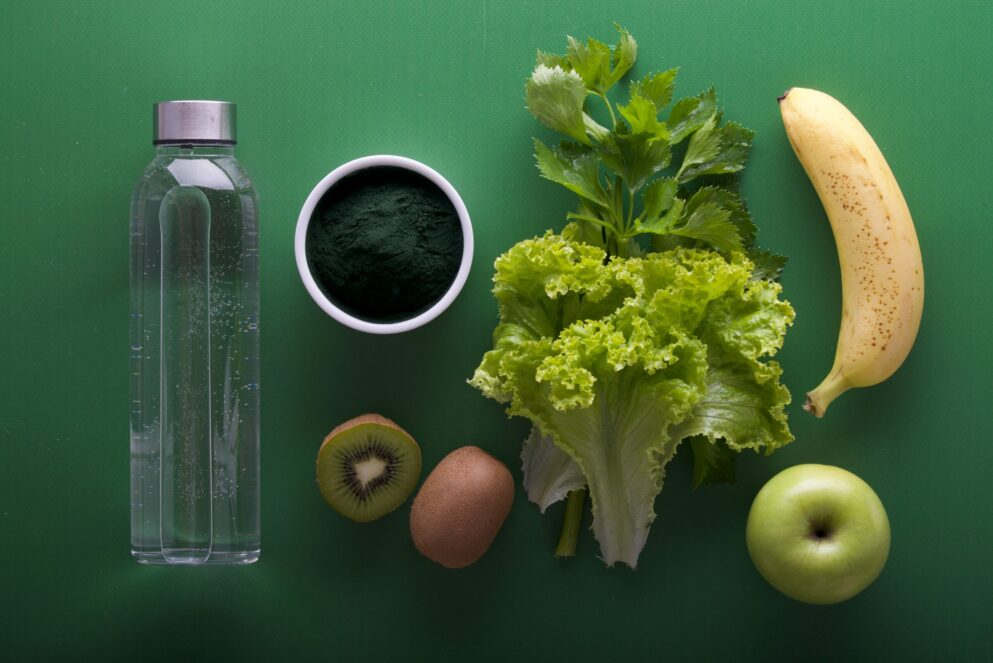
Health
How to Make Your Gut Health Better

Last Updated on April 3, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
How to Make Your Gut Health Better
An In-Depth Guide The digestive tract, or gut, is sometimes referred to as the “second brain” because of the significant role it plays in the maintenance and improvement of our overall health and well-being.
When the gut is healthy, digestion, nutrient absorption, and immunity are all improved; when the gut is diseased, however, this can contribute to a variety of health problems.
the extensive spectrum of health issues, including digestive difficulties, dietary allergies, and chronic inflammation.
This article will discuss the many methods by which you can improve the health of your digestive tract, including changes in your food and lifestyle. and vitamins.
Diet and Gut Health
Diet and gut health are inextricably linked because the foods you consume can alter the composition of the bacteria that live in your digestive tract.
Maintaining a healthy gut microbiota, which is essential for digestive health, can be encouraged by eating a diet that is both balanced and varied. immunological function, as well as general health and wellness. The following factors can affect gut health:
foods high in fiber: Fiber is beneficial because it both nourishes the good bacteria in the digestive tract and encourages regular bowel movements. Fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains are some examples of foods that are high in fiber content.
Probiotics are live bacteria that can be found in fermented foods including yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and pickles. Probiotics have been shown to have health benefits. The healthy balance of gut flora can be helped by taking probiotics.
Prebiotics are foods that are not digested but provide nourishment for the beneficial bacteria that are found in the digestive tract.mOnions, garlic, bananas, and oats are some examples of such foods.
Avoiding processed meals is important since these foods typically include high amounts of sugar, salt, and harmful fats, all of which can disrupt the natural balance of bacteria in the gut and have a detrimental effect on gut health.
Hydration: Consuming an adequate amount of water is vital for maintaining digestive health since it assists in the movement of waste through the digestive system.
It is essential to keep in mind that everybody has a different digestive system, so the things that work for one person could not work for another.
