Health
How to Get Rid of Pimples Fast: 10 Easy Home Remedies

Last Updated on March 11, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
How to Get Rid of Pimples Fast: 10 Easy Home Remedies
Pimples are a common skin condition that affects many people, especially during puberty.
They are caused by excess oil production, clogged pores, and bacteria.
Pimples can be painful and embarrassing, and many people are eager to get rid of them as fast as possible.
While there are many over-the-counter products that claim to help with acne, there are also several natural remedies that you can try at home.
In this article, we will discuss 10 easy home remedies that can help you get rid of pimples fast.
What are pimples and what causes them?
Pimples are a type of acne that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
This can lead to inflammation and the formation of a raised, red bump on the skin.
Pimples are most common on the face, but they can also occur on the neck, chest, back, and shoulders.
The exact cause of pimples is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of factors, including:
- Hormonal changes: Pimples are most common during puberty when hormone levels fluctuate.
- Excess oil production: When the skin produces too much oil, it can clog pores and lead to pimples.
- Bacteria: The bacteria that live on our skin can contribute to the formation of pimples.
Can you get rid of pimples fast?
Yes, it is possible to get rid of pimples quickly, but it depends on the severity of the acne and the type of treatment used.
Mild to moderate acne can often be treated at home with natural remedies, while more severe cases may require prescription medication.
What are some easy home remedies for pimples?
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial agent that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
To use tea tree oil for pimples, dilute a few drops in a carrier oil like coconut oil and apply it to the affected area with a cotton swab.
Honey
Honey has antibacterial properties that can help kill the bacteria that cause pimples.
It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce redness and swelling.
To use honey for pimples, apply a small amount of raw, organic honey to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
It also contains salicylic acid, which can help unclog pores.
To use aloe vera for pimples, apply a small amount of fresh aloe vera gel to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
It also contains alpha-hydroxy acids, which can help exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
To use apple cider vinegar for pimples, dilute a few teaspoons in water and apply to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Witch Hazel
Witch hazel has astringent properties that can help tighten pores and reduce inflammation.
It also contains tannins, which can help kill bacteria on the skin.
To use witch hazel for pimples, apply a small amount to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Lemon Juice
Lemon juice has antibacterial and exfoliating properties that can help kill bacteria on the skin and unclog pores.
It also contains vitamin C, which can help reduce inflammation and promote healing. To use lemon juice for pimples, Sure, there’s an expanded version of the article:
Pimples can be a frustrating and embarrassing skin condition that affects many people, especially during adolescence.
Pimples are caused by a combination of factors, including hormonal changes, excess oil production, and bacterial growth.
While there are many over-the-counter products that claim to treat pimples, they can be harsh on the skin and may not always work as quickly as desired.
Fortunately, there are several natural remedies that can help you get rid of pimples fast.
In this article, we will discuss 10 easy home remedies for pimples.
What are Pimples and What Causes Them?
Pimples are a type of acne that occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells.
The clogged pore creates an environment that allows bacteria to grow, leading to inflammation and the formation of a raised, red bump on the skin.
Pimples can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, chest, back, and shoulders.
Several factors can contribute to the development of pimples.
Hormonal changes are one of the most significant factors, which is why pimples often appear during puberty.
Hormones can cause the skin to produce more oil, leading to clogged pores.
Bacteria on the skin can also contribute to the formation of pimples by infecting clogged pores.
Other factors that can contribute to the development of pimples include genetics, stress, and certain medications.
Can You Get Rid of Pimples Fast?
The length of time it takes to get rid of pimples varies depending on the severity of the acne and the type of treatment used.
Mild to moderate acne can often be treated at home with natural remedies, while more severe cases may require prescription medication.
It is possible to get rid of pimples quickly, but it’s important to be patient and consistent with your treatment. 10 Easy Home Remedies for Pimples
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is a natural antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory agent that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
A study found that tea tree oil was as effective as benzoyl peroxide, an ingredient commonly found in acne treatments.
To use tea tree oil for pimples, dilute a few drops in a carrier oil like coconut oil and apply it to the affected area with a cotton swab.
Honey
Honey has antibacterial properties that can help kill the bacteria that cause pimples.
It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce redness and swelling.
One study found that honey was more effective than benzoyl peroxide at reducing inflammation and improving overall skin condition.
To use honey for pimples, apply a small amount of raw, organic honey to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Aloe Vera
Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
It also contains salicylic acid, which can help unclog pores.
A study found that aloe vera was effective in reducing the severity of acne.
To use aloe vera for pimples, apply a small amount of fresh aloe vera gel to the affected area and leave it on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar has antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
It also contains alpha-hydroxy acids, which can help exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
A study found that applying a mixture of water and apple cider vinegar to the skin twice a day for eight weeks led to a significant improvement in acne.
Use apple cider vinegar for
pimples, dilute a small amount of apple cider vinegar with water, and apply to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a natural anti-inflammatory agent that can help reduce redness and swelling.
It also has antimicrobial properties that can kill bacteria on the skin.
To use turmeric for pimples, mix a small amount of turmeric powder with water to form a paste and apply it to the affected area.
Leave on for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Green Tea
Green tea contains antioxidants and antimicrobial compounds that can help reduce inflammation and kill bacteria on the skin.
A study found that applying a mixture of green tea and 2% topical erythromycin (an antibiotic) to the skin twice a day for six weeks led to a significant improvement in acne.
To use green tea for pimples, brew a cup of green tea and allow it to cool.
Apply the cooled tea to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is a natural astringent that can help reduce inflammation and oiliness of the skin. It also has antimicrobial properties that can kill bacteria on the skin.
To use witch hazel for pimples, apply a small amount of witch hazel to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Lemon Juice
Lemon juice contains alpha-hydroxy acids that can help exfoliate the skin and unclog pores.
It also has antimicrobial properties that can kill bacteria on the skin.
To use lemon juice for pimples, dilute a small amount of lemon juice with water and apply it to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Garlic
Garlic contains allicin, a compound that has antimicrobial properties that can kill bacteria on the skin.
To use garlic for pimples, crush a few cloves of garlic and apply the juice to the affected area with a cotton ball.
Leave on for 5-10 minutes before rinsing off with warm water.
Ice
Ice can help reduce inflammation and redness associated with pimples.
To use ice for pimples, wrap a few ice cubes in a clean cloth and apply them to the affected area for a few minutes at a time.
Conclusion
Pimples can be a frustrating and embarrassing skin condition, but there are several natural remedies that can help you get rid of them fast.
Tea tree oil, honey, aloe vera, apple cider vinegar, turmeric, green tea, witch hazel, lemon juice, garlic, and ice are all easy home remedies that can help reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and unclog pores.
It’s important to be patient and consistent with your treatment, as it may take time to see results.
If your acne is severe or doesn’t improve with home remedies, it’s important to seek medical advice from a dermatologist.
Health
Understanding the Risk Factors for Developing Preeclampsia

Understanding the Risk Factors for Developing Preeclampsia
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and potential damage to organs such as the liver and kidneys.
It usually occurs after the 20th week of pregnancy and can have significant implications for both the mother and the baby.
Identifying the risk factors associated with preeclampsia is crucial for early intervention and management.
This article delves into the various risk factors, how they contribute to the development of preeclampsia and strategies for monitoring and prevention.
What Is Preeclampsia?
Preeclampsia is a condition that affects approximately 5-8% of pregnancies worldwide. It typically manifests with elevated blood pressure and proteinuria (excess protein in the urine).
If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications such as eclampsia, which involves seizures and can jeopardize both maternal and fetal health.
Risk Factors for Preeclampsia
Understanding the risk factors for preeclampsia can help in early diagnosis and management. Below are the primary risk factors associated with this condition:
1. Previous History of Preeclampsia
Women who have experienced preeclampsia in previous pregnancies are at a higher risk of developing the condition in subsequent pregnancies. The recurrence risk is approximately 20-30% if preeclampsia occurs in a previous pregnancy.
2. First Pregnancy
The risk of preeclampsia is higher in women who are pregnant for the first time. This is thought to be related to the body’s adjustment to the physiological changes associated with pregnancy.
3. Advanced Maternal Age
Women who are over the age of 35 are more likely to develop preeclampsia. The increased risk is associated with age-related changes in blood vessels and the body’s ability to manage pregnancy-related stress.
4. Multiple Gestations
Carrying more than one baby (e.g., twins or triplets) increases the risk of preeclampsia. The body’s increased demands and altered placental development contribute to this heightened risk.
5. Obesity
Obesity is a significant risk factor for preeclampsia. Excess body weight can lead to increased blood pressure and insulin resistance, both of which are associated with a higher likelihood of developing preeclampsia.
6. Chronic Hypertension
Women with pre-existing high blood pressure are at a greater risk of developing preeclampsia. Chronic hypertension can exacerbate the blood pressure problems associated with preeclampsia.
7. Diabetes
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia. Diabetes can affect blood vessel function and increase the likelihood of high blood pressure during pregnancy.
8. Kidney Disease
Pre-existing kidney conditions can elevate the risk of preeclampsia. The kidneys play a crucial role in managing blood pressure and fluid balance, and any pre-existing conditions can compromise their function.
9. Autoimmune Disorders
Certain autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can increase the risk of developing preeclampsia. These conditions can affect the body’s immune response and vascular health.
10. Family History
A family history of preeclampsia can indicate a genetic predisposition to the condition. Women with a family history are at an increased risk compared to those without such a history.
11. Poor Nutrition
Inadequate nutrition, particularly a lack of essential vitamins and minerals such as calcium and magnesium, can contribute to the development of preeclampsia. Proper prenatal care and nutrition are crucial for minimizing risk.
12. Infections
Certain infections during pregnancy, such as urinary tract infections, can be associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia. Infections can exacerbate the inflammatory processes involved in preeclampsia.
13. High Stress Levels
Chronic stress and poor mental health can impact overall well-being and contribute to conditions like preeclampsia. Managing stress through healthy lifestyle choices and support systems is important.
Monitoring and Prevention Strategies
Early monitoring and preventive measures can help manage the risk factors associated with preeclampsia:
- Regular Prenatal Visits: Frequent check-ups with a healthcare provider can help monitor blood pressure and other indicators of preeclampsia.
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing weight can reduce the risk.
- Medication: In some cases, medications such as aspirin may be recommended to lower the risk of preeclampsia, especially for women with a high risk.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and counseling can help manage stress and support overall health.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding the symptoms and risk factors of preeclampsia can help in early detection and timely intervention.
Conclusion
Preeclampsia is a complex condition with multiple risk factors. By recognizing these factors and taking proactive steps, expectant mothers can work with their healthcare providers to manage their risk and promote a healthier pregnancy.
Regular prenatal care, lifestyle modifications, and stress management are key to minimizing the impact of preeclampsia and ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
FAQs
1. What are the early signs of preeclampsia?
Early signs of preeclampsia include high blood pressure, proteinuria, swelling of the hands and feet, sudden weight gain, and severe headaches. It’s important to report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
2. Can preeclampsia be prevented?
While not all cases of preeclampsia can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, attending regular prenatal visits, and following your healthcare provider’s recommendations can help reduce the risk.
3. How is preeclampsia diagnosed?
Preeclampsia is diagnosed through routine prenatal screenings that monitor blood pressure and urine protein levels. If preeclampsia is suspected, additional tests may be conducted to assess kidney function and other health indicators.
4. What are the treatment options for preeclampsia?
Treatment options for preeclampsia depend on the severity of the condition. They may include medications to manage blood pressure, bed rest, and in severe cases, early delivery of the baby to protect both the mother and child.
5. Can preeclampsia affect future pregnancies?
Having preeclampsia in one pregnancy can increase the risk of developing it in future pregnancies. However, many women go on to have healthy pregnancies by managing risk factors and following their healthcare provider’s advice.
References:
Health
Top 5 Immunity-Boosting Fruits to Include in Your Diet
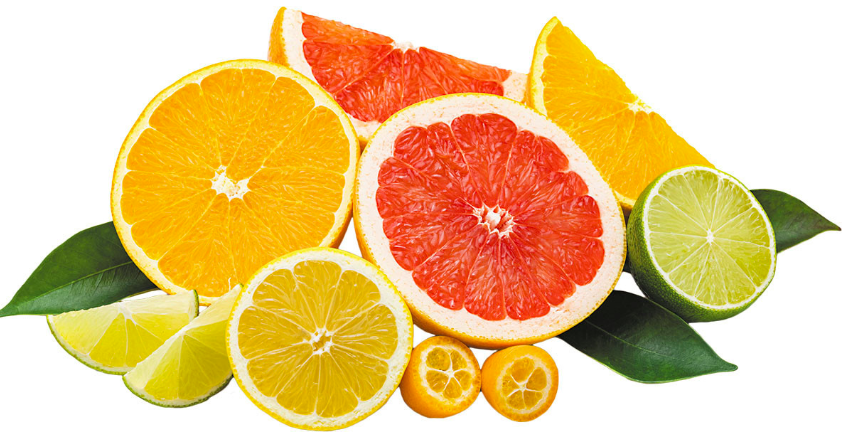

Top 5 Immunity-Boosting Fruits to Include in Your Diet
In our quest for better health, the immune system often takes center stage. One of the simplest and most effective ways to support this vital system is through a nutritious diet.
Fruits, rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, can play a significant role in strengthening your immune system.
In this article, we’ll explore the best fruits for boosting immunity, backed by scientific research, and provide practical tips for incorporating them into your daily routine.
Why Immune Health Matters
The immune system is our body’s defense mechanism against harmful pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and toxins.
A robust immune system can help fend off illnesses and infections, and a balanced diet is crucial for maintaining its optimal function.
Fruits, in particular, offer a wealth of nutrients that can enhance immune response, improve overall health, and even prevent chronic diseases.
1. Citrus Fruits: Vitamin C Powerhouses
Oranges
Oranges are synonymous with vitamin C, a crucial nutrient for immune health. Vitamin C supports the production and function of white blood cells, which are essential for fighting infections.
Just one medium-sized orange provides about 70 mg of vitamin C, meeting the daily recommended intake for most adults.
Grapefruits
Grapefruits, another excellent source of vitamin C, also contain antioxidants like lycopene, which have been linked to reduced inflammation and improved immune function.
Enjoying half a grapefruit a day can contribute significantly to your vitamin C needs.
Lemons
Lemons are versatile fruits that not only boost your vitamin C intake but also support detoxification.
Adding lemon juice to water or dishes can enhance your immune system while providing a refreshing flavor.
2. Berries: Antioxidant-Rich Superfoods
Blueberries
Blueberries are packed with antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
These antioxidants can enhance immune function and protect against chronic diseases. A cup of fresh blueberries is a delicious way to boost your immunity.
Strawberries
Strawberries are another berry with a high vitamin C content, along with various antioxidants that contribute to overall health.
A handful of strawberries can provide a significant portion of your daily vitamin C requirement.
Raspberries
Raspberries are rich in vitamins C and E, as well as fiber and antioxidants.
These nutrients work together to support immune health and maintain digestive well-being.
Incorporate raspberries into smoothies or salads for a tasty immune boost.
4. Papaya
Papaya is an excellent source of vitamin C, vitamin A, and digestive enzymes such as papain. These nutrients contribute to a stronger immune system by supporting cellular repair and reducing inflammation.
5. Pomegranate
Pomegranates are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, which help combat oxidative stress and boost immune function. The anti-inflammatory properties of pomegranates also support overall health and wellness.
Incorporating these fruits into your daily diet can provide essential nutrients that support immune health and help protect your body against illnesses.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How does vitamin C boost the immune system?
Vitamin C enhances the production of white blood cells, which are crucial for combating infections and illnesses. It also acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals.
2. Can berries help reduce inflammation?
Yes, berries are rich in antioxidants and vitamins that help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can support overall immune function.
3. What are the benefits of kiwi for immune health?
Kiwi provide a high amount of vitamin C, which supports the immune system by increasing white blood cell production. It also contains vitamin K and folate, which are essential for maintaining overall health.
4. How does papaya contribute to immune health?
Papaya is high in vitamin C and vitamin A, which help strengthen the immune system. Additionally, the enzyme papain in papaya aids in digestion and reduces inflammation.
5. What makes pomegranates beneficial for immunity?
Pomegranates are rich in antioxidants and vitamin C, which help fight oxidative stress and inflammation, thereby supporting the immune system and overall health.
References:
Healthline – Best Fruits for Boosting Immunity
Health
Effective Medications to Lower Cholesterol: A Comprehensive Guide
Effective Medications to Lower Cholesterol: A Comprehensive Guide
High cholesterol is a common health issue that can significantly increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health conditions. Fortunately, various medications are available to help manage and lower cholesterol levels.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most effective medications for lowering cholesterol, their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and other crucial information to help you make informed decisions about your health.
Understanding Cholesterol and Its Impact on Health
Cholesterol is a fatty substance found in your blood. Your body needs cholesterol to build healthy cells, but having high levels of cholesterol can increase your risk of heart disease.
Cholesterol travels through your bloodstream in two main types of lipoproteins:
low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
- LDL Cholesterol: Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, LDL can build up in the walls of your arteries, leading to atherosclerosis, which can restrict blood flow and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- HDL Cholesterol: Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove LDL cholesterol from your arteries, reducing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
Why Medication May Be Necessary
Even with a healthy diet and regular exercise, some individuals may still struggle to manage their cholesterol levels.
This is where cholesterol-lowering medications come into play. These medications work in various ways to help lower LDL cholesterol and, in some cases, raise HDL cholesterol.
Types of Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
1. Statins
Statins are the most commonly prescribed medications for lowering LDL cholesterol.
They work by blocking a substance your body needs to make cholesterol, thus reducing the amount of LDL cholesterol in your bloodstream.
- Examples: Atorvastatin (Lipitor), Simvastatin (Zocor), Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- Mechanism of Action: Statins inhibit the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is involved in cholesterol production in the liver.
- Common Side Effects: Muscle pain, digestive problems, increased liver enzymes
- Benefits: Statins are highly effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels and have been shown to lower the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Bile Acid Sequestrants
Bile acid sequestrants work by binding to bile acids in the intestine, preventing them from being reabsorbed. This process forces the liver to use cholesterol to produce more bile acids, thus lowering LDL cholesterol levels.
- Examples: Cholestyramine (Prevalite), Colestipol (Colestid), Colesevelam (Welchol)
- Mechanism of Action: These drugs bind bile acids in the intestines, reducing cholesterol absorption.
- Common Side Effects: Constipation, bloating, nausea
- Benefits: Effective at lowering LDL cholesterol and can be used in conjunction with statins for enhanced results.
3. Niacin
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3) helps lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL cholesterol levels.
It works by decreasing the liver’s production of LDL cholesterol and increasing HDL cholesterol.
- Examples: Niacor, Niaspan
- Mechanism of Action: Niacin reduces the production of LDL cholesterol and increases HDL cholesterol.
- Common Side Effects: Flushing, itching, liver damage (with high doses)
- Benefits: Effective in raising HDL cholesterol and lowering LDL cholesterol.
4. Fibric Acids
Fabric acids, or fibrates, are primarily used to lower triglyceride levels and can also help increase HDL cholesterol levels.
They work by activating a protein that helps break down triglycerides in the blood.
- Examples: Fenofibrate (Tricor), Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
- Mechanism of Action: They activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which help in the breakdown of triglycerides.
- Common Side Effects: Muscle pain, liver abnormalities, gastrointestinal issues
- Benefits: Particularly useful for individuals with high triglyceride levels.
5. PCSK9 Inhibitors
PCSK9 inhibitors are a newer class of cholesterol-lowering medications that help the liver remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream more effectively.
- Examples: Alirocumab (Praluent), Evolocumab (Repatha)
- Mechanism of Action: These drugs inhibit the PCSK9 protein, which normally reduces the liver’s ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the blood.
- Common Side Effects: Injection site reactions, flu-like symptoms
- Benefits: Very effective at lowering LDL cholesterol, especially in individuals who cannot tolerate statins.
6. Cholesterol Absorption Inhibitors
Cholesterol absorption inhibitors work by blocking the absorption of cholesterol from the diet, which reduces the amount of cholesterol that enters your bloodstream.
- Examples: Ezetimibe (Zetia)
- Mechanism of Action: They inhibit the absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine.
- Common Side Effects: Diarrhea, stomach pain, muscle pain
- Benefits: Can be used alone or in combination with statins to lower LDL cholesterol.
Choosing the Right Medication
The choice of medication depends on various factors, including your overall health, the specific cholesterol issue you have, and how well you tolerate certain medications.
Your healthcare provider will help you determine the most appropriate medication based on your individual needs and medical history.
Lifestyle Modifications to Complement Medication
While medications are effective in managing cholesterol levels, they work best when combined with lifestyle changes.
Consider incorporating the following into your routine:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while avoiding saturated fats and trans fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to help control cholesterol levels.
- Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake can negatively impact cholesterol levels.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is crucial to monitor your cholesterol levels and assess the effectiveness of your medication. Your doctor may adjust your treatment plan based on your progress and any side effects you experience.
Final Thoughts
Managing cholesterol is a critical aspect of maintaining cardiovascular health.
With a variety of effective medications available, it’s possible to lower LDL cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease and other complications.
However, medication alone is not a cure-all; combining it with lifestyle changes is essential for optimal results.
Always consult your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans tailored to your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the primary goal of cholesterol-lowering medications?
Cholesterol-lowering medications primarily aim to reduce LDL cholesterol levels in the blood, thereby decreasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes.
2. Are there any natural alternatives to cholesterol-lowering medications?
Yes, some natural alternatives include dietary changes (e.g., increased intake of soluble fiber and omega-3 fatty acids), regular exercise, and weight management. However, these should be used in conjunction with, not as a replacement for, prescribed medications.
3. How long does it take for cholesterol-lowering medications to show results?
The effects of cholesterol-lowering medications can usually be observed within a few weeks, but it may take several months to see significant changes in cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular risk.
4. Can cholesterol-lowering medications cause side effects?
Yes, some common side effects include muscle pain, digestive issues, and liver enzyme changes. It’s important to report any side effects to your healthcare provider for proper management.
5. Can I stop taking my cholesterol medication if my levels improve?
It’s important to consult your healthcare provider before making any changes to your medication regimen. Discontinuing medication without medical advice can lead to a rebound in cholesterol levels and an increased risk of heart disease.
References
Cholesterol-lowering Medications
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know