Health
Why My Mouth Is Sweet? 5 Things you need to know

Last Updated on May 15, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
Why My Mouth Is Sweet? 5 Things you need to Know
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the sweet taste in our mouths and why it occurs.
Have you ever wondered why your mouth sometimes tastes sweet?
In this article, we will delve into the various factors that contribute to the sensation of sweetness in the mouth. From underlying medical conditions to dietary factors, we will explore five key aspects that can help you better understand why your mouth might have a sweet taste. So, let’s dive right in!
Understanding Taste Perception
How Taste Works in Our Mouths
Taste perception is a fascinating process that involves multiple sensory receptors on our tongues. Our taste buds play a crucial role in detecting different flavors, including sweetness.
When we consume food or beverages, the taste receptors on our taste buds send signals to our brain, enabling us to experience and differentiate various tastes, such as sweet, sour, bitter, salty, and umami.
The Role of Sweet Taste Receptors
Sweet taste receptors are responsible for detecting the presence of sugars in our mouth. These receptors are primarily located on the tip of the tongue. When stimulated by sugars or artificial sweeteners, the receptors send signals to the brain, resulting in the perception of sweetness.
Natural Causes of Sweet Taste in the Mouth
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can sometimes lead to a sweet taste in the mouth. Conditions such as diabetes, hypoglycemia, and hyperinsulinemia can affect glucose metabolism, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. This excess glucose may spill into the saliva, leading to a sweet taste.
Medications and Supplements
Certain medications and supplements can cause an altered taste perception, including a sweet taste in the mouth. Examples include antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, and some cardiovascular medications. If you notice a persistent sweet taste while taking these medications, it’s essential to consult your healthcare provider.
Oral Health and Sweet Taste Dental Issues and Oral Infections
Dental problems can contribute to a sweet taste in the mouth. Tooth decay, gum disease, or oral infections can result in the accumulation of bacteria or plaque, leading to an unpleasant taste. Maintaining good oral hygiene, such as regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can help prevent these issues.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
A dry mouth occurs when there is insufficient saliva production. This condition can be caused by various factors, such as certain medications, dehydration, or underlying health conditions. A dry mouth can create an altered taste sensation, including a sweet or metallic taste. Drinking plenty of water and using saliva-stimulating products may alleviate this symptom.
Dietary Factors and Sweet Taste High Sugar Intake
Consuming excessive amounts of sugary foods and beverages can lead to a persistent sweet taste in the mouth. When we overload our taste buds with sugar, they may become desensitized, resulting in a lingering sweet sensation. It is crucial to maintain a balanced diet and limit sugar intake to prevent such taste disturbances.
Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners, commonly used as sugar substitutes, can also contribute to a sweet taste in the mouth. These low-calorie additives can trigger sweet taste receptors without actually providing the calories associated with sugar. Overconsumption or sensitivity to artificial sweeteners may result in a constant sweet taste.
Seeking Medical Advice When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
If you experience a persistent sweet taste in your mouth, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment. They will evaluate
There are many reasons why you may have a sweet taste in your mouth. Several of them have to do with nerve damage, bad eating habits, or pregnancy. Others have no obvious explanation.
But if you find that you have a sweet taste in your mouth, you may want to check out our tips below. Here we’ll look at some of the more common causes of this annoying problem.
You can start by identifying the frequency of your sweet mouth. If you’ve experienced it frequently, you should also determine if there are any unusual symptoms.
Those signs might help you determine the next course of action. You may approach a medical specialist to help you figure out the cause of your mouth’s sweet taste, or you can simply wait it out and let the taste subside on its own.
Retiring sweetness is attributed to drinking water
When we drink water, we sometimes perceive its taste as sweet, which is due to the presence of residue on our tongue. Those residues can be traced back to sugary or sour foods, altering the chemicals in our mouths.
This temporarily changes the taste of water, and this flavor dissipates when we rinse our mouths. While the sweet taste will fade with time, it’s important to understand why some people perceive water as having a sweetness that lasts for just a short period of time.
Retiring sweetness is an affliction of the olfactory system. Its chemical response to foods and drinks can give water a sweet flavor.
However, a water-testing lab is necessary to diagnose this condition and determine the cause. Though water tastes sweet to the untrained taste, it may also be affected by certain trace minerals and water sources. A thorough investigation will help determine the cause of your aversion to water.