Maintaining a healthy weight can be made easier by eating a diet that is both varied and well-balanced, as well as by paying attention to how particular foods affect your mood.
the condition of one’s gut Sure, here is some further information regarding diet and the health of the gut:
foods that are high in antioxidants Antioxidants help reduce inflammation in the body, which is essential for maintaining good gut health. Berries, dark leafy greens, nuts, and seeds are some examples of foods that are rich in antioxidants.
Reducing your intake of sugar and artificial sweeteners: Consuming an excessive amount of sugar can have a
detrimental effect on gut health since it encourages the growth of dangerous bacteria.
It has also been demonstrated that artificial sweeteners have a detrimental effect on the bacteria in the stomach.
Consuming alcohol in moderation is important since drinking too much can injure the lining of the digestive tract as well as the bacteria that live there.
Consuming a wide range of meals: Consuming a wide range of foods can give the gut a variety of nutrients as well as healthy microorganisms.
Eating with awareness: It is possible to improve your digestive health by, among other things, paying attention to your feelings of hunger and fullness, avoiding distractions while you eat, and digesting each bite of food thoroughly.
In conclusion, a healthy diet should include a variety of foods that are high in nutrients and should reduce the use of processed and sugary meals.
foods, and is accompanied by mindful eating behaviors that can have a beneficial influence on gut health and overall well-being. foods and mindful eating habits can also have a favorable impact on overall well-being.
However, it is essential to pay attention to your body and make dietary adjustments that are suitable for you, seeking the advice of a qualified medical practitioner if you feel that you require it.
What kind of diet is best for the digestive tract?
A diet that includes a wide variety of foods that are rich in nutrients, such as fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and sources of lean protein, is the diet that is most beneficial to gut health.
Foods that are rich in prebiotics, such as garlic, onions, and leeks, are also essential for encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is essential to cut back on the consumption of processed meals, as well as sugar and artificial sweeteners because these things might have a bad effect on the health of the gastrointestinal tract. Gut health can be supported by eating a diet high in fiber, foods that have been fermented, and whole foods.
The following are some of the foods that are very beneficial to gut health:
foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains Fermented foods: such yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi foods that are high in probiotics, such as miso, tempeh, and pickles meals derived from plants, such as vegetables and fruits, as well as foods high in healthy fats, such as olive oil and avocados Foods that are prebiotic, such as onions, garlic, and leeks In addition, it is essential to cut back on or completely avoid consuming processed foods, added sugars, and artificial sweeteners, all of which have the potential to damaging to the bacteria in the gut.
Incorporating a variety of protein sources into your diet, such as lean meats, poultry, fish, and plant-based foods is another important step. sources can provide the essential components for the development of healthy gut bacteria.
A healthy stomach can also be supported by consuming a lot of water and minimizing the amount of alcohol one drinks.
Before beginning any new treatment or routine, it is strongly suggested to seek the advice of a qualified medical practitioner or a licensed dietician. new nutritional routine, especially if you already suffer from any preexisting health concerns.
Because everyone’s gut microbiome is different, it is essential to take a personalized approach to dietary choices and gut health.
Are there any meals that are known to cause digestive issues?
It’s true that some foods, such as dairy products, wheat, and soy, can wreak havoc on your digestive system.
These meals include proteins that can be difficult to digest for some people, causing them to experience symptoms such as bloating, gas, and stomach pain.
It is crucial to pay attention to your body and identify any items that may be causing troubles with your gut so that you can take appropriate action.
Remove them from your diet to promote better health in your digestive tract. Yes, specific meals can be responsible for the digestive issues experienced by some people. The following
are some foods that are known to cause digestive issues:
Lactose intolerance is a common digestive disorder that affects the capacity to digest lactose, a sugar that is found in dairy products.
This sugar is responsible for the symptoms of lactose intolerance.
Gluten: People who have celiac disease or are sensitive to gluten may have digestive symptoms such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea when they consume gluten.
People who have irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other functional gut diseases may experience digestive problems as a result of a category of short-chain carbohydrates known as FODMAPs.
These carbohydrates have the potential to be poorly absorbed in the stomach. Foods that are high in fat: Fatty meals might cause some people to experience bloating, gas, and diarrhea since they slow down digestion and cause these symptoms.
Sweeteners made with artificial ingredients:
certain individuals have a sensitivity to artificial sweeteners, which can result in bloating, gas, and pain in the digestive tract.
