Health
How to Treat Eczema: A Comprehensive Guide
Last Updated on May 18, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
How to Treat Eczema: A Comprehensive Guide
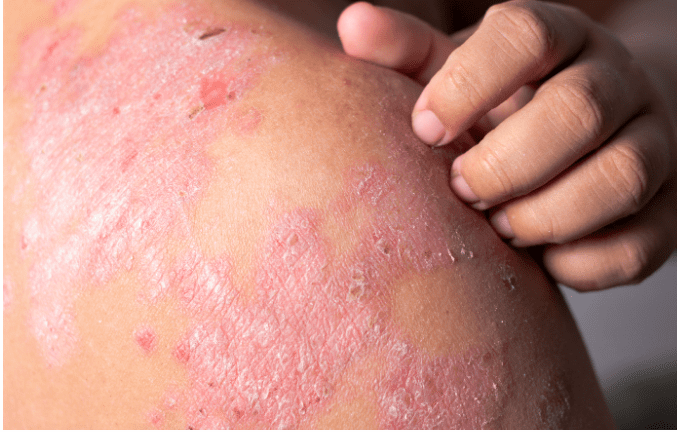
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that causes itching, redness, and dryness. It is a common condition, affecting millions of people worldwide, and can occur at any age, but is most common in children.
The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some common triggers include stress, changes in temperature, exposure to irritants, and certain foods.
Understanding Eczema and its Symptoms
Eczema is a skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide.It is characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Eczema can be a chronic condition, which means that it can last for an extended period and recur at different times.
Types of Eczema There are several types of eczema, including:
- Atopic Dermatitis: This is the most common type of eczema and is often hereditary. It affects people of all ages and can be accompanied by hay fever or asthma.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type of eczema is caused by direct contact with an irritant or allergen, such as detergents, soap, or certain materials.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: This type of eczema is characterized by small, fluid-filled blisters on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet.
- Nummular Eczema: This type of eczema is characterized by coin-shaped patches on the skin that are dry and scaly.
- Stasis Dermatitis: This type of eczema occurs as a result of poor blood flow in the legs and is more common in older adults.
Causes of Eczema The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Some common triggers of eczema include:
- Allergens: Exposure to allergens such as dust mites, pet dander, and pollen can trigger eczema symptoms.
- Irritants: Exposure to certain chemicals, soaps, and detergents can cause skin irritation and trigger eczema.
- Dry skin: Dry skin can make eczema symptoms worse and can also trigger eczema.
- Stress: Stress can also trigger eczema symptoms and make them worse.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal changes, such as during puberty or pregnancy, can also trigger eczema.
Symptoms of Eczema The symptoms of eczema can vary from person to person and can range from mild to severe.
Common symptoms of eczema include:
- Itchy skin: Eczema can cause the skin to become extremely itchy, which can be unbearable and lead to scratching and further irritation.
- Dry skin: Eczema can cause the skin to become dry, scaly, and rough.
- Red and inflamed skin: Eczema can cause the skin to become red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Blisters: Some types of eczema can cause fluid-filled blisters to form on the skin.
- Cracks and sores: Eczema can cause the skin to crack and form sores, which can become infected if not treated.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Eczema
Diagnosing Eczema If you suspect that you have eczema, it is essential to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Your doctor will perform a physical examination of your skin and ask about your symptoms and medical history.
They may also perform a skin test to determine if you have any allergies that could be triggering your eczema. Skin Tests for Eczema Several skin tests can be performed to determine if you have eczema and what may be triggering your symptoms.
These tests include:
Patch Test:
- Prick Test: During a prick test, small amounts of allergens are placed on the skin, and a needle is used to prick the skin and allow the allergen to penetrate.
- The skin is then observed for any reactions.
- Intradermal Test: During an intradermal test, a small amount of allergen is injected into the skin, and the skin is observed for any reaction
- Treating Eczema can be challenging, as there is no cure.
- However, there are several ways to manage and control the symptoms of eczema.
