Health
What Causes Scabies in the Body?

What Causes Scabies in the Body?
What causes scabies in the body? This common skin problem is caused by a type of mite called a scabies mite. It spreads through skin-to-skin contact.
The mite can also be passed to humans from animals. Unlike other mites, which live on animal skin, the scabies mite cannot reproduce and will die within a few days.
While scabies can affect anyone, it is particularly common in congested environments such as nursing homes and hospitals.
The mites are often spread through contact between different types of people in these locations.
Mites

The disease is spread through prolonged skin-to-skin contact and via personal items that are shared between people with scabies.
It is also very easily spread between family members and sexual partners, although this is unlikely to happen in handshakes.
Because the mites are unable to fly or jump, scabies cannot be spread through a handshake.
Nevertheless, scabies is highly contagious, and if you have them, make sure to see a doctor.
Infested clothing and bedding are the most common source of transmission, but regular contact with a dirty toilet seat is not a reliable source of transmission.
Once the mites penetrate your skin, they burrow deep under the surface and lay eggs.
The eggs hatch in about 10 days. The symptoms will usually begin four weeks after contact because the skin becomes sensitive to the immature mites.
Humans, pets, and other animals can contract scabies.
Animal mites can cause a mild skin rash in humans, although this is rare.
The rash is an immune system response to the mites. However, if your symptoms are severe and persistent, see a doctor.
Your doctor may try to diagnose the disease by taking a sample of your skin under a microscope.
Scabies can affect people of all ages and races. It is most prevalent in children and young adults and is more likely to be contracted by sharing bed sheets and clothing.
Infested clothing is also a risk factor. It can easily be passed from person to person through sexual contact and is a serious health risk.
And if you’re sexually active, you should limit contact with those with scabies.
Skin-to-skin contact

Scabies is a disease that is spread through skin-to-skin contact. Patients generally exhibit itching and burrow-like patches of skin.
The affected areas are typically the elbow, armpit, wrist, webbing between the fingers, and nipple or penis of adult males.
Some infants may also develop thick, crusted areas. Skin-to-skin contact can also cause scabies to spread to other parts of the body, including the penis.
Scabies symptoms are not always immediately apparent, and it may take up to four to eight weeks for an infected person to begin to show signs and symptoms of the condition.
The infected person is still infectious for up to 24 hours after being infected, so it’s important to get the treatment right away.
Treatment is necessary for those who have been exposed to the disease, and it should include household members, sexual partners, and close family members.
Treatment should be done at the same time for all those with contact with the infected person.
Most adults contract scabies through sex, but there are also ways to get it without sex.
It’s also easy to spread scabies through personal clothing and bedding.
It’s not spread by sharing a bathroom, either, as the mites can live on your clothes for two to three days before developing a mite egg. But don’t worry, there’s a cure for scabies.
The symptoms of scabies are similar to the symptoms of a cold or flu and are most often spread through skin-to-skin contact.
Affected individuals may have one to ten mites at a time. They may also carry a few eggs.
However, most people with scabies will only have 10 to 15 mites at a time.
A doctor will need to perform a microscopic examination to find out if they have any mite eggs or fecal matter.
Symptoms

In the first few days after becoming infected, a person should wash his or her clothes thoroughly in hot water and dry them on a high-heat dryer.
If the area is infected with new spots or pimples, antibiotics may be necessary to treat them.
Consult your GP or pharmacist for advice. Washing items used for the last two days and storing them in a plastic bag for at least 72 hours after use is also important.
Treatment is recommended for household members and sexual partners as well.
Treatment for scabies consists of killing the mites that cause the disease.
Treatment should be started as soon as you notice the first symptoms, which may take up to 2 weeks for an infected person to show.
Treatment can also include treating those who have recently been infected, as the mites can infect others even after they are not showing any signs.
To get rid of scabies, it is important to wash your clothes, pillows, and soft toys in hot water.
Symptoms of scabies may include intense itching and rash. While oral anti-itch medications will not eliminate the scabies mite, they can relieve the itch temporarily.
A rash may develop, which looks like a rash and can occur in the armpits, between the fingers, and on the buttocks.
Symptoms of scabies may progress to other areas as well, including the genitals and breasts.
Scabies is spread by direct skin contact with a person infected with the parasite.
The risk increases with the degree of infestation. Crusted scabies is most likely to be transmitted by skin-to-skin contact.
While transmission through infested personal items is unlikely, a person can be infected with scabies without noticing it.
It is important to keep your skin clean and dry so you can effectively treat the condition.
Treatments