Bad eating habits
If you’re experiencing this problem, there are a few things you can do to help rid your mouth of that sweet taste. First, make sure you’re eating healthy by eating lots of fresh fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Sugars in your diet can cause many diseases, such as diabetes.
The sweetness of your mouth can also indicate that you have an underlying health problem such as diabetes. Diabetes is associated with a sweet taste in the mouth.
Nerve damage What are the symptoms of a neurological disease that can change the way people perceive flavor?
It may be due to a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection. Other conditions resulting in a change in taste include HIV, COVID-19, Ramsey hunt, dengue fever, influenza, and Hepatitis C.
Although the exact cause of your change in taste is unknown, you may have an underlying genetic condition that affects your taste sensitivity. If your mouth is constantly smelling something sweet, you may have a neurological condition.
Your olfactory nerves run through your ear and split from your facial nerve. Those with Bell’s palsy, for example, may experience a sweet flavor. Other disorders may affect your sense of smell, including infections in the sinuses, throat, and nose.
In addition to neurological disorders, certain medical conditions can interfere with your sense of taste, including thyroid disorders and small-cell cancer.
Pregnancy
Whether you’re pregnant or not, you’ve probably experienced a metallic taste in your mouth at some point. This metallic taste is often worse than a sour or rancid taste and it can plague you even when you’re not eating or drinking.
It can even haunt your dreams! While many pregnant women will experience this sensation, you may wonder whether it’s something normal or if you should worry. Read on to discover whether your metallic taste is actually a sign of pregnancy.
The first trimester is a time when you experience a shift in your sense of taste or dysgeusia. This sensation can be both sweet and salty, and it can also be accompanied by a metallic taste.
This is caused by a rise in hormone levels in your body. While some people prefer sweet tastes over salty ones, this is not always the case.
While you might feel guilty if you enjoy eating something sweet, it’s important to talk to your healthcare provider about dietary changes and how to cope with these changes.
Prescription medications
It may seem strange to have a sweet taste in your mouth, but you may have a medical condition that’s causing this condition. If you suffer from diabetes or a respiratory infection, your doctor may prescribe insulin or antibiotics to help cure the problem. Depending on the cause of the problem, your treatment will vary.
If you’re not sure which medicine to take, consider subscribing to a diabetes newsletter, which compiles the latest information on diet, risk factors, and treatment.
Some medical conditions can cause a sweet taste in the mouth, including neurological problems, infections in the nose, throat, and sinuses, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Other causes include small cell carcinoma and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Consult with your doctor to determine if there are any underlying health conditions. Some drugs can have a sweet taste in the mouth because of their interaction with the olfactory system.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
There are many reasons why you may be experiencing a bad taste in your mouth. This condition, known as gastroesophageal reflux disease, occurs when digestive acids back up into the food pipe and enter the mouth.
The underlying cause of this condition is a dysfunctional or interrupted taste pathway in the brain. People who have GERD may experience a metallic or sour taste in their mouths.
There are many ways to manage your symptoms and find a solution. Pregnancy can also cause your sense of taste to become impaired, affecting your digestion.
Your doctor may prescribe a course of treatment for you to follow. You should not stop taking the medication prescribed to you if the sweet taste doesn’t go away.
But if you continue to notice it, see a doctor for a checkup. If the condition is not treated, it may be a side effect of medications. However, if you are already taking medication for gastroesophageal reflux disease, there are several ways to reduce the problem. First, drink plenty of water.
This will help the blood circulate in the mouth. Second, brush and floss your teeth twice a day. Make sure you change your toothbrush regularly. Finally, rinse your mouth after meals to remove any excess acid.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
While stress itself may not directly cause a sweet taste, it can contribute to a dry mouth, which can lead to an altered taste sensation, including sweetness.
Is a sweet taste in the mouth always a sign of diabetes?
No, a sweet taste in the mouth can have various causes. While it can be associated with diabetes, it is not the only explanation. Consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Can allergies cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
Allergies typically do not cause a sweet taste in the mouth. However, certain medications used to treat allergies might have side effects that alter taste perception.
How can I reduce the sweet taste in my mouth after eating sugary foods?
Drinking water, rinsing your mouth with plain water, or chewing sugar-free gum can help wash away the residual sweetness and freshen your mouth.
Can a vitamin deficiency cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
Vitamin deficiencies are not typically associated with a sweet taste. However, certain deficiencies may affect taste perception indirectly. Consulting a healthcare professional can help determine the underlying cause.