These include:
Medications Several medications can be used to treat eczema, including:
- Topical Corticosteroids: Topical corticosteroids are creams or ointments that are applied to the skin to reduce inflammation and itching. They come in varying strengths and can be used for short-term or long-term treatment.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Topical calcineurin inhibitors are creams that can be used to treat eczema. They work by suppressing the immune system and reducing inflammation.
- Antihistamines: Antihistamines can be taken orally or applied topically to relieve itching and help you sleep.
- Antibiotics: If your eczema becomes infected, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear up the infection.
Moisturizing is an essential part of treating eczema.
Moisturizing can help to soothe dry, itchy skin and prevent cracking and sores. Some tips for moisturizing include:
- Use fragrance-free moisturizers: Fragrances can irritate the skin and make eczema symptoms worse. Look for fragrance-free moisturizers that are specifically formulated for sensitive skin.
- Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing: After bathing, pat the skin dry and apply moisturizer while the skin is still damp.
- This will help to lock in moisture and prevent dry skin.
- Use ointments: Ointments, such as petroleum jelly, are more effective at moisturizing the skin than creams or lotions.
Avoiding Triggers: Avoiding triggers is another important part of treating eczema.
Common triggers include:
- Allergens: Avoid exposure to allergens, such as dust mites, pet dander, and pollen.
- Irritants: Avoid exposure to irritants, such as harsh soaps and detergents.
- Stress: Try to manage stress through exercise, meditation, or other stress-management techniques.
- Extreme temperatures: Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures, as hot or cold weather can make eczema symptoms worse.
Bathing and Clothing Proper bathing and clothing can also help to manage eczema symptoms.
Some tips include:
- Use warm, not hot, water: Hot water can strip the skin of its natural oils and make eczema symptoms worse. Use warm water when bathing, and limit your bath time to 10-15 minutes.
- Avoid harsh soaps: Use fragrance-free, gentle soaps when bathing, and avoid scrubbing the skin.
- Pat the skin dry: After bathing, dry the skin with a soft towel. Avoid
Diagnosing eczema can be difficult, as the symptoms can be similar to those of other skin conditions.
To diagnose eczema, a doctor will typically perform a physical exam, review the patient’s medical history, and rule out any other underlying conditions that may be causing the symptoms. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Treating Eczema
There is no cure for eczema, but there are various treatments that can help manage the symptoms and reduce the severity of outbreaks.
The following are some of the most common treatments for eczema:
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are one of the most commonly prescribed treatments for eczema. They work by reducing inflammation and itching and come in a variety of forms, including creams, ointments, and lotions.
Moisturizers
Moisturizing the skin is an essential part of eczema treatment. Using a thick, fragrance-free moisturizer can help soothe dry and irritated skin and prevent itching.
Antihistamines
Antihistamines can help relieve itching and reduce redness associated with eczema. They work by blocking the effects of histamine, a chemical that triggers itching.
Light Therapy
Light therapy, also known as phototherapy, involves exposing the skin to artificial ultraviolet (UV) light. It is often used to treat moderate to severe cases of eczema and can help reduce inflammation and itching.
Oral Medications
In severe cases, oral medications may be necessary to control eczema symptoms. These medications include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antibiotics, and immunosuppressants.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Eczema
In addition to medical treatments, several lifestyle changes can help improve eczema and prevent outbreaks. These include:
Avoiding Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is one of the most effective ways to prevent eczema outbreaks. Common triggers include stress, exposure to irritants, and certain foods.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and nutrients can help improve the overall health of the skin and reduce the severity of eczema symptoms. Some foods that have been shown to help improve eczema include omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, and vitamin D.
Staying Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water can help keep the skin hydrated and reduce the risk of eczema outbreaks.
Managing Stress
Stress can be a trigger for eczema, so it is important to manage stress levels to prevent outbreaks. This can be done through relaxation techniques, exercise, and therapy.
