Health
What is Psoriasis?

Last Updated on March 25, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a common, chronic skin condition that causes the skin to become inflamed and produce red, scaly patches. It is often itchy and uncomfortable and can have a significant impact on quality of life. Symptoms may range from mild to severe, and while there is no cure, there are treatments available to help manage it.
What Causes Psoriasis?
The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be due to an overactive immune system. Genetics may also be a factor, as certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing psoriasis. Stress, certain medications, and environmental factors can also trigger flare-ups.
Psoriasis is a skin condition that affects more than 8 million people in the United States alone. It is a chronic condition that can cause a lot of physical, mental, and emotional distress. It is important to understand what causes psoriasis in order to better manage the condition.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis that are classified according to the severity of the condition and the area of the body that is affected. The most common types of psoriasis are plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, and pustular psoriasis.
What Causes Plaque Psoriasis?
Plaque psoriasis is the most common type of psoriasis and is characterized by thick, red, scaly patches on the skin. It can occur anywhere on the body but is more common on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Plaque psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly.
What Causes Guttate Psoriasis?
Guttate psoriasis is characterized by small, red, scaly patches on the skin. It is most common in children and young adults and is often triggered by a bacterial infection such as strep throat. Guttate psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly.
What Causes Inverse Psoriasis?
Inverse psoriasis is characterized by red, smooth patches on the skin that can be very itchy and painful. It is more common in areas of skin that are covered by clothing, such as the groin, armpits, and under the breasts. Inverse psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that attacks healthy skin cells.
What Causes Erythrodermic Psoriasis?
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a very serious form of psoriasis that affects large areas of the body. It is characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin that can be very itchy and painful. Erythrodermic psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly.
What Causes Pustular Psoriasis?
Pustular psoriasis is characterized by white, pus-filled blisters on the skin. It is most common on the hands and feet and is often very itchy and painful. Pustular psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system that causes the skin cells to grow too quickly.
What Are the Risk Factors for Psoriasis?
There are several risk factors for psoriasis that can increase the likelihood of developing the condition. These include genetic factors, environmental factors, and certain medical conditions.
What Are the Genetic Factors for Psoriasis?
Genetic factors are one of the main risk factors for psoriasis. If someone in your family has psoriasis, you are more likely to develop the condition.
What Are the Environmental Factors for Psoriasis?
Environmental factors can also increase the risk of psoriasis. These factors include stress, smoking, and certain medications.
What Are the Medical Conditions That Increase the Risk of Psoriasis?
Certain medical conditions can increase the risk of psoriasis. These include HIV/AIDS, inflammatory bowel disease, and certain types of arthritis.
How Is Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Psoriasis is usually diagnosed by a physical exam and a review of the patient’s medical history. The doctor may also order tests such as blood tests and skin biopsies to rule out other conditions.
What Are the Symptoms of Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition that causes cells to build up rapidly on the surface of the skin, leading to the formation of scales and red patches that can be itchy and sometimes painful. The severity of the symptoms can vary greatly from person to person. Here are some common symptoms associated with psoriasis:
- Red, inflamed patches of skin: These patches, called plaques, are the most characteristic symptom of psoriasis. They can vary in size and shape and are often covered with silvery-white scales.
- Silvery-white scales: These scales are formed due to the rapid accumulation of skin cells on the surface of the skin. They can be thick and crusty, and they may flake off easily when scratched or rubbed.
- Dry, cracked skin: Psoriasis can cause the skin to become extremely dry and prone to cracking, which can be painful and lead to bleeding.
- Itching and burning sensations: The affected skin can be very itchy and sometimes cause a burning sensation, especially during flare-ups.
- Soreness or pain: The inflamed skin can be tender to the touch, and the pain can range from mild to severe.
- Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails: Psoriasis can affect the nails, causing them to become thickened, discolored, or develop small pits or ridges.