Can acid reflux cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
Acid reflux can lead to a sour or bitter taste due to stomach acid regurgitation. A sweet taste is less common but may occur if there is a concurrent condition affecting taste perception.
Is a sweet taste in the mouth during pregnancy normal?
Hormonal changes during pregnancy can sometimes affect taste perception, resulting in a sweet or metallic taste. It is advisable to discuss any unusual taste sensations with your healthcare provider.
Can smoking cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
Smoking can lead to a range of oral health issues and an altered taste perception. However, a persistent sweet taste is not typically associated with smoking alone.
Can a sinus infection cause a sweet taste in the mouth?
Sinus infections usually do not cause a sweet taste in the mouth. However, the associated post-nasal drip can sometimes lead to an unpleasant taste.
What can I do to maintain a fresh and pleasant taste in my mouth?
Practicing good oral hygiene, staying hydrated, and consuming a balanced diet with limited sugar intake can help maintain a fresh taste in your mouth. Regular dental check-ups are also essential for oral health.
Remember, if you have any concerns about a persistent sweet taste in your mouth, it is best to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and guidance.
Conclusion
A sweet taste in the mouth can stem from various factors, including hormonal imbalances, medications, oral health issues, dietary factors, and more. It’s important to pay attention to persistent or unusual taste sensations and seek medical advice if needed.
Maintaining good oral hygiene, adopting a balanced diet, and following prescribed medications can help alleviate the sweet taste. Remember, this article serves as a guide to understanding the possible causes, but it’s always best to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Health
6 Daily Habits to Naturally Lower Cholesterol Levels
Health
Understanding the Rapid Spread of Monkeypox’s New Strain Clade 1b
Understanding the Rapid Spread of Monkeypox’s New Strain Clade 1b: Key Facts on Transmission, Symptoms, Severity, and Vaccination
Monkeypox, a viral disease with symptoms resembling smallpox, has recently gained attention due to the emergence of a newstrain, Clade 1b.
This article delves into the essential details about this new variant, including how it spreads, its symptoms, its severity, and the current state of vaccinations.
Our goal is to provide a comprehensive and clear understanding of this evolving situation, enabling readers to stay informed and prepared.
Monkeypox, once a rare and somewhat obscure disease, has recently become a significant public health concern due to the emergence of new strains.
Among these, Clade 1b has been noted for its rapid spread and distinct characteristics.
As we navigate through the complexities of this variant, it is crucial to grasp the fundamentals of its transmission, symptoms, severity, and preventive measures, including vaccination.
Understanding Monkeypox Clade 1b
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes smallpox.
First identified in monkeys, it can infect humans through close contact with infected animals or individuals.
While it shares similarities with smallpox, monkeypox tends to be less severe and less transmissible.
Clade 1b Overview
Monkeypox has several clades (strains), with Clade 1b being the most recent and notable for its rapid spread.
This strain has shown increased transmissibility compared to previous clades, raising concerns among public health officials.
Transmission of Clade 1b
Modes of Transmission
Clade 1b spreads primarily through:
- Direct Contact: Contact with bodily fluids, skin lesions, or contaminated surfaces of an infected person.
- Respiratory Droplets: Prolonged face-to-face interaction can lead to transmission through respiratory droplets.
- Animal Contact: Infected animals, particularly rodents and primates, can transmit the virus to humans.
Environmental Factors
Transmission rates can also be influenced by environmental factors such as:
- Crowded Living Conditions: Higher transmission rates are observed in densely populated areas.
- Sanitation Practices: Poor hygiene and sanitation can facilitate the spread of the virus.
Symptoms of Monkeypox Clade 1b
Early Symptoms
The symptoms of Clade 1b may resemble those of other viral infections, making initial diagnosis challenging.
Early symptoms include:
- Fever: A sudden onset of high temperature.
- Headache: Severe headaches that can persist for days.
- Muscle Aches: Generalized muscle pain and discomfort.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and weakness.