It is essential to keep in mind that not all people will experience digestive issues as a result of consuming certain meals and that everybody’s digestive system is different.
If you have reason to believe that a specific food is the source of your digestive problems, it is in your best interest to eliminate that food from your diet and seek the advice of a healthcare practitioner or a qualified dietitian.
In addition, some people may have discomfort in their digestive system as a result of specific spices, and foods that are heavy in sugar or alcohol. Some people have bloating and gas issues when they consume beverages containing caffeine or carbonation.
Food intolerances and food allergies, which can result in symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and skin rashes, are also very significant factors to take into consideration.
It is recommended that you seek the advice of a healthcare professional if you continue to have problems related to your digestive system.
In general, supporting digestive health can be accomplished by consuming a diet that is well-balanced and contains a range of whole foods, minimizing consumption of processed and high-fat meals, and drinking lots of water.
If you suffer from digestive issues, avoiding foods that are known to aggravate the condition and eating meals that are kind to the gut may help minimize symptoms.
However, the best course of action is to seek the individualized guidance of a healthcare professional at all times.
Alterations to one’s way of life that have a beneficial impact on gut health: Maintaining a healthy weight by consuming a diet that is rich in fiber and contains plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Taking in a lot of water throughout the day.
- consuming less highly processed and fatty foods.
- Reducing sugar intake.
Reducing one’s intake of alcohol as much as possible
- Included in one’s diet are both items that have been fermented and probiotics.
- Participation in consistent physical activity.
- practices of relaxation, physical activity, and/or therapy for the management of stress.
- Getting proper sleep.
When possible, you should stay away from antibiotics.
These adjustments can help improve the diversity of the bacteria that live in the gut, increase the number of
beneficial bacteria, and lower inflammation, all of which can lead to improved gut health and general well-being.
Additional suggestions for enhancing the health of your gut:
- Completely masticating one’s food.
- Consuming food slowly and free from interruptions.
- Not missing meals or overeating.
Keeping away from foods like gluten and lactose, which are known to provoke digestive problems, can help. The use of prebiotics, which is foods such as garlic, onions, and bananas that assist promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the intestines can be beneficial.
Putting into practice mindful eating and paying attention to indications of fullness and hunger while you eat. Making use of natural medicines to alleviate digestive difficulties, such as ginger or peppermint, is recommended. Quit smoking, as this habit can cause damage to the lining of the gut and has a bad impact on gut health.
Maintaining a regular checkup schedule and communicating any digestive issues with your primary care physician are both important. These behaviors can support the maintenance of a healthy environment in the gut, which in turn can benefit digestion, immunological function, and general health.
What kind of effects does stress have on one’s gut health?
The delicate balance of bacteria that normally lives in the gut can be thrown off by stress, which can then lead to a variety of health problems.
cause problems with digestion, including acid reflux, bloating, and constipation. Stress can also damage the barrier that prevents hazardous substances from entering the body in the gut, which makes it simpler for these substances to do so.
can provoke an immunological response. It is crucial to managing stress through activities such as yoga, meditation, and breathing exercises to promote the health of your stomach.
exercises including deep breathing
In several different ways, stress can be detrimental to one’s digestive health:
Changes both the composition and diversity of the bacteria in the gut. Reduces the release of digestive enzymes and the activity of the digestive tract Raises the risk of inflammation
Raise the risk of acquiring gastrointestinal conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) (IBD).
This can lead to changes in eating patterns, such as overeating or not eating enough, both of which are harmful to the health of the gastrointestinal tract.
His can cause the gut-brain axis to become more compromised, which in turn can lead to issues with digestion and the general health of the gut.
What part does sleep play in making sure your gut is healthy?
causes an increase in the production of the stress hormone cortisol, which can interfere with the gut’s natural ability to operate normally. This can lead to a variety of digestive problems including cramping in the stomach region, diarrhea, and constipation.
Can make preexisting digestive problems, such as acid reflux or ulcers, significantly worse. Can cause damage to the intestinal barrier, making it more porous and increasing the risk of potentially dangerous substances entering the circulation as a result.
Because it helps to regulate hormones and the immune system, sleep is a very important factor in digestion Our bodies manufacture growth hormones when we are sleeping, which assists in the process of repairing and regenerating intestinal cells.
