Women's Health
Understanding Ovarian Cysts and their Impact on Fertility
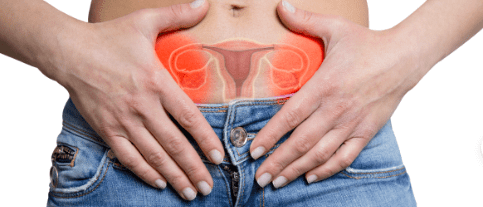
How Ovarian Cysts Can Cause Infertility Understanding Ovarian Cysts
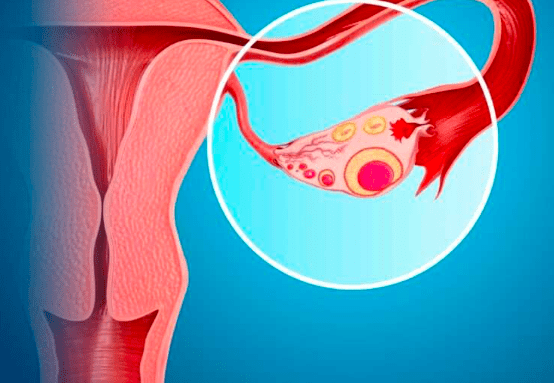
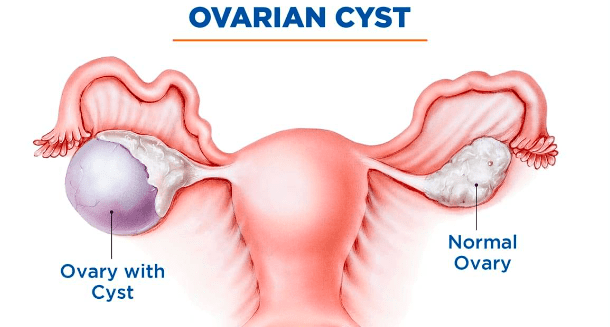
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that develop on the ovaries, which are the reproductive organs in women. While most cysts are harmless and resolve on their own, some can cause complications, including infertility.
In this article, we will explore how ovarian cysts can impact a woman’s fertility and the available treatment options.
The Link Between Ovarian Cysts and Infertility
Effects on Ovulation
One of the primary ways ovarian cysts can lead to infertility is by affecting the ovulation process. Ovarian cysts can disrupt the regular hormonal balance and interfere with the release of mature eggs from the ovaries. This can result in irregular or absent ovulation, making it difficult for women to conceive.
Distorted Fallopian Tubes
In some cases, ovarian cysts can cause the fallopian tubes to become distorted or blocked. The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in fertility as they are responsible for transporting the eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. When the tubes are damaged or obstructed, the sperm cannot reach the egg, preventing fertilization from occurring.
Increased Risk of Endometriosis
Certain types of ovarian cysts, such as endometriomas, are associated with endometriosis. Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue that lines the uterus grows outside of it.
This can lead to the formation of scar tissue and adhesions, which can affect the function of the reproductive organs and cause infertility.
Treatment Options
If you suspect that ovarian cysts are affecting your fertility, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They will evaluate your condition and recommend the most appropriate treatment options. Here are some common approaches:
Medication
In cases where the cysts are small and not causing significant symptoms, your doctor may prescribe medications to help shrink or dissolve the cysts. These medications can regulate hormone levels and promote regular ovulation.
Surgical Intervention
If the cysts are large, causing severe pain, or affecting fertility, surgery may be necessary. The surgical procedure, known as cystectomy, involves removing the cyst while preserving the healthy ovarian tissue. In some cases, the entire ovary may need to be removed.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)
For women with severe ovarian cysts or other underlying fertility issues, in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be recommended. IVF involves fertilizing the eggs with sperm in a laboratory and then transferring the resulting embryos into the uterus. This bypasses any issues caused by the cysts or other fertility complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can all types of ovarian cysts cause infertility?
No, not all types of ovarian cysts can cause infertility. Some cysts, such as functional cysts, are harmless and do not affect fertility. However, certain types, such as endometriomas, can increase the risk of infertility.
2. Can ovarian cysts resolve on their own?
Yes, many ovarian cysts resolve on their own without any treatment. However, if the cysts are causing significant symptoms or affecting fertility, medical intervention may be necessary.
3. Are there any lifestyle changes that can help prevent ovarian cysts?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent ovarian cysts, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk. This includes regular exercise, a balanced diet, and managing stress levels.
4. Can ovarian cysts cause pain?
Yes, ovarian cysts can cause pain, especially if they become large or rupture. The pain may be sharp or dull and can occur in the lower abdomen or pelvis.
5. Can ovarian cysts increase the risk of ovarian cancer?
Most ovarian cysts are benign and do not increase the risk of ovarian cancer. However, certain types of cysts, such as dermoid cysts or cystadenomas, may have a higher risk of developing cancer.