- Swollen and stiff joints: In some cases, psoriasis can be associated with a form of arthritis called psoriatic arthritis, which causes inflammation, swelling, and stiffness in the joints.
Remember that not all individuals with psoriasis will experience all of these symptoms, and the severity and duration of symptoms can vary. If you suspect you have psoriasis or are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What Are the Treatments for Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the rapid growth of skin cells, resulting in red, scaly patches on the skin.
There is no cure for psoriasis, but there are various treatments available to help manage the symptoms and improve the appearance of affected skin.
Treatment options can be categorized as topical treatments, light therapy, systemic medications, and biological medications.
- Topical treatments: These are creams, ointments, and gels applied directly to the skin. Common topical treatments for psoriasis include:
Corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth. They are available in different strengths and can be used for mild to moderate psoriasis. b. Vitamin
- analogs: These help normalizes skin cell growth, such as calcipotriene and calcitriol. c.
- Retinoids: Tazarotene is a topical retinoid that can help reduce inflammation and skin cell growth.
- Coal tar: This is a traditional treatment that can help reduce inflammation and slow skin cell growth.
- Salicylic acid: This is a keratolytic agent that helps remove scales and soften the skin.
- Moisturizers and emollients: These help soothes the skin and reduces dryness and itching.
- Light therapy (phototherapy): This treatment involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. There are different types of phototherapy, including:
- UVB phototherapy: Narrowband or broadband UVB light is used to treat psoriasis. b. Psoralen plus UVA (PUVA): This combines UVA light exposure with a photosensitizing medication called psoralen.
- Excimer laser: This laser treatment uses a focused beam of UVB light on specific areas of the skin.
- These are oral or injectable medications that work throughout the body. They are usually prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis or when topical treatments and light therapy are not effective.
- Common systemic medications include:
Methotrexate: An anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive medication that helps reduce psoriasis symptoms.
- Cyclosporine: An immunosuppressive medication that can help control severe psoriasis.
- Acitretin: An oral retinoid that can help slow down skin cell growth.
- Biologic medications: These are protein-based drugs derived from living cells that target specific parts of the immune system involved in psoriasis. Biologics are usually prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis that does not respond to other treatments. Some common biologic medications include:
It is essential to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation, as the choice of treatment depends on the severity and location of psoriasis, as well as individual factors and potential side effects.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, including plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. The most common type is plaque psoriasis, which is characterized by thick, red patches of skin covered in white scales.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The most common symptom of psoriasis is itchy, scaly patches of skin. Other symptoms may include redness, swelling, burning or stinging, dry skin, cracking or bleeding and thickened, pitted, or ridged nails.
Diagnosing Psoriasis
A doctor or dermatologist can diagnose psoriasis by examining the skin and asking questions about medical history and symptoms. A skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatments for Psoriasis
Treatment for psoriasis may include topical medications, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, as well as light therapy, oral medications, and biological drugs. It is important to work with a doctor to find the best treatment option for an individual’s needs.
Topical Treatments
Topical treatments are creams or ointments applied directly to the skin. Corticosteroids are the most common type of topical treatment, as they can help reduce inflammation and suppress the body’s immune system. Vitamin D analogs, such as calcipotriene and calcitriol, can help slow down the growth of skin cells.
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, uses ultraviolet light to help reduce the symptoms of psoriasis. It can be done in a doctor’s office or at home with special equipment.
Oral Medications
Oral medications, such as methotrexate and cyclosporine, can be used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. These medications can have serious side effects, so it is important to discuss them with a doctor before starting treatment.
Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs, such as adalimumab, etanercept, and ustekinumab, are powerful medications used to treat moderate to severe psoriasis. They work by blocking certain proteins involved in the body’s immune response.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can also be beneficial in managing psoriasis. These may include avoiding triggers, such as stress and certain foods, as well as avoiding excessive sun exposure and smoking. Keeping the skin well-moisturized can also help reduce flare-ups.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is a common, chronic skin condition that can have a significant impact on quality of life. While there is no cure, there are treatments available to help manage it.