Inadequate sleep can also throw off the balance of microorganisms in the gut, which can result in digestive problems and a weakened immune system. impaired immune system.
Establishing a regular sleep schedule and making it a priority to get between seven and nine hours of excellent sleep each night can have a positive impact on the health of your digestive tract.
Sleep is an extremely important factor in the maintenance of good gut health since it helps to regulate hormones, improve gut motility, and lower inflammation.
It assists in the regulation of hormones such as cortisol and ghrelin, both of which can affect hunger as well as digestion. A sufficient amount of sleep can also increase gut motility, which is important for the effective movement of food through the digestive tract.
Additionally, not getting enough sleep can result in an increase in inflammation in the stomach, which can have a detrimental effect on gut health and raise the likelihood of developing digestive diseases.
It is essential to strive for consistent and quality sleep if you want to keep your gut in the best possible health. In addition, sleep can also affect the microbiome, which is the collection of bacteria that live in the digestive tract.
Studies have shown that not getting enough sleep can change the composition of the microbiome in the gut, leading to a decrease in the variety and quantity of helpful bacteria. A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall gut health and can affect digestion, metabolism, and the immune system.
Getting enough high-quality sleep each night can assist to establish a healthy gut microbiota. In addition, while we are sleeping, our bodies release chemicals like melatonin, which can assist to calm the digestive tract and reduce inflammation.
Additionally, during sleep, the digestive system is given time to rest and heal, which enables it to concentrate on mending injuries and regenerating damaged cells.
In conclusion, sleep is a very important factor in maintaining gut health because it helps to regulate hormones while also boosting gut function.
motility, lowering inflammation, encouraging healthy microbiota, and giving the digestive system a chance to relax and recover are all benefits that probiotics offer.
It has been shown that not getting enough sleep can have a detrimental impact on gut health and raise the risk of digestive diseases. Medications and the Condition of the Gut
Which dietary supplements are best for improving digestive health?
Probiotics, prebiotics, digestive enzymes, and glutamine are all examples of dietary supplements that could potentially aid enhance gut health.
While prebiotics serves as a source of food for the beneficial bacteria already present in the gut, probiotics encourage the growth of these bacteria.
To better digest food and promote better digestion, digestive enzymes can be helpful. Glutamine, on the other hand, is an amino acid that helps to maintain the integrity of the gut lining.
Are there any potential downsides associated with taking vitamins for gut health?
It is always important to check with your healthcare professional before beginning any new supplement regimen, but in general, supplements for gut health are safe and well-taken by the majority of people who use them.
When taking a probiotic supplement for the first time, some people may experience adverse effects such as bloating, gas, and diarrhea; however, these symptoms typically disappear after a few days of using the supplement.
Because the gut plays such a significant role in the digestion, absorption, and usage of supplements, gut health, and supplement use are closely related. nutrients obtained not only from the food we consume but also from any supplements we may take.
A healthy gut has a profound impact on overall health, including mental health, immunity, and metabolism, in addition to having a direct relationship with gut microbes. Common supplements for gut health include probiotics, which are live bacteria and yeast, and prebiotics,
which are the fiber that feeds probiotics.
intestinal flora), digestive enzymes, and fiber. These can help boost the diversity of the microbiome in the gut, which in turn can help improve digestion and alleviate symptoms of gut-related diseases including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
It is essential to remember that not all dietary supplements are made equal, and it is necessary to discuss your supplement needs with a medical professional. before beginning any new supplement routine with your healthcare professional.
Particular populations, such as pregnant women or the elderly, may be more at risk for certain supplement-medication interactions than others. have distinct supplement needs.
improving gut health by maintaining a healthy diet and using specific supplements can have a favorable impact. overall health, but it is essential to proceed with caution and under the direction of a trained practitioner if you choose to pursue it.
Sure! Additional considerations include the following:
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeast that have the potential to improve the diversity and balance of the. microbiome found in the gut. It has been demonstrated that various strains of probiotics have a variety of positive effects on gut health, including the reduction of inflammation, the improvement of gut barrier function, and the enhancement of digestion.
Prebiotics: These are indigestible fibers that serve as nourishment for the healthy bacteria in the gut. Prebiotics can assist enhance gut health and support general well-being because they encourage the growth of bacteria that are favorable to human health.
