Health
Causes of Diabetes: Understanding the Risk Factors

Causes of Diabetes: Understanding the Risk Factors
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a condition where your body is unable to produce or use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. While diabetes can affect anyone, some people are more at risk than others. In this article, we will discuss the causes of diabetes and the risk factors associated with it.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your body cannot properly use and store glucose (a type of sugar). Glucose is a critical source of energy for your body, and insulin (a hormone produced by your pancreas) helps your body to use it properly. If your body doesn’t produce enough insulin or is unable to use insulin effectively, glucose can build up in your blood, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Types of Diabetes There are three main types of diabetes:
type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes: This type of diabetes is caused by an autoimmune response where the body attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. This results in the body not being able to produce enough insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, and it requires insulin injections to manage the condition.
Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It occurs when your body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin to meet your body’s needs. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed through diet and exercise, although some people may require medication or insulin injections.
Gestational Diabetes: Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after the baby is born. However, women who develop gestational diabetes are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes of Type 1 Diabetes The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies suggest that certain viruses or infections may trigger the autoimmune response that leads to type 1 diabetes.
Causes of Type 2 Diabetes Type 2 diabetes is often caused by lifestyle factors, such as poor diet and lack of exercise. Other risk factors include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, and being over the age of 45.
Lifestyle Factors Poor diet: A diet high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce your risk.
Lack of exercise: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, which can reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Losing weight and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce your risk.
Other Risk Factors Family history: If you have a parent or sibling with diabetes, you are at a higher risk of developing the condition.
Age: The risk of developing type 2 diabetes increases as you get older, especially after the age of 45.
Ethnicity: People of certain ethnicities, including African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and Native Americans, are at a higher risk of developing diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes Gestational diabetes is caused by hormonal changes during pregnancy that can affect insulin sensitivity. Women who are overweight or have a family history of diabetes are at a higher risk of developing
Type 1 Diabetes: Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or an insulin pump, as the body cannot produce insulin on its own.
Type 2 Diabetes: Treatment for type 2 diabetes often involves lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, as well as medication to help manage blood sugar levels.
Gestational Diabetes: Treatment for gestational diabetes involves monitoring blood sugar levels and making lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise. In some cases, medication may be necessary to help manage blood sugar levels.
Complications of Diabetes If left untreated or poorly managed, diabetes can lead to a number of serious health complications, including:
Cardiovascular disease: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Nerve damage: Diabetes can cause nerve damage, which can lead to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
Kidney damage: High blood sugar levels can damage the kidneys, leading to kidney disease or even kidney failure.
Eye damage: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems or even blindness.
Prevention of Diabetes While not all cases of diabetes can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing the condition:
Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight or obese can increase your risk of developing diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can help reduce your risk.
Eat a healthy diet: Eating a diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
Exercise regularly: Regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, which can reduce your risk of developing diabetes. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Get regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your doctor can help detect early signs of diabetes or other health conditions.
FAQs
Can diabetes be cured?
While there is currently no cure for diabetes, the condition can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication. For type 1 diabetes, insulin injections or an insulin pump are necessary for survival, as the body cannot produce insulin on its own. For type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight loss can help manage the condition. In some cases, medication may also be necessary to help manage blood sugar levels.
It is important to note that while diabetes cannot be cured, it can be controlled with proper management. This means consistently monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, and taking medication as prescribed. Failing to properly manage diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, and eye damage.
It is important for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan that takes into account their specific needs and lifestyle. Regular check-ups and monitoring of blood sugar levels are also crucial to ensure that the condition is being managed effectively. By taking an active role in their diabetes management, individuals with diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
While there is currently no cure for diabetes, it can be managed through lifestyle changes and medication.
Can stress cause diabetes?
While stress does not directly cause diabetes, it can be a contributing factor in the development of type 2 diabetes. Stress triggers the release of hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase blood sugar levels. Over time, chronic stress can lead to insulin resistance, a condition in which the body becomes less responsive to insulin and is less able to control blood sugar levels.
In addition to increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes, chronic stress has also been linked to other health complications associated with diabetes, including cardiovascular disease and high blood pressure. Stress can also make it more difficult for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition, as it can affect their ability to follow a healthy diet, exercise regularly, and take medication as prescribed.
Is diabetes hereditary?