Conclusion
Eczema is a common skin condition that can cause itching, redness, and dryness. While there is no cure for the conclusion, eczema is a common skin condition that can be difficult to treat. However, by working with a doctor, identifying and avoiding triggers, using medications, moisturizing
regularly, and practicing proper bathing and clothing techniques, it is possible to manage and control the symptoms of eczema. With proper treatment, many people with eczema can achieve clearer, healthier-looking skin.
If you suspect you may have eczema, it’s important to see a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan. With the right approach, it is possible to find relief from the symptoms of eczema and improve the appearance and overall health of your skin.
Health
6 Daily Habits to Naturally Lower Cholesterol Levels
Health
Understanding the Rapid Spread of Monkeypox’s New Strain Clade 1b
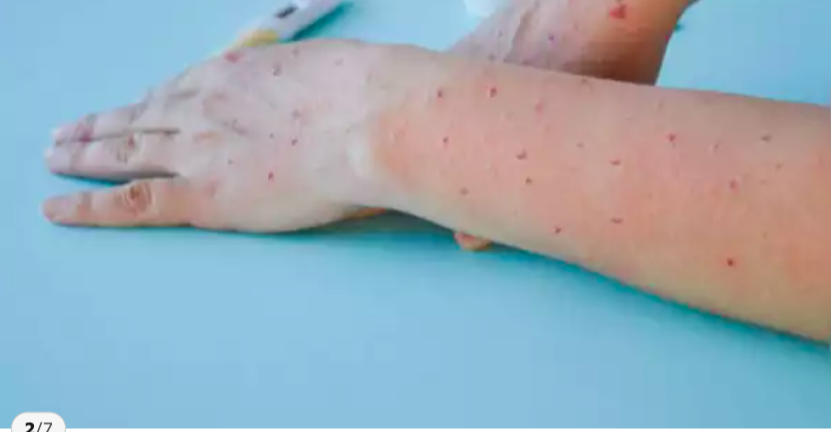
Understanding the Rapid Spread of Monkeypox’s New Strain Clade 1b: Key Facts on Transmission, Symptoms, Severity, and Vaccination
Monkeypox, a viral disease with symptoms resembling smallpox, has recently gained attention due to the emergence of a newstrain, Clade 1b.
This article delves into the essential details about this new variant, including how it spreads, its symptoms, its severity, and the current state of vaccinations.
Our goal is to provide a comprehensive and clear understanding of this evolving situation, enabling readers to stay informed and prepared.
Monkeypox, once a rare and somewhat obscure disease, has recently become a significant public health concern due to the emergence of new strains.
Among these, Clade 1b has been noted for its rapid spread and distinct characteristics.
As we navigate through the complexities of this variant, it is crucial to grasp the fundamentals of its transmission, symptoms, severity, and preventive measures, including vaccination.
Understanding Monkeypox Clade 1b
What is Monkeypox?
Monkeypox is a zoonotic virus belonging to the Orthopoxvirus genus, which also includes smallpox.
First identified in monkeys, it can infect humans through close contact with infected animals or individuals.
While it shares similarities with smallpox, monkeypox tends to be less severe and less transmissible.
Clade 1b Overview
Monkeypox has several clades (strains), with Clade 1b being the most recent and notable for its rapid spread.
This strain has shown increased transmissibility compared to previous clades, raising concerns among public health officials.
Transmission of Clade 1b
Modes of Transmission
Clade 1b spreads primarily through:
- Direct Contact: Contact with bodily fluids, skin lesions, or contaminated surfaces of an infected person.
- Respiratory Droplets: Prolonged face-to-face interaction can lead to transmission through respiratory droplets.
- Animal Contact: Infected animals, particularly rodents and primates, can transmit the virus to humans.
Environmental Factors
Transmission rates can also be influenced by environmental factors such as:
- Crowded Living Conditions: Higher transmission rates are observed in densely populated areas.
- Sanitation Practices: Poor hygiene and sanitation can facilitate the spread of the virus.
Symptoms of Monkeypox Clade 1b
Early Symptoms
The symptoms of Clade 1b may resemble those of other viral infections, making initial diagnosis challenging.
Early symptoms include:
- Fever: A sudden onset of high temperature.