Digestive enzymes are molecules that assist in the breakdown of food into smaller components, making it simpler for the body to absorb the nutrients that are present in the meal.
Some digestive enzyme supplements are designed to assist with general digestive function, while others are geared specifically toward assisting with the digestion of particular types of food (such as carbs, proteins, or fats).
Fiber: Fiber is an essential component of a balanced diet and can assist in the promotion of gut health by encouraging regular bowel movements, lowering the risk of constipation, and encouraging the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Vitamins and minerals: Certain vitamins and minerals, including vitamin D, zinc, and iron, are essential for maintaining healthy gut function.
These vitamins and minerals can be received through dietary sources or the use of supplements.
However, it is essential to exercise caution while consuming large doses of these nutrients because an excess of them might be harmful to one’s health.
In conclusion, taking supplements may be an efficient strategy to maintain gut health, but it is essential to speak with a healthcare professional before doing so.
Before beginning any new supplement regimen, it is important to consult a healthcare expert. A diet that is both well-balanced and rich in fiber and foods that have been fermented can be beneficial to the health of the digestive tract.
Conclusion
Improving the health of one’s stomach is critical to improving one’s overall health and well-being. Altering your eating habits will allow you to:
You may enhance your health and the health of your gut bacteria by making changes to your diet, lifestyle, and supplement routine.
Health
Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?

Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?
In recent years, hair gummies have taken the health and beauty world by storm, boasting promises of luscious locks and a speedy route to hair health.
But with an array of products flooding the market, it’s essential to separate fact from fiction.
Are these colorful, chewy supplements a miracle solution for your hair troubles, or are they simply a trendy snack with little efficacy?
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the science behind hair gummies, their ingredients, potential benefits, and the questions surrounding their effectiveness.
Understanding Hair Health
The Basics of Hair Growth
To fully grasp the impact of hair gummies, it’s vital to understand how hair grows.
Each strand of hair goes through three main phases:
- Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase, which can last several years. The length of this phase varies among individuals.
- Catagen Phase: A transitional phase lasting a few weeks, where hair growth slows, and the hair follicle shrinks.
- Telogen Phase: The resting phase, lasting a few months before the hair falls out, making way for new growth.
Hair health is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, diet, and overall health.
As such, a balanced approach to hair care, encompassing nutrition, proper hair care routines, and avoiding damaging practices, is essential.
Common Causes of Hair Issues
Hair loss or poor hair health can arise from numerous factors:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals can hinder hair growth.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders can significantly affect hair health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger hair loss through a condition known as telogen effluvium.
- Medical Conditions: Certain diseases and medications can also contribute to hair loss.
What Are Hair Gummies?
Hair gummies are dietary supplements designed to promote hair health.
They are usually made with a combination of vitamins, minerals, and sometimes botanical extracts, often marketed as a convenient and tasty alternative to traditional vitamin pills.
Key Ingredients in Hair Gummies
While formulations vary, here are some common ingredients found in hair gummies:
- Biotin: A B-vitamin known for its role in hair and nail health. Biotin deficiencies can lead to brittle hair and hair loss.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: Antioxidants that help protect hair from oxidative stress, promoting a healthy scalp and hair growth.
- Folic Acid: Important for cell growth and regeneration, folic acid is believed to support healthy hair follicles.
- Zinc: Plays a role in hair tissue growth and repair, making it a crucial mineral for maintaining healthy hair.
- Collagen: An essential protein for skin elasticity that may also benefit hair strength and growth.
Do Hair Gummies Really Work?
The Science Behind Hair Gummies
While the ingredients in hair gummies are known to contribute to hair health, the question remains:
Do they work as effectively as claimed?
Here’s what the research suggests:
- Biotin: Studies have shown that biotin can improve hair thickness in those with deficiencies, but most people get sufficient biotin from their diet. Supplementing with biotin may not yield significant benefits for individuals who are not deficient.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Research indicates that vitamins A, C, D, E, and minerals like zinc and iron play a role in maintaining healthy hair. However, simply taking these vitamins in gummy form doesn’t guarantee results unless there’s a deficiency present.