Diabetes is a disease that affects how your body uses glucose, a type of sugar that is a source of energy for your cells. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not produce enough insulin or is unable to use insulin effectively, which leads to high levels of glucose in the blood.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can have a genetic component. Research has shown that if a person has a family history of diabetes, they may be at a higher risk of developing the disease themselves. However, genetics alone do not determine whether someone will develop diabetes. Lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise also play a significant role.
In the case of type 1 diabetes, certain genes have been identified that increase the risk of developing the disease. However, having these genes does not necessarily mean that a person will develop type 1 diabetes. In fact, only a small percentage of people with these genes actually develop the disease.
For type 2 diabetes, genetics can also play a role in a person’s risk of developing the disease. Studies have shown that if one or both parents have type 2 diabetes, their children are more likely to develop the disease as well. However, lifestyle factors such as poor diet and lack of exercise can also increase a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes, even if they have no family history of the disease.
Overall, while genetics can increase a person’s risk of developing diabetes, lifestyle factors also play a significant role in the development of the disease. It’s important for individuals to maintain a healthy lifestyle to help prevent or manage diabetes, even if they have a family history of the disease.
Can type 2 diabetes be reversed?
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition that affects how the body processes glucose, leading to high blood sugar levels. While there is currently no cure for type 2 diabetes, it is possible to achieve remission and reverse some of the effects of the condition through lifestyle changes and medical interventions.
One of the most effective ways to reverse type 2 diabetes is through weight loss and healthy eating habits. Losing even a small amount of weight, such as 5-10% of body weight, can significantly improve blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. This can be achieved through a healthy, balanced diet that is low in processed and sugary foods and high in fiber, whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and healthy fats.
Exercise is also an important component of reversing type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help the body use glucose more efficiently. Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Medications such as metformin and insulin can also help to control blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. However, these medications are not a long-term solution and should be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes.
In some cases, bariatric surgery may be recommended for individuals with type 2 diabetes who are severely overweight or obese. This procedure can lead to significant weight loss and remission of diabetes in many patients.
It is important to note that while it is possible to reverse some of the effects of type 2 diabetes, it is a chronic condition that requires ongoing management and monitoring. Individuals with type 2 diabetes should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that includes lifestyle changes and medical interventions as needed.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Diabetes is a metabolic disorder that affects how the body processes glucose, a type of sugar. The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the individual.
Some common symptoms of diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and urination: This is often one of the first symptoms of diabetes. As blood sugar levels rise, the kidneys may be unable to keep up with filtering excess glucose. This can lead to increased urination, which in turn can cause dehydration and increased thirst.
- Fatigue: People with diabetes often feel tired and sluggish, even after getting enough sleep. This is because the body is unable to use glucose for energy, so it begins to break down fat and muscle for fuel.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens of the eye to swell, which can lead to blurred vision.
- Slow healing of cuts and bruises: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation and damage nerves, which can slow down the healing process.
- Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to a loss of sensation in the hands and feet.
- Frequent infections: High blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections.
- Unexplained weight loss: People with type 1 diabetes may experience rapid weight loss despite eating normally, as the body begins to break down fat and muscle for fuel.
- Increased hunger: People with type 2 diabetes may experience increased hunger, as the body is unable to use glucose for energy and begins to break down fat and muscle for fuel.
It is important to note that not everyone with diabetes will experience all of these symptoms, and some people with diabetes may not experience any symptoms at all. It is important to speak with a healthcare provider if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as early diagnosis and treatment of diabetes can help prevent complications.
conclusion,
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people worldwide. While the exact causes of diabetes are not fully understood, there are several risk factors that can increase your chances of developing the condition.
By making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly, you can reduce your risk of developing diabetes and its associated health complications.
If you are at risk of developing diabetes or are experiencing symptoms such as increased thirst or frequent urination, it is important to speak with your doctor to get tested and begin treatment if necessary.