It is important to work with a doctor to find the best treatment option for an individual’s needs, as well as psoriasis is a chronic skin condition that can cause a lot of physical, mental, and emotional distress.
It is important to understand what causes psoriasis in order to better manage the condition. There are several risk factors for psoriasis that can increase the likelihood of developing the condition.
Psoriasis is usually diagnosed by a physical exam and a review of the patient’s medical history. The most common treatments for psoriasis include topical medications, light therapy, oral medications, and biological drugs.
Health
Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?

Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?
In recent years, hair gummies have taken the health and beauty world by storm, boasting promises of luscious locks and a speedy route to hair health.
But with an array of products flooding the market, it’s essential to separate fact from fiction.
Are these colorful, chewy supplements a miracle solution for your hair troubles, or are they simply a trendy snack with little efficacy?
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the science behind hair gummies, their ingredients, potential benefits, and the questions surrounding their effectiveness.
Understanding Hair Health
The Basics of Hair Growth
To fully grasp the impact of hair gummies, it’s vital to understand how hair grows.
Each strand of hair goes through three main phases:
- Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase, which can last several years. The length of this phase varies among individuals.
- Catagen Phase: A transitional phase lasting a few weeks, where hair growth slows, and the hair follicle shrinks.
- Telogen Phase: The resting phase, lasting a few months before the hair falls out, making way for new growth.
Hair health is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, diet, and overall health.
As such, a balanced approach to hair care, encompassing nutrition, proper hair care routines, and avoiding damaging practices, is essential.
Common Causes of Hair Issues
Hair loss or poor hair health can arise from numerous factors:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals can hinder hair growth.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders can significantly affect hair health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger hair loss through a condition known as telogen effluvium.
- Medical Conditions: Certain diseases and medications can also contribute to hair loss.
What Are Hair Gummies?
Hair gummies are dietary supplements designed to promote hair health.
They are usually made with a combination of vitamins, minerals, and sometimes botanical extracts, often marketed as a convenient and tasty alternative to traditional vitamin pills.
Key Ingredients in Hair Gummies
While formulations vary, here are some common ingredients found in hair gummies:
- Biotin: A B-vitamin known for its role in hair and nail health. Biotin deficiencies can lead to brittle hair and hair loss.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: Antioxidants that help protect hair from oxidative stress, promoting a healthy scalp and hair growth.
- Folic Acid: Important for cell growth and regeneration, folic acid is believed to support healthy hair follicles.
- Zinc: Plays a role in hair tissue growth and repair, making it a crucial mineral for maintaining healthy hair.
- Collagen: An essential protein for skin elasticity that may also benefit hair strength and growth.
Do Hair Gummies Really Work?
The Science Behind Hair Gummies
While the ingredients in hair gummies are known to contribute to hair health, the question remains:
Do they work as effectively as claimed?
Here’s what the research suggests:
- Biotin: Studies have shown that biotin can improve hair thickness in those with deficiencies, but most people get sufficient biotin from their diet. Supplementing with biotin may not yield significant benefits for individuals who are not deficient.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Research indicates that vitamins A, C, D, E, and minerals like zinc and iron play a role in maintaining healthy hair. However, simply taking these vitamins in gummy form doesn’t guarantee results unless there’s a deficiency present.
- Collagen: Some studies suggest that collagen supplements can improve hair and skin health by providing amino acids essential for protein synthesis. However, more research is needed to establish direct benefits for hair growth.
User Experiences and Anecdotes
While anecdotal evidence often highlights positive experiences with hair gummies, it’s important to approach these testimonials with caution. Individual results may vary, and factors such as diet, overall health, and genetics play significant roles in hair health.
Potential Benefits of Hair Gummies
While not a miracle solution, hair gummies may offer certain benefits:
- Convenient Form: For those who struggle with swallowing pills, gummies provide a palatable alternative.