- Collagen: Some studies suggest that collagen supplements can improve hair and skin health by providing amino acids essential for protein synthesis. However, more research is needed to establish direct benefits for hair growth.
User Experiences and Anecdotes
While anecdotal evidence often highlights positive experiences with hair gummies, it’s important to approach these testimonials with caution. Individual results may vary, and factors such as diet, overall health, and genetics play significant roles in hair health.
Potential Benefits of Hair Gummies
While not a miracle solution, hair gummies may offer certain benefits:
- Convenient Form: For those who struggle with swallowing pills, gummies provide a palatable alternative.
- Added Nutrients: If you have a deficiency in specific vitamins or minerals, hair gummies can supplement your diet effectively.
- Increased Awareness of Nutrition: Taking supplements can prompt individuals to pay more attention to their overall nutritional intake.
- Improved Hair Appearance: Users may notice shinier and healthier-looking hair due to the vitamins and antioxidants present in these products.
Are There Risks?
While hair gummies are generally safe, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Overconsumption: Gummies are often flavored and sweetened, which may lead to overconsumption and potential digestive issues.
- Sugar Content: Many gummies contain added sugars, which can contribute to other health problems if consumed excessively.
- Interactions with Other Supplements: If you’re taking other vitamins or supplements, it’s essential to ensure you’re not exceeding recommended doses, particularly for fat-soluble vitamins like A and E, which can accumulate in the body.
What Experts Say
Dermatologists and nutritionists often emphasize a balanced diet over reliance on supplements.
They suggest that whole foods—rich in vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats—are the best source for hair health.
Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, and eggs can provide essential nutrients without the added sugars and potential downsides of gummies.
Conclusion:
Fad or Fact?
In conclusion, hair gummies may not be the ultimate solution for hair health, but they can serve as a helpful supplement for those with specific nutritional deficiencies.
They are convenient and may improve the overall appearance of hair for some users. However, it’s crucial to approach them with realistic expectations and prioritize a balanced diet rich in whole foods.
If you’re considering adding hair gummies to your routine, consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to ensure you’re making an informed decision that aligns with your health goals.
FAQs
1. Can hair gummies replace a balanced diet?
No, hair gummies are supplements and should not replace a balanced diet. They can help fill nutritional gaps but should be taken alongside a healthy eating plan.
2. How long does it take to see results from hair gummies?
Results vary, but users may start noticing improvements in hair texture and appearance after 4-12 weeks of consistent use.
3. Are hair gummies safe for everyone?
Most hair gummies are safe for general use; however, individuals with specific health conditions or allergies should consult a healthcare professional before taking them.
4. Can I take hair gummies with other supplements?
Yes, but be cautious of total vitamin and mineral intake to avoid exceeding recommended daily allowances. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
5. Are there any side effects of hair gummies?
Some users may experience digestive issues, allergic reactions, or headaches due to high sugar content or specific ingredients. It’s best to start with a small dose to assess tolerance.
References:
Health
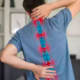
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
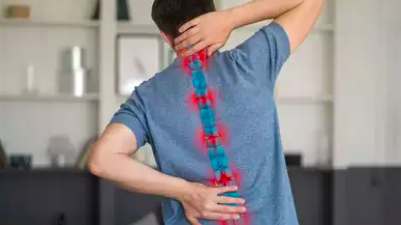
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
The spine is an essential structure in the human body, acting as a central pillar that supports our posture, facilitates movement, and protects the spinal cord.
Despite its importance, many individuals experience various spine-related conditions that can impact their quality of life.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore common spinal conditions, their causes, symptoms, and effective methods to address them.
What is the Spine?
The spine, also known as the vertebral column, is composed of 33 vertebrae arranged in a flexible yet sturdy structure.
It serves several critical functions:
- Support: The spine supports the head and allows for an upright posture.
- Protection: It encases and protects the spinal cord, a crucial component of the central nervous system.
- Mobility: The spine allows for a wide range of movements, including bending, twisting, and turning.
- Weight Distribution: It helps distribute weight and absorbs shock during activities like walking or running.
Understanding the structure and function of the spine is vital for recognizing and addressing the conditions that can affect it.
Common Spinal Conditions
Several conditions can adversely impact the spine, leading to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. Here are some of the most common spinal conditions:
1. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear in the outer layer. This can compress nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Heavy lifting or sudden movements
- Trauma or injury
Symptoms:
- Localized back pain
- Radiating pain to the limbs
- Numbness or tingling
Treatment:
- Physical therapy
- Pain management through medications
- In severe cases, surgery may be required.
2. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition often occurs in the cervical (neck) or lumbar (lower back) regions.
Causes:
- Age-related changes in the spine
- Osteoarthritis
- Herniated discs
Symptoms:
- Pain or cramping in the legs
- Weakness or numbness
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Medications for pain relief
- In some cases, surgical decompression may be necessary.
3. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, often appearing in childhood or adolescence. While many cases are mild, severe scoliosis can lead to complications.
Causes:
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
- Congenital (present at birth)
- Neuromuscular conditions
Symptoms:
- Uneven shoulders or hips
- Visible curvature of the spine
- Back pain
Treatment:
- Monitoring and observation for mild cases
- Bracing for growing children
- Surgery for severe curvatures.
4. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. This is particularly concerning for the vertebrae, which can lead to compression fractures.
Causes:
- Aging
- Hormonal changes
- Lack of calcium and vitamin D
Symptoms:
- Height loss
- Back pain due to fractures
- A stooped posture
Treatment:
- Medications to strengthen bones
- Nutritional supplements (calcium and vitamin D)
- Weight-bearing exercises to improve bone density.
5. Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease refers to the wear and tear of spinal discs over time, leading to pain and reduced flexibility.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Repetitive stress on the spine
- Genetics
Symptoms:
- Chronic back pain
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Possible radiating pain in the limbs
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Pain management strategies
- Surgical options for severe cases.
Preventing Spinal Conditions
While some spinal conditions are unavoidable due to genetics or aging, many can be prevented or mitigated through healthy lifestyle choices.
Here are some preventative measures:
1. Maintain Good Posture
Proper posture helps reduce strain on the spine. When sitting, keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and feet flat on the ground. When standing, distribute your weight evenly on both feet.
2. Stay Active
Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles that support the spine and improves flexibility. Aim for a balanced routine that includes strength training, aerobic exercise, and stretching.
3. Ergonomic Work Environment
If you spend long hours at a desk, ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed. Adjust your chair, desk height, and computer monitor to reduce strain on your back and neck.
4. Healthy Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine and helps prevent conditions like degenerative disc disease and spinal stenosis.
5. Avoid Smoking
Smoking impairs blood flow and can lead to spinal degeneration. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of spinal issues.
Effective Treatments for Spinal Conditions
If you experience spine-related pain or discomfort, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists develop personalized exercise programs to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. They may also use techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to manage discomfort.
2. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage mild to moderate pain. Prescription medications may be necessary for more severe pain or inflammation.
3. Injections
Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These are typically used when other treatments have failed.
4. Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. Common surgical procedures include discectomy (removal of herniated disc material), spinal fusion, and laminectomy (removal of part of the vertebra).
5. Alternative Therapies
Complementary treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may provide relief for some individuals. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying alternative therapies.
Conclusion
Understanding the spine and its common conditions is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing potential issues.
By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can address spinal conditions effectively.
Implementing preventative measures, such as maintaining good posture and staying active, can significantly reduce the risk of developing spine-related issues.
Prioritize your spinal health, consult with professionals when necessary, and take proactive steps to ensure a healthy and pain-free back.
FAQs
1. What are the common symptoms of spinal conditions?
Common symptoms include localized back pain, radiating pain in the limbs, numbness, tingling sensations, and difficulty with movement.
2. How can I improve my posture while working?
To improve your posture at work, adjust your chair and desk height, use a supportive chair, and ensure your computer screen is at eye level.
3. Can physical therapy help with spinal conditions?
Yes, physical therapy can help strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain associated with various spinal conditions.
4. When should I see a doctor for back pain?
If you experience persistent back pain that does not improve with rest, is accompanied by numbness or weakness, or interferes with daily activities, it’s essential to see a doctor.
5. Are there lifestyle changes I can make to prevent spinal issues?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, practicing good posture, and avoiding smoking can help prevent spinal conditions.
References:
Health
Understanding the Causes of Premature Menopause in Women
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know