Health
Understanding Menstrual Allergy: What You Need to Know

Understanding Menstrual Allergy: What You Need to Know
REFERENCE:
https://www.healthwellnessjournal.com/menstrual-allergy-guide
Health
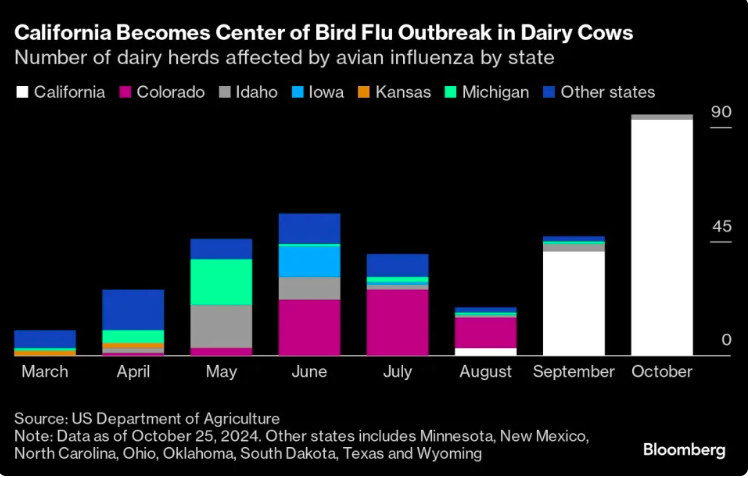
California’s Bird Flu Crisis in Cattle: Understanding the Threat to Farming and Public Health
Health
Prenatal Cannabis Use: How It Impacts Child Development, Aggression, and Cognitive Skills

Prenatal Cannabis Use: How It Impacts Child Development, Aggression, and Cognitive Skills
Cannabis use during pregnancy has garnered significant attention in recent years due to its potential impact on child development.
With growing research and anecdotal claims surfacing, many wonder whether cannabis might affect a child’s neurodevelopment, particularly in areas such as cognitive function, behavioral tendencies, and social adaptability.
As prenatal cannabis exposure becomes increasingly examined, understanding its influence on childhood aggression and cognitive deficits has become crucial.
Here, we delve into the latest research on prenatal cannabis use and its implications for child development, highlighting key takeaways for parents and healthcare providers alike.
The Rise in Prenatal Cannabis Use
In recent years, cannabis legalization in various states and countries has led to a significant increase in use, even among pregnant women.
While some mothers-to-be use it to alleviate nausea or reduce anxiety, the potential risks to the developing fetus are often understated or misunderstood.
Studies suggest that cannabis use during pregnancy may disrupt fetal neurodevelopment, which can have long-lasting effects on a child’s behavior and cognitive abilities.
How Cannabis Affects Fetal Brain Development
During pregnancy, a baby’s brain undergoes rapid and complex development. Introducing cannabis, particularly the active compound THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), into a pregnant body can interfere with this process.
THC can cross the placenta, reaching the fetal brain and binding to cannabinoid receptors.
These receptors are crucial for normal brain development, affecting neuron growth, brain structure, and the overall wiring of neural connections.
The Role of Cannabinoid Receptors in Neurodevelopment
Cannabinoid receptors, part of the endocannabinoid system, play a pivotal role in prenatal brain development.
The interference caused by external cannabinoids like THC can disrupt normal brain function, potentially leading to cognitive and behavioral issues in childhood and beyond.
Research shows that children exposed to cannabis in utero may have lower scores in areas of memory, attention, and decision-making—skills that are essential for cognitive development and emotional regulation.
Studies on Cannabis and Childhood Aggression
One of the most concerning findings in recent research is the potential link between prenatal cannabis exposure and increased aggression in children.
Children exposed to cannabis during gestation may be more prone to aggression and other behavioral issues as they grow. Such behaviors may stem from altered neurotransmitter function and disrupted brain connections caused by exposure to THC.
Potential Behavioral Outcomes
Cannabis use in pregnancy has been associated with a range of behavioral concerns in young children.
These may include:
- Increased Aggressiveness: Children may exhibit more aggressive behaviors, which can hinder social interactions and pose challenges in school and other social environments.
- Attention Deficit Issues: Prenatal cannabis exposure has also been linked to attention-deficit disorders, making it harder for children to concentrate or complete tasks.
- Impulsivity and Hyperactivity: Children may show higher levels of impulsivity, leading to difficulties in controlling their behavior in structured settings.
Cognitive Deficits Associated with Prenatal Cannabis Use
The cognitive impacts of prenatal cannabis exposure often manifest in deficits related to memory, executive function, and problem-solving skills.
In many cases, these deficits become evident as children grow and face increasingly complex cognitive tasks at school and in social situations.
Memory and Learning Impairments
Children exposed to cannabis during pregnancy may have difficulties in memory retention and recall. Memory is a fundamental skill that impacts learning, decision-making, and emotional regulation.
When prenatal cannabis exposure disrupts memory development, children may struggle academically and face challenges in forming and maintaining relationships.