- Added Nutrients: If you have a deficiency in specific vitamins or minerals, hair gummies can supplement your diet effectively.
- Increased Awareness of Nutrition: Taking supplements can prompt individuals to pay more attention to their overall nutritional intake.
- Improved Hair Appearance: Users may notice shinier and healthier-looking hair due to the vitamins and antioxidants present in these products.
Are There Risks?
While hair gummies are generally safe, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Overconsumption: Gummies are often flavored and sweetened, which may lead to overconsumption and potential digestive issues.
- Sugar Content: Many gummies contain added sugars, which can contribute to other health problems if consumed excessively.
- Interactions with Other Supplements: If you’re taking other vitamins or supplements, it’s essential to ensure you’re not exceeding recommended doses, particularly for fat-soluble vitamins like A and E, which can accumulate in the body.
What Experts Say
Dermatologists and nutritionists often emphasize a balanced diet over reliance on supplements.
They suggest that whole foods—rich in vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats—are the best source for hair health.
Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, and eggs can provide essential nutrients without the added sugars and potential downsides of gummies.
Conclusion:
Fad or Fact?
In conclusion, hair gummies may not be the ultimate solution for hair health, but they can serve as a helpful supplement for those with specific nutritional deficiencies.
They are convenient and may improve the overall appearance of hair for some users. However, it’s crucial to approach them with realistic expectations and prioritize a balanced diet rich in whole foods.
If you’re considering adding hair gummies to your routine, consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to ensure you’re making an informed decision that aligns with your health goals.
FAQs
1. Can hair gummies replace a balanced diet?
No, hair gummies are supplements and should not replace a balanced diet. They can help fill nutritional gaps but should be taken alongside a healthy eating plan.
2. How long does it take to see results from hair gummies?
Results vary, but users may start noticing improvements in hair texture and appearance after 4-12 weeks of consistent use.
3. Are hair gummies safe for everyone?
Most hair gummies are safe for general use; however, individuals with specific health conditions or allergies should consult a healthcare professional before taking them.
4. Can I take hair gummies with other supplements?
Yes, but be cautious of total vitamin and mineral intake to avoid exceeding recommended daily allowances. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
5. Are there any side effects of hair gummies?
Some users may experience digestive issues, allergic reactions, or headaches due to high sugar content or specific ingredients. It’s best to start with a small dose to assess tolerance.
References:
Health
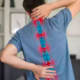
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
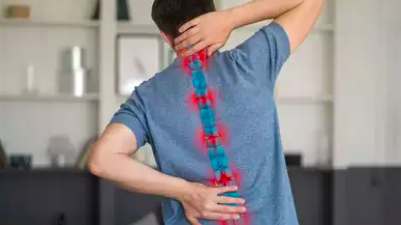
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
The spine is an essential structure in the human body, acting as a central pillar that supports our posture, facilitates movement, and protects the spinal cord.
Despite its importance, many individuals experience various spine-related conditions that can impact their quality of life.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore common spinal conditions, their causes, symptoms, and effective methods to address them.
What is the Spine?
The spine, also known as the vertebral column, is composed of 33 vertebrae arranged in a flexible yet sturdy structure.
It serves several critical functions:
- Support: The spine supports the head and allows for an upright posture.
- Protection: It encases and protects the spinal cord, a crucial component of the central nervous system.
- Mobility: The spine allows for a wide range of movements, including bending, twisting, and turning.
- Weight Distribution: It helps distribute weight and absorbs shock during activities like walking or running.
Understanding the structure and function of the spine is vital for recognizing and addressing the conditions that can affect it.
Common Spinal Conditions
Several conditions can adversely impact the spine, leading to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. Here are some of the most common spinal conditions:
1. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear in the outer layer. This can compress nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Heavy lifting or sudden movements
- Trauma or injury
Symptoms:
- Localized back pain
- Radiating pain to the limbs
- Numbness or tingling
Treatment:
- Physical therapy
- Pain management through medications
- In severe cases, surgery may be required.
2. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition often occurs in the cervical (neck) or lumbar (lower back) regions.
Causes:
- Age-related changes in the spine
- Osteoarthritis
- Herniated discs
Symptoms:
- Pain or cramping in the legs
- Weakness or numbness
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Medications for pain relief
- In some cases, surgical decompression may be necessary.
3. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, often appearing in childhood or adolescence. While many cases are mild, severe scoliosis can lead to complications.
Causes:
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
- Congenital (present at birth)
- Neuromuscular conditions
Symptoms:
- Uneven shoulders or hips
- Visible curvature of the spine
- Back pain
Treatment:
- Monitoring and observation for mild cases
- Bracing for growing children
- Surgery for severe curvatures.
4. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. This is particularly concerning for the vertebrae, which can lead to compression fractures.
Causes:
- Aging
- Hormonal changes
- Lack of calcium and vitamin D
Symptoms:
- Height loss
- Back pain due to fractures
- A stooped posture
Treatment:
- Medications to strengthen bones
- Nutritional supplements (calcium and vitamin D)
- Weight-bearing exercises to improve bone density.
5. Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease refers to the wear and tear of spinal discs over time, leading to pain and reduced flexibility.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Repetitive stress on the spine
- Genetics
Symptoms:
- Chronic back pain
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Possible radiating pain in the limbs
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Pain management strategies
- Surgical options for severe cases.
Preventing Spinal Conditions
While some spinal conditions are unavoidable due to genetics or aging, many can be prevented or mitigated through healthy lifestyle choices.
Here are some preventative measures:
1. Maintain Good Posture
Proper posture helps reduce strain on the spine. When sitting, keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and feet flat on the ground. When standing, distribute your weight evenly on both feet.
2. Stay Active
Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles that support the spine and improves flexibility. Aim for a balanced routine that includes strength training, aerobic exercise, and stretching.
3. Ergonomic Work Environment
If you spend long hours at a desk, ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed. Adjust your chair, desk height, and computer monitor to reduce strain on your back and neck.
4. Healthy Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine and helps prevent conditions like degenerative disc disease and spinal stenosis.
5. Avoid Smoking
Smoking impairs blood flow and can lead to spinal degeneration. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of spinal issues.
Effective Treatments for Spinal Conditions
If you experience spine-related pain or discomfort, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists develop personalized exercise programs to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. They may also use techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to manage discomfort.
2. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage mild to moderate pain. Prescription medications may be necessary for more severe pain or inflammation.
3. Injections
Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These are typically used when other treatments have failed.
4. Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. Common surgical procedures include discectomy (removal of herniated disc material), spinal fusion, and laminectomy (removal of part of the vertebra).
5. Alternative Therapies
Complementary treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may provide relief for some individuals. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying alternative therapies.
Conclusion
Understanding the spine and its common conditions is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing potential issues.
By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can address spinal conditions effectively.
Implementing preventative measures, such as maintaining good posture and staying active, can significantly reduce the risk of developing spine-related issues.
Prioritize your spinal health, consult with professionals when necessary, and take proactive steps to ensure a healthy and pain-free back.
FAQs
1. What are the common symptoms of spinal conditions?
Common symptoms include localized back pain, radiating pain in the limbs, numbness, tingling sensations, and difficulty with movement.
2. How can I improve my posture while working?
To improve your posture at work, adjust your chair and desk height, use a supportive chair, and ensure your computer screen is at eye level.
3. Can physical therapy help with spinal conditions?
Yes, physical therapy can help strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain associated with various spinal conditions.
4. When should I see a doctor for back pain?
If you experience persistent back pain that does not improve with rest, is accompanied by numbness or weakness, or interferes with daily activities, it’s essential to see a doctor.
5. Are there lifestyle changes I can make to prevent spinal issues?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, practicing good posture, and avoiding smoking can help prevent spinal conditions.
References:
Health
Understanding the Causes of Premature Menopause in Women
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know