6. Can ovarian cysts affect hormone levels?
Yes, ovarian cysts can disrupt the normal hormonal balance in the body. This can lead to irregular menstrual cycles, mood changes, and other hormonal symptoms.
7. Can fertility treatments increase the risk of ovarian cysts?
Some fertility treatments, such as ovarian stimulation medications used in IVF, can increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts. However, these cysts are typically temporary and resolve on their own.
Conclusion
Ovarian cysts can have a significant impact on a woman’s fertility. They can disrupt ovulation, damage the fallopian tubes, and increase the risk of conditions like endometriosis.
However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, many women with ovarian cysts can still conceive and have a healthy pregnancy. If you suspect that ovarian cysts are affecting your fertility, it is crucial to seek medical advice and explore the available treatment options.
Women's Health
Understanding and Managing Breast Discomfort during Pregnancy

Tips for Managing Breast Discomfort during Pregnancy
Health and well-being are essential aspects of our lives that should never be overlooked. Taking care of our physical and mental health is crucial for leading a fulfilling and productive life. In this blog post, we will explore the significance of health and provide valuable insights on how to prioritize and maintain it.
The Early Stages of Pregnancy: Understanding Discomfort
Pregnancy is a miraculous journey that brings joy and anticipation to expectant parents. However, it is also a time when women may experience various discomforts, especially in the early stages. One common question that arises is, “What area of the breast is most uncomfortable during pregnancy?”
During the early stages of pregnancy, hormonal changes and increased blood flow can lead to breast tenderness and sensitivity. Many women report feeling discomfort in the outer areas of their breasts, closer to the armpits. This discomfort is often described as a feeling of heaviness or soreness.
It is important to note that every woman’s experience is unique, and some may not experience any breast discomfort at all. If you have concerns or experience severe pain, it is always advisable to consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
The Importance of Health and Well-being
While breast discomfort during pregnancy is common, several strategies can help alleviate the discomfort:
- Wear a supportive bra: Investing in a well-fitting, supportive bra can provide relief by reducing breast movement and providing extra support.
- Apply warm or cold compresses: Experiment with warm or cold compresses to find what brings you the most relief. Some women find comfort in warm compresses, while others prefer cold compresses.
- Practice gentle exercises: Engaging in gentle exercises, such as walking or prenatal yoga, can help improve circulation and reduce discomfort.
- Avoid caffeine: Limiting your intake of caffeine, found in coffee, tea, and some sodas, may help reduce breast tenderness.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day can help maintain overall breast health and minimize discomfort.
Remember, it is essential to listen to your body and prioritize self-care during this transformative time. If you have any concerns or questions, do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Frequently Asked Questions about Breast Discomfort during Pregnancy
1. Can breast discomfort be a sign of pregnancy?
Yes, breast discomfort can be one of the early signs of pregnancy. Hormonal changes in the body can lead to breast tenderness and sensitivity.
2. How long does breast discomfort last during pregnancy?
The duration of breast discomfort during pregnancy varies from woman to woman. Some may experience it throughout their pregnancy, while others may find relief as their bodies adjust to hormonal changes.
3. Are there any natural remedies for relieving breast discomfort?
Yes, several natural remedies may help alleviate breast discomfort during pregnancy. These include wearing a supportive bra, applying warm or cold compresses, practicing gentle exercises, avoiding caffeine, and staying hydrated.
4. When should I seek medical advice for breast discomfort during pregnancy?
If you experience severe or persistent breast pain, or if you notice any unusual changes in your breasts, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider for proper evaluation and guidance.
5. Can breastfeeding worsen breast discomfort?
While breastfeeding can cause temporary breast discomfort, it is usually a result of engorgement or improper latch. Seeking guidance from a lactation consultant can help address any breastfeeding-related discomfort.
6. Are there any specific foods that can help reduce breast discomfort during pregnancy?
While there are no specific foods proven to alleviate breast discomfort, maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet can contribute to overall breast health. Focus on consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
7. Is it normal to experience no breast discomfort during pregnancy?
Yes, it is entirely normal for some women to experience no breast discomfort during pregnancy. Every woman’s experience is unique, and the absence of breast discomfort does not indicate any problems with the pregnancy.
Conclusion
During the early stages of pregnancy, breast discomfort is a common occurrence for many women. Understanding the areas of the breast that are most uncomfortable and implementing strategies to manage the discomfort can greatly improve the overall pregnancy experience. Remember to prioritize self-care, seek guidance from healthcare professionals when needed, and embrace the transformative journey of pregnancy with confidence and joy.