Treatments for scabies in the entire body are generally available over-the-counter.
Medications that contain permethrin, which kills the mites that cause scabies, are available.
Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine which medication is right for them.
For scabies on the neck and head, the medication permethrin 5% cream is usually recommended.
People with scabies typically experience itchy, crusty skin, and linear burrows.
While the lesions in children may be small and difficult to see, they are typically quite visible.
However, in some cases, the infection may be more widespread, including the back of the body, the head, and the genital area.
In rare cases, crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, affects older adults and people with certain conditions, such as Down syndrome.
Scabies treatment should be based on severity. If the symptoms and signs are still present six weeks after the treatment has been started, the patient should see a doctor rule out other conditions.
A physician may recommend alternative treatments or a different course of therapy.
Common pruritic dermatoses, bullous pemphigoid, and dermatitis herpetiformis should be considered. Moreover, the risk of psoriasis increased in patients who have scabies on the body.
Another treatment for scabies in the body is topical creams.
Topical treatments can be applied to the affected areas at night and rinsed off the next day .
Many of these medications contain sulfur, which can be found over-the-counter. Some people find topical creams effective at relieving their symptoms.
If over-the-counter solutions don’t work, the healthcare provider can prescribe a prescription-strength scabicide.
Prevention

The most effective way to prevent scabies from spreading is to wash and dry items that have been touched by a person with scabies.
You should also treat your bed linen, clothing, and other items frequently used by infected individuals.
Washing items in hot water or dry-cleaning them is an effective way to kill the mites and prevent the spread of scabies.
During outbreaks, the affected person should be treated at the same time as everyone in the household.
When washing clothes and linens, always dry them on a hot cycle or dry-clean them.
Scabies is not transmitted from person to person, but they can spread from skin to skin and from person to object.
Infested surfaces can be passed from one person to another.
Older adults and young children are most susceptible to developing crusted scabies, while those with weakened immune systems may develop Norwegian scabies.
Scabies is caused by microscopic mites that burrow into the skin.
The most effective prevention of scabies is to avoid direct skin-to-skin contact with the infected person.
While avoiding direct skin-to-skin contact is an effective method to prevent scabies, it is not always effective.
People with scabies may be asymptomatic, and they can pass on the disease to others long before any symptoms appear.
As such, it is important to consult a healthcare provider immediately if you suspect you have scabies.
Scabies symptoms are difficult to detect. Fortunately, scabies can be prevented by learning about the symptoms and preventing the spread of mites.
Infected areas may show the first signs of scabies, including itchy skin. A doctor may recommend a topical cream or oral medication to fight the mites.
These products are only available through a physician and should not be used without a prescription.
Conclusion
Tell us anything you know about ” What Causes Scabies in the Body?
Remember your health is wealth
Please, let us know your thoughts in the comments section.
Health
7 Fascinating Facts About Magnesium You Probably Didn’t Know

