
To prevent viral infections, ensure that children receive recommended vaccinations, practice good hand hygiene, and avoid close contact with infected individuals.
2. What should I do if my child has diarrhoea due to a bacterial infection?
If your child has diarrhoea due to a bacterial infection, it is essential to seek medical attention. The healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics or recommend specific treatment measures based on the severity of the infection.
3. Are there any natural remedies for diarrhoea in children?
While maintaining hydration is crucial, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. Natural remedies should be used with caution and under medical guidance.
4. Can food allergies cause diarrhoea in children?
Food allergies can cause various symptoms, including diarrhoea, in children. If you suspect a food allergy, it is important to consult an allergist for proper diagnosis and guidance on managing the condition.
5. How long does diarrhoea usually last in children?
The duration of diarrhoea can vary depending on the cause and individual factors. In most cases, diarrhoea resolves within a few days to a week. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
6. Can stress or anxiety cause diarrhoea in children?
Stress and anxiety can affect the digestive system and potentially contribute to diarrhoea in children. If you suspect stress or anxiety is a contributing factor, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and management.
7. When should I be concerned about my child’s diarrhoea?
If your child experiences severe dehydration, persistent high fever, bloody stools, or signs of lethargy, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention.
Remember, understanding the causes of diarrhoea in children and taking preventive measures can significantly contribute to their overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Diarrhoea in children can have various causes, including viral and bacterial infections, parasitic infections, food intolerance, and medications. Understanding these causes is crucial for prevention, early detection, and appropriate treatment.
Maintaining good hygiene practices, providing clean and safe drinking water, and promoting a balanced diet are essential steps in reducing the risk of diarrhoea in children.
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know