Women's Health
The Effectiveness of Non-Surgical Treatments for Fibroids

The Effectiveness of Non-Surgical Treatments for Fibroids
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They can cause a range of symptoms, including heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on the bladder or bowel. While surgery is often recommended for severe cases, non-surgical treatments have gained popularity in recent years. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of these non-surgical options and their potential benefits for women with fibroids.
1. Hormonal Therapy
Hormonal therapy, such as birth control pills or hormone-releasing intrauterine devices (IUDs), can help manage the symptoms of fibroids. These treatments work by regulating the menstrual cycle and reducing heavy bleeding. While hormonal therapy does not shrink or eliminate fibroids, it can provide relief from symptoms and improve a woman’s quality of life.
2. Uterine Artery Embolization (UAE)
Uterine artery embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that involves blocking the blood supply to the fibroids. This causes them to shrink and die over time. UAE has been shown to be effective in reducing fibroid size and alleviating symptoms. It is a viable alternative to surgery for women who wish to preserve their fertility or avoid the risks associated with surgery.
3. Magnetic Resonance-guided Focused Ultrasound (MRgFUS)
MRgFUS is a non-invasive procedure that uses high-intensity focused ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the fibroids. This treatment is performed inside an MRI scanner, allowing doctors to precisely target the fibroids while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue. MRgFUS has been found to be effective in reducing fibroid size and relieving symptoms, with minimal side effects and a quick recovery time.
While these non-surgical treatments offer promising results, it is important to note that their effectiveness may vary depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids. It is crucial for women to consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment option for their individual case.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Are non-surgical treatments suitable for all women with fibroids?
Non-surgical treatments may not be suitable for all women with fibroids. The effectiveness of these treatments can vary depending on the size, number, and location of the fibroids. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
2. Can non-surgical treatments completely eliminate fibroids?
Non-surgical treatments do not typically eliminate fibroids completely. However, they can help reduce the size of the fibroids and alleviate symptoms. In some cases, additional treatments or surgery may be necessary for complete fibroid removal.
3. What are the advantages of non-surgical treatments over surgery?
Non-surgical treatments offer several advantages over surgery, including a quicker recovery time, less risk of complications, and the ability to preserve fertility. These treatments can provide relief from fibroid symptoms without the need for invasive procedures.
4. Are there any side effects associated with non-surgical treatments?
While non-surgical treatments generally have fewer side effects compared to surgery, they can still cause certain discomforts. Common side effects may include temporary pelvic pain, cramping, or vaginal discharge. It is important to discuss potential side effects with a healthcare provider before undergoing any treatment.
5. How long do the effects of non-surgical treatments last?
The effects of non-surgical treatments can vary from woman to woman. Some women may experience long-term relief from symptoms, while others may require additional treatments in the future. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor the progress and effectiveness of the chosen treatment.
6. Can non-surgical treatments affect fertility?
Non-surgical treatments, such as hormonal therapy, may have an impact on fertility. It is important to discuss fertility concerns with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment. Some non-surgical options, like UAE, may be more suitable for women who wish to preserve their fertility.
7. How do I know which non-surgical treatment is right for me?
The choice of non-surgical treatment depends on various factors, including the size, number, and location of the fibroids, as well as the individual’s symptoms and fertility goals. It is recommended to consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in fibroid treatment to determine the most appropriate option for your specific case.
Conclusion
Non-surgical treatments for fibroids have revolutionized the management of this common condition. From hormonal therapy to minimally invasive procedures like UAE and MRgFUS, women now have more options to alleviate their symptoms and improve their quality of life. While surgery may still be necessary in some cases, these non-surgical treatments offer a less invasive alternative with fewer risks and a quicker recovery time. It is essential for women to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most effective treatment plan for their specific needs.
Women's Health
The Truth About Fibroids: Can They Come Back After Non-Surgical Treatment?
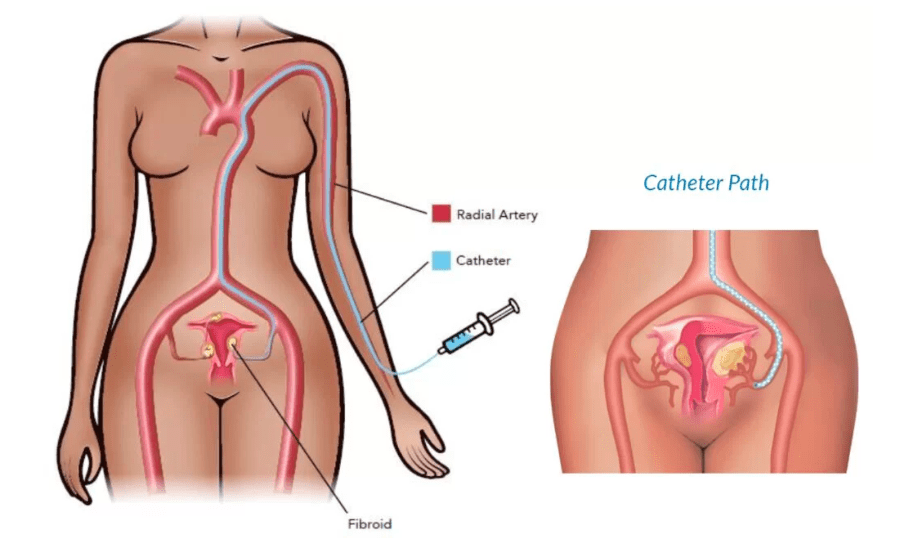
The Truth About Fibroids: Can They Come Back After Non-Surgical Treatment?
Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in the uterus. They can vary in size and may cause symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and frequent urination.
Non-surgical treatments, such as medication and minimally invasive procedures, are often recommended to manage fibroids. However, a common concern among patients is whether fibroids can come back after undergoing these treatments.
Understanding Fibroids and Non-Surgical Treatment
Before we delve into the possibility of fibroids returning after non-surgical treatment, let’s first understand what fibroids are and how non-surgical treatment options work.
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are benign tumors that develop from the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus. They can range in size from small, undetectable growths to large masses that can distort the shape of the uterus. Fibroids are common, with studies estimating that up to 70% of women will develop them during their lifetime.
Non-surgical treatments for fibroids aim to alleviate symptoms and reduce the size of the fibroids. These treatments can include hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, which help regulate the menstrual cycle and shrink the fibroids.
Minimally invasive procedures, such as uterine artery embolization or focused ultrasound surgery, use targeted methods to destroy or shrink the fibroids.
The Possibility of Fibroids Returning
While non-surgical treatments can provide relief from fibroid symptoms and reduce their size, there is a possibility of fibroids returning after treatment. The likelihood of recurrence depends on various factors, including the size and location of the fibroids, the effectiveness of the treatment, and individual patient characteristics.
It’s important to note that fibroids are a chronic condition, and even with successful treatment, new fibroids can develop over time. Additionally, if any small fibroids were not fully treated during the initial procedure, they may grow and cause symptoms in the future.
Preventing Fibroid Recurrence
While it may not be possible to completely prevent fibroids from recurring, there are steps that can be taken to minimize the risk:
- Regular follow-up appointments: After undergoing non-surgical treatment for fibroids, it’s crucial to attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. These appointments allow for monitoring of any new fibroid growth and prompt intervention if necessary.
- Lifestyle modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help manage fibroids and reduce the chances of recurrence. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, managing stress levels, and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
- Continued symptom monitoring: Stay attuned to your body and be mindful of any changes or symptoms that may indicate fibroid recurrence. If you experience heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, or other concerning symptoms, consult with your healthcare provider.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can fibroids come back after non-surgical treatment?
Yes, there is a possibility of fibroids returning after non-surgical treatment. The likelihood of recurrence depends on various factors, including the size and location of the fibroids, the effectiveness of the treatment, and individual patient characteristics.
2. What are the non-surgical treatment options for fibroids?
Non-surgical treatment options for fibroids include hormonal medications, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists, as well as minimally invasive procedures like uterine artery embolization or focused ultrasound surgery.
3. How can I prevent fibroid recurrence?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent fibroids from recurring, regular follow-up appointments, lifestyle modifications, and continued symptom monitoring can help minimize the risk of recurrence. Working closely with your healthcare provider is essential in developing an individualized plan.
4. What are the symptoms of fibroid recurrence?
The symptoms of fibroid recurrence can vary but may include heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination, and pressure in the pelvic area. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any concerning symptoms.
5. Are there any natural remedies to prevent fibroid recurrence?
While there is limited scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of natural remedies in preventing fibroid recurrence, some women find relief through practices such as acupuncture, herbal supplements, and dietary changes. It’s important to discuss these options with your healthcare provider before trying them.
6. Can fibroids turn into cancer?
Fibroids are non-cancerous tumors and do not typically turn into cancer. However, in rare cases, a type of cancer called leiomyosarcoma can develop in the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus. It’s important to consult with your healthcare provider if you have any concerns or unusual symptoms.
7. Can pregnancy affect fibroid recurrence?
Pregnancy can potentially affect fibroid recurrence, as hormonal changes and the expansion of the uterus during pregnancy may stimulate fibroid growth. However, every pregnancy and its impact on fibroids are unique to each individual. Consulting with your healthcare provider is essential for personalized guidance.
Conclusion
Fibroids are a common condition that can cause significant discomfort and disrupt daily life. Non-surgical treatments offer effective options for managing fibroids and reducing symptoms. While there is a possibility of fibroids returning after non-surgical treatment, regular follow-up appointments, lifestyle modifications, and symptom monitoring can help minimize the risk of recurrence. It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan and address any concerns or questions you may have.
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know