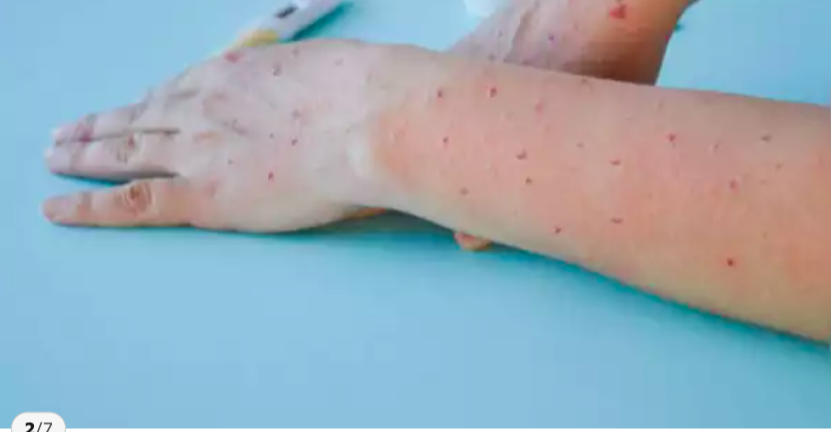
Rash and Skin Lesions
A defining feature of monkeypox is the rash, which typically progresses through several stages:
- Macules: Flat, discolored spots on the skin.
- Papules: Raised bumps.
- Vesicles: Fluid-filled blisters.
- Pustules: Pus-filled lesions that eventually crust over.
Severe Symptoms
In more severe cases, symptoms may include:
- Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain, leading to neurological symptoms.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs that can cause difficulty breathing.
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial infections that may complicate the healing process.
Severity of Clade 1b
General Outlook
Clade 1b has been associated with a higher transmission rate and more severe outcomes compared to other strains. However, the overall severity can vary widely among individuals.
Factors influencing severity include:
- Immune System Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing conditions may experience more severe symptoms.
- Age: Young children and elderly individuals are at higher risk of severe illness.
- Timeliness of Medical Care: Early medical intervention can significantly affect the outcome.
Mortality Rates
The mortality rate for Clade 1b is currently under study, but initial data suggest it may be higher than previous strains. Prompt medical attention and supportive care are crucial in reducing the risk of severe outcomes.
Vaccination and Prevention
Current Vaccines
Vaccination is a key strategy in controlling the spread of monkeypox.
The following vaccines are relevant:
- Smallpox Vaccine: The smallpox vaccine is effective against monkeypox due to the similarities between the viruses. It provides protection for those who have been recently vaccinated or who received it in the past.
- Monkeypox-Specific Vaccine: Research is ongoing into vaccines specifically targeting monkeypox, with several candidates showing promise in trials.
Vaccination Recommendations
Public health authorities recommend vaccination for:
- Healthcare Workers: Individuals who are at higher risk due to their profession.
- High-Risk Populations: People in areas experiencing outbreaks or those with frequent exposure to infected individuals.
Preventive Measures
In addition to vaccination, preventive measures include:
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and use of hand sanitizers.
- Avoiding Contact: Minimizing close contact with individuals displaying symptoms or with infected animals.
- Isolation: Infected individuals should isolate themselves to prevent the spread of the virus.
Conclusion
The emergence of Monkeypox Clade 1b represents a significant challenge to global health. Its increased transmissibility and potential for severe outcomes highlight the importance of staying informed and proactive.
By understanding its transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals and communities can better protect themselves and mitigate the impact of this new strain.
FAQs
1. What makes Clade 1b different from other monkeypox strains?
Clade 1b is noted for its increased transmissibility and potentially more severe outcomes compared to other strains.
It spreads faster and may lead to more serious health issues, necessitating closer monitoring and enhanced preventive measures.
2. How can I tell if I have monkeypox or another viral infection?
Monkeypox often begins with flu-like symptoms and progresses to a distinct rash.
If you experience these symptoms, especially if you’ve been in contact with someone who has monkeypox or are in an outbreak area, seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and testing.
3. Is the smallpox vaccine effective against Monkeypox Clade 1b?
Yes, the smallpox vaccine offers protection against monkeypox, including Clade 1b, due to the similarities between the two viruses.
However, its effectiveness may vary based on factors such as time since vaccination and individual health conditions.
4. Are there any new vaccines specifically for monkeypox?
Research is ongoing to develop and approve vaccines specifically targeting monkeypox.
Several candidates are in various stages of clinical trials, with some showing promising results in enhancing protection against monkeypox strains, including Clade 1b.
5. What should I do if I suspect I have monkeypox?
If you suspect you have monkeypox, contact a healthcare provider immediately. They can guide you through testing, diagnosis, and appropriate care.
In the meantime, practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with others to prevent spreading the virus.
References:
Health
Understanding the Low Risk of Mpox Outbreak in India and Our Preparedness Measures

-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know