- Headache: Severe headaches that can persist for days.
- Muscle Aches: Generalized muscle pain and discomfort.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness and weakness.
Rash and Skin Lesions
A defining feature of monkeypox is the rash, which typically progresses through several stages:
- Macules: Flat, discolored spots on the skin.
- Papules: Raised bumps.
- Vesicles: Fluid-filled blisters.
- Pustules: Pus-filled lesions that eventually crust over.
Severe Symptoms
In more severe cases, symptoms may include:
- Encephalitis: Inflammation of the brain, leading to neurological symptoms.
- Pneumonia: Infection of the lungs that can cause difficulty breathing.
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial infections that may complicate the healing process.
Severity of Clade 1b
General Outlook
Clade 1b has been associated with a higher transmission rate and more severe outcomes compared to other strains. However, the overall severity can vary widely among individuals.
Factors influencing severity include:
- Immune System Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems or pre-existing conditions may experience more severe symptoms.
- Age: Young children and elderly individuals are at higher risk of severe illness.
- Timeliness of Medical Care: Early medical intervention can significantly affect the outcome.
Mortality Rates
The mortality rate for Clade 1b is currently under study, but initial data suggest it may be higher than previous strains. Prompt medical attention and supportive care are crucial in reducing the risk of severe outcomes.
Vaccination and Prevention
Current Vaccines
Vaccination is a key strategy in controlling the spread of monkeypox.
The following vaccines are relevant:
- Smallpox Vaccine: The smallpox vaccine is effective against monkeypox due to the similarities between the viruses. It provides protection for those who have been recently vaccinated or who received it in the past.
- Monkeypox-Specific Vaccine: Research is ongoing into vaccines specifically targeting monkeypox, with several candidates showing promise in trials.
Vaccination Recommendations
Public health authorities recommend vaccination for:
- Healthcare Workers: Individuals who are at higher risk due to their profession.
- High-Risk Populations: People in areas experiencing outbreaks or those with frequent exposure to infected individuals.
Preventive Measures
In addition to vaccination, preventive measures include:
- Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and use of hand sanitizers.
- Avoiding Contact: Minimizing close contact with individuals displaying symptoms or with infected animals.
- Isolation: Infected individuals should isolate themselves to prevent the spread of the virus.
Conclusion
The emergence of Monkeypox Clade 1b represents a significant challenge to global health. Its increased transmissibility and potential for severe outcomes highlight the importance of staying informed and proactive.
By understanding its transmission, symptoms, and preventive measures, individuals and communities can better protect themselves and mitigate the impact of this new strain.
FAQs
1. What makes Clade 1b different from other monkeypox strains?
Clade 1b is noted for its increased transmissibility and potentially more severe outcomes compared to other strains.
It spreads faster and may lead to more serious health issues, necessitating closer monitoring and enhanced preventive measures.
2. How can I tell if I have monkeypox or another viral infection?
Monkeypox often begins with flu-like symptoms and progresses to a distinct rash.
If you experience these symptoms, especially if you’ve been in contact with someone who has monkeypox or are in an outbreak area, seek medical advice for accurate diagnosis and testing.
3. Is the smallpox vaccine effective against Monkeypox Clade 1b?
Yes, the smallpox vaccine offers protection against monkeypox, including Clade 1b, due to the similarities between the two viruses.
However, its effectiveness may vary based on factors such as time since vaccination and individual health conditions.
4. Are there any new vaccines specifically for monkeypox?
Research is ongoing to develop and approve vaccines specifically targeting monkeypox.
Several candidates are in various stages of clinical trials, with some showing promising results in enhancing protection against monkeypox strains, including Clade 1b.
5. What should I do if I suspect I have monkeypox?
If you suspect you have monkeypox, contact a healthcare provider immediately. They can guide you through testing, diagnosis, and appropriate care.
In the meantime, practice good hygiene and avoid close contact with others to prevent spreading the virus.
References:
Health
Understanding the Low Risk of Mpox Outbreak in India and Our Preparedness Measures

-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health4 months ago
Health4 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know