Executive Function Challenges
Executive functions, including decision-making, planning, and problem-solving, are essential for daily life.
Cannabis exposure in utero has been linked to impairments in these areas, making it harder for affected children to succeed in academic and social settings.
These challenges can persist into adolescence and adulthood, potentially impacting career choices, interpersonal relationships, and overall quality of life.
Impact on Social Development
Children who experience neurodevelopmental impacts from prenatal cannabis exposure may struggle in social situations.
Aggression, impulsivity, and attention deficits can hinder their ability to interact positively with peers, teachers, and family members.
Additionally, the cognitive deficits associated with prenatal cannabis exposure may impair their ability to understand social cues, leading to misunderstandings and conflicts.
Long-Term Effects on Social Relationships
Research suggests that the effects of prenatal cannabis exposure on social behavior can extend into adolescence and beyond.
Children who exhibit aggressive behavior or struggle with attention-related issues may find it challenging to form close friendships or maintain healthy relationships.
In some cases, this can lead to feelings of isolation and low self-esteem, which may increase the risk of mental health issues later in life.
Gender Differences in Cannabis Exposure Outcomes
Interestingly, some studies indicate that the effects of prenatal cannabis exposure may differ between boys and girls.
Boys, for instance, may exhibit more noticeable signs of aggression and hyperactivity, while girls may experience cognitive challenges such as attention deficits.
Understanding these gender-specific differences can help healthcare providers tailor interventions and support strategies to meet each child’s unique needs.
Strategies for Pregnant Women Considering Cannabis Use
While cannabis might seem like a natural remedy for managing pregnancy symptoms, its potential impacts on fetal development suggest the need for caution. Pregnant women considering cannabis use should discuss it with their healthcare provider to understand the risks and explore safer alternatives.
Alternative Remedies for Pregnancy Symptoms
Many healthcare providers recommend alternative approaches to managing pregnancy symptoms, such as:
- Acupuncture or Acupressure: Helpful for managing nausea and anxiety.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: These can aid in stress reduction and mood regulation.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in prenatal yoga or light exercises can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Ongoing Research and Future Perspectives
Researchers are still uncovering the full spectrum of prenatal cannabis exposure’s effects on child development. As more data becomes available, guidelines may evolve to provide clearer recommendations for pregnant women.
Currently, the precautionary approach is widely endorsed by medical professionals due to the growing body of evidence suggesting that prenatal cannabis use can negatively impact child neurodevelopment.
The Importance of Parental Awareness and Support
Understanding the risks associated with prenatal cannabis use is vital for expecting parents and families. By becoming informed, parents can make healthier choices for themselves and their unborn children.
Additionally, recognizing the potential impacts on child development can help families seek early interventions if needed, supporting better developmental outcomes.
Conclusion
The evidence suggests that prenatal cannabis exposure may contribute to increased aggression, cognitive deficits, and social challenges in children.
As cannabis becomes more accessible, the importance of understanding its potential risks during pregnancy cannot be overstated.
Pregnant women should consult with their healthcare providers about alternative symptom management methods to minimize any potential risks to fetal brain development.
Through informed decision-making, expecting parents can better support the long-term health and development of their children.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can cannabis use during pregnancy cause lasting effects on a child’s brain?
Yes, research suggests that prenatal cannabis exposure may lead to long-term cognitive and behavioral challenges, including memory deficits and aggression.
2. Are there safe alternatives to cannabis for managing pregnancy symptoms?
Yes, many healthcare providers recommend alternatives such as acupuncture, mindfulness, and prenatal yoga, which can effectively manage symptoms without posing risks to fetal development.
3. Do all children exposed to cannabis during pregnancy experience cognitive or behavioral issues?
Not all children will exhibit these issues, as outcomes can vary based on factors like frequency of exposure, genetic predispositions, and environmental influences. However, studies show a higher likelihood of cognitive and behavioral challenges.
4. Are there any differences in the impact of prenatal cannabis exposure between boys and girls?
Yes, research suggests gender-specific differences; boys may show more aggression, while girls may experience greater cognitive deficits, such as attention challenges.
5. What are some potential long-term social impacts for children exposed to cannabis in utero?
Children exposed to cannabis during pregnancy may face difficulties with social interactions and relationship-building due to aggression or attention deficits, potentially impacting self-esteem and mental health into adulthood.
References:
https://neurosciencenews.com/cud-pregnancy-aggression-neurodevelopment-27950/.
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know