Health
Improving kidney health is crucial for maintaining overall wellness.

Last Updated on March 20, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
Improving kidney health is crucial for maintaining overall wellness.
Our kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste and excess fluids from the body, regulating electrolyte balance, and controlling blood pressure. Unfortunately, many people don’t pay much attention to their kidney health until they develop a problem.
However, by taking proactive steps to protect and improve kidney function, you can reduce your risk of serious kidney disease and enjoy better overall health.
The kidneys are a vital organ in the human body that are responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the body, regulating electrolyte balance, and controlling blood pressure.
These functions are essential for overall health, but many people don’t pay much attention to their kidney health until a problem arises. In this article, we will discuss various ways to improve kidney health and reduce the risk of serious kidney disease.
Maintain a Healthy Weight Obesity is a major risk factor for kidney disease.
Excess body fat puts extra strain on the kidneys and can lead to high blood pressure and diabetes, both of which are major risk factors for kidney disease. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help protect your kidneys and improve overall health.
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health and can help reduce the risk of developing kidney disease. Obesity, defined as having a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, is a major risk factor for kidney disease.
It is estimated that up to 50% of people with chronic kidney disease have obesity. Excess weight puts added stress on the kidneys and can lead to high blood pressure, diabetes, and other conditions that can damage the kidneys over time.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a combination of regular physical activity and a balanced diet can help lower the risk of developing kidney disease and other obesity-related health problems.
How much weight should I aim to lose?
The goal is to reach and maintain a healthy weight. This can vary depending on your height and body composition. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine a healthy weight range for you.
The amount of weight that you should aim to lose depends on your current weight, body composition, and overall health.
It’s generally recommended that people try to lose weight gradually, at a rate of 1-2 pounds per week. This can be achieved through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and lifestyle changes.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or registered dietitian, to determine a safe and appropriate goal for you. They will be able to assess your current health status and help you set realistic and achievable weight loss goals that are tailored to your individual needs.
It’s also important to consider that weight loss is not just about the number on the scale, but also about improving overall health and body composition. In some cases, people may focus on losing body fat and gaining muscle mass, rather than solely aiming to lose weight.
This can lead to improved health markers and a better overall appearance. A body mass index (BMI) of 18.5-24.9 is considered healthy, while a BMI of 25-29.9 is considered overweight and a BMI of 30 or higher is considered obese.
However, it’s important to note that BMI is not always an accurate indicator of health, as it doesn’t take into an account muscle mass or other factors.
In summary, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine a safe and appropriate weight loss goal for you, and to focus on overall health and body composition rather than just the number on the scale.
It’s also important to remember that weight loss is a gradual process and it’s important to be patient and consistent with your efforts.
A: Eating a balanced diet that is low in fat, salt, and sugar and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is the best way to maintain a healthy weight and protect your kidneys. Avoiding processed foods and sugary drinks can also be beneficial. Control Blood Pressure High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a major risk factor for kidney disease.
It puts extra strain on the kidneys and can damage the blood vessels that supply them with blood. By controlling your blood pressure, you can help protect your kidneys and improve overall health. A diet that is healthy for maintaining a healthy weight and protecting your kidneys is one that is balanced, nutrient-dense, and low in processed foods and added sugars. Some specific recommendations include:
- Eating a variety of fruits and vegetables: These foods are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that are important for overall health. They are also low in calories and high in fiber, which can help with weight management.
- Choosing lean protein sources: Good options include fish, skinless poultry, lean cuts of meat, and plant-based protein sources such as beans, lentils, and tofu.
- Limiting processed foods and added sugars: These foods are often high in calories and low in nutrients. They can also contribute to weight gain and increase the risk of chronic diseases.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking enough water is important for kidney health and can also help with weight management.
- Monitoring your portion sizes: Eating smaller portions can help prevent overeating and weight gain.
- Limiting sodium intake: High sodium intake can increase blood pressure and put stress on the kidneys.
- It is suggested to limit sodium intake to less than 2,300 mg per day (1500mg if you have hypertension, diabetes, or chronic kidney disease)
- Following a Mediterranean diet: This diet emphasizes whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, and includes moderate amounts of fish, poultry, and olive oil.
- This diet is not only helpful for weight management but also has been shown to have a protective effect on kidney health.
It is important to note that if you have kidney disease, you should talk to a kidney specialist or a registered dietitian for a personalized diet plan, as you may have specific nutrient needs. In summary, a diet that emphasizes nutrient-dense foods, limits processed foods and added sugars, and is balanced is best for maintaining a healthy weight and protecting your kidneys. It’s also important to stay hydrated and monitor portion sizes and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
How can I control my blood pressure?
A: Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise can help control blood pressure. In some cases, medication may also be necessary. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best plan for controlling your blood pressure.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a common condition that can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke. There are several ways to control your blood pressure and reduce the risk of these health problems. Some of the most effective methods include:
- Lifestyle changes: Making changes to your diet, exercise routine, and overall lifestyle can have a significant impact on your blood pressure.
- Eating a diet that is low in salt and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, getting regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and limiting alcohol consumption can all help lower blood pressure.
- Medications: If lifestyle changes alone aren’t enough to control blood pressure, your healthcare provider may recommend taking medication to help lower it.
- There are several types of medications that can be used to treat hypertension, including diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and beta blockers.
- Monitoring blood pressure regularly: It’s important to monitor your blood pressure regularly, especially if you have been diagnosed with hypertension or have risk factors for the condition.
- Your healthcare provider can help you determine how often you should check your blood pressure and what your target range should be.
- Stress management: High-stress levels can lead to increased blood pressure.
- Techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, and regular exercise can help reduce stress and regulate blood pressure.
- Quit smoking: Nicotine in cigarettes can cause blood vessels to narrow and make blood pressure rise.