7 Fascinating Facts About Magnesium You Probably Didn’t Know
Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals for our health, yet many people are unaware of its significance.
This vital nutrient plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, from energy production to maintaining a healthy heart.
In this article, we will delve into seven intriguing facts about magnesium that may surprise you and help you appreciate its importance in your daily life.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a naturally occurring mineral found in various foods and is vital for human health.
It is the fourth most abundant mineral in the body and is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions.
Magnesium contributes to nerve function, muscle contraction, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation.
It can be obtained from various dietary sources, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes.
1. Magnesium is Involved in Energy Production
Did you know that magnesium is essential for converting food into energy? This mineral plays a critical role in the activation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of our cells.
Without sufficient magnesium, your body struggles to produce energy effectively, which can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
How Does It Work?
ATP production occurs in the mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell.
Magnesium helps activate enzymes involved in this energy production process, ensuring that your body has enough energy to perform daily activities.
2. A Key Player in Bone Health
Magnesium is vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Approximately 60% of the magnesium in your body is stored in your bones.
It contributes to bone density and strength by regulating calcium levels in the body, which is crucial for bone formation.
The Calcium Connection
Calcium is often touted as the primary mineral for bone health, but magnesium plays an equally important role.
An imbalance of these two minerals can lead to bone-related issues such as osteoporosis.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is essential for maintaining optimal bone health.
3. Supports Heart Health
Magnesium is a crucial mineral for cardiovascular health. It helps maintain normal heart rhythms and can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Adequate magnesium levels are associated with lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart attacks.
Regulation of Blood Pressure
Magnesium helps relax blood vessels, which can lead to lower blood pressure.
Studies have shown that individuals with higher magnesium intake tend to have better cardiovascular health. Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet can be an effective strategy for supporting heart health.
4. Magnesium and Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a strong link between magnesium levels and mental health.
Magnesium plays a role in regulating neurotransmitters, which are essential for mood stabilization.
Low magnesium levels have been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
Cognitive Function
Magnesium may also enhance cognitive function. Studies have indicated that adequate magnesium intake can improve memory and learning abilities.
This mineral is essential for brain health, making it vital for overall mental well-being.
5. Magnesium Deficiency is Common
Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is surprisingly common.
Factors such as poor diet, chronic stress, and certain medical conditions can lead to low magnesium levels.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include muscle cramps, fatigue, and irritability.
Risk Factors for Deficiency
Certain populations are at a higher risk for magnesium deficiency, including the elderly, those with gastrointestinal diseases, and individuals who consume a diet low in whole foods.
It’s essential to recognize the signs of deficiency and consider increasing your magnesium intake through diet or supplements if necessary.
6. Natural Relaxant
Magnesium is often referred to as a natural relaxant due to its calming effects on the nervous system.
It helps regulate cortisol levels (the stress hormone) and promotes relaxation, making it beneficial for those dealing with anxiety and stress.
Improving Sleep Quality
In addition to its relaxing properties, magnesium can improve sleep quality.
Many people find that magnesium supplements help them fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer, making it a popular choice for those struggling with insomnia.
7. Magnesium in Sports Performance
Athletes and active individuals often benefit from magnesium’s role in muscle function and recovery.
Magnesium helps prevent muscle cramps and can aid in post-exercise recovery by reducing inflammation and promoting relaxation.
Enhancing Athletic Performance
Research has shown that adequate magnesium levels can enhance athletic performance.
It is involved in muscle contraction and relaxation, making it essential for peak performance during exercise.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral that plays an essential role in various bodily functions. From supporting energy production to promoting heart health and mental well-being, its importance cannot be overstated.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake through a balanced diet rich in whole foods can significantly enhance your overall health and quality of life.
If you suspect you may be deficient in magnesium, consider consulting with a healthcare provider to assess your levels and discuss dietary changes or supplements that may be beneficial.
FAQs about Magnesium
1. What are the best dietary sources of magnesium?
The best sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables (like spinach), nuts (especially almonds and cashews), seeds (such as pumpkin seeds), whole grains (like brown rice and quinoa), and legumes (like beans and lentils).
2. How much magnesium do I need daily?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies by age and gender. Generally, adult men should aim for about 400-420 mg per day, while adult women should aim for about 310-320 mg.
3. Can I take magnesium supplements?
Yes, magnesium supplements are available and can be beneficial, especially for individuals who may not get enough from their diet. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
4. What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency?
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, irritability, and irregular heart rhythms. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
5. Is it possible to get too much magnesium?
Yes, while magnesium from food sources is generally safe, excessive supplementation can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Always consult a healthcare provider before increasing your magnesium intake significantly.
References:
Health
Whooping Cough: Understanding Its Resurgence and Prevention
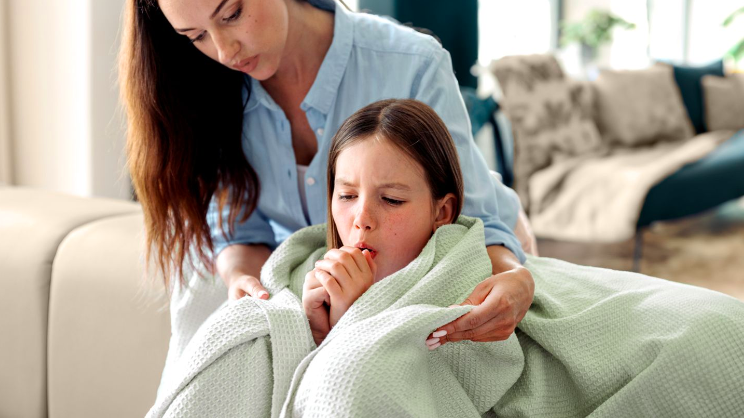

Health
The Power of Beans: Why This Superfood is a Nutritional Treasure
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know