In summary, controlling blood pressure requires a combination of lifestyle changes, such as healthy eating, regular physical activity, and stress management, as well as medications if necessary. It’s also important to monitor your blood pressure regularly and consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
What is considered healthy blood pressure?
A: A healthy blood pressure is considered to be less than 120/80 mmHg. If your blood pressure is higher than this, it is important to take steps to control it. Subheading 3: Manage Chronic Conditions Chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease are major risk factors for kidney disease. By managing these conditions, you can help protect your kidneys and improve overall health.
Healthy blood pressure is considered to be a systolic pressure (the top number) of less than 120 mmHg and a diastolic pressure (the bottom number) of less than 80 mmHg. Blood pressure measurements are often given as two numbers, such as 120/80 mmHg. The first number (120 in this case) is the systolic pressure, which measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats.
The second number (80 in this case) is diastolic pressure, which measures the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats. High blood pressure is considered to be a systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher or a diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher.
Normal blood pressure is generally considered to be below 120/80 mmHg, and hypertension (high blood pressure) is defined as a systolic pressure of 140 mmHg or higher, or a diastolic pressure of 90 mmHg or higher. However, it’s worth noting that different organizations and experts may have slightly different definitions of what constitutes healthy blood pressure.
Additionally, it is important to consider that ideal blood pressure varies by age, sex, and other health conditions. People who are older or have a history of hypertension may be considered to have normal blood pressure at higher levels than younger adults or people without hypertension.
Blood pressure can also change throughout the day and may be affected by factors such as stress, caffeine, and physical activity. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine what is considered healthy blood pressure for you.
How can I manage my chronic condition?
A: Managing a chronic condition involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular medical check-ups. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and getting regular exercise can help manage chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop a plan for managing your condition. Managing a chronic condition can be challenging, but there are several steps you can take to help manage
your condition and improve your quality of life:
- Work with your healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs. This may include medications, therapy, lifestyle changes, or a combination of these.
- Stay on top of your medications and follow your treatment plan as directed. This can help you manage symptoms and prevent complications.
- Monitor your symptoms and keep track of any changes. This can help you identify triggers and make adjustments to your treatment plan as needed.
- Take care of yourself physically and emotionally. This may include getting regular exercise, eating a healthy diet, getting enough sleep, and managing stress.
- Build a support network of friends, family, and healthcare providers who can provide you with emotional support and help you navigate the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
- Keep all your appointments and communicate with your healthcare provider regularly to stay informed about new treatments and research, and to discuss any concerns or problems you may be having.
- Educate yourself about your condition and learn as much as you can about it, so that you can be an active participant in your own healthcare.
- Don’t be afraid to ask for help if you need it, and don’t hesitate to reach out to support groups or other resources that can help you manage your condition.
- Practice good self-management techniques, such as goal setting, problem-solving, and action planning. This will help you to take control of your condition and make positive changes in your life.
- Be flexible and open to change. Managing a chronic condition can be unpredictable, and you may need to adjust your treatment plan or lifestyle as your condition changes.
- Set realistic expectations for yourself and don’t put too much pressure on yourself. Remember to take time for yourself and to celebrate small successes.
- Lastly, keep in mind that you are not alone in managing your chronic condition. There are many resources and support groups available to help you navigate the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
What are some common medications for managing chronic conditions?
A: Common medications for managing chronic conditions include blood pressure drugs, diabetes drugs, and cholesterol-lowering drugs. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the best medication for you. Drink Plenty of Water Drinking enough water is essential for kidney health.
It helps flush out waste and toxins from the body and can help prevent kidney stones. Aim to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day, or more if you are physically active or live in a hot climate. It is also important to limit your intake of sugary drinks and alcohol, as they can dehydrate the body and put extra strain on the kidneys.
Some common medications for managing chronic conditions include:
- Blood pressure medications: ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, diuretics, and calcium channel blockers
- Cholesterol-lowering medications: statins, bile acid sequestrants, niacin, and fibrates
- Diabetes medications: metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors, and insulin
- Anti-inflammatory medications: NSAIDs and corticosteroids
- Medications for heart disease: beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and diuretics
- Medications for asthma and COPD: bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and leukotriene modifiers
- Medications for depression and anxiety: SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and benzodiazepines
- Medications for arthritis: NSAIDs, DMARDs, and biological medications
It is important to note that the medication regimens for chronic conditions are generally tailored to the individual patient and may vary depending on the specific condition, the severity of symptoms, and the patient’s overall health. It is important to talk to your doctor or healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan for you.
How much water should I drink per day?
The general guideline is to aim for 8 glasses of water per day or about 2 liters. However, this can vary depending on your level of physical activity and the climate you live in. If you are physically active or live in a hot climate, you may need to drink more water to stay hydrated.
Are there any foods that can help improve kidney health?
A: Eating a diet that is high in fruits and vegetables can help improve kidney health. Fruits and vegetables are high in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help protect the kidneys.
Berries, grapes, and apples are particularly beneficial for kidney health. Additionally, foods high in potassium such as bananas, sweet potatoes, and avocados can also help.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, improving kidney health is crucial for maintaining overall wellness. By maintaining a healthy weight, controlling blood pressure, managing chronic conditions, drinking plenty of water, and eating a healthy diet, we can reduce the risk of serious kidney disease and enjoy better overall health.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best plan for improving your kidney health. Remember, taking care of your kidneys today can help ensure they’ll be there to take care of you in the future.
Health
7 Fascinating Facts About Magnesium You Probably Didn’t Know

7 Fascinating Facts About Magnesium You Probably Didn’t Know
Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals for our health, yet many people are unaware of its significance.
This vital nutrient plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions, from energy production to maintaining a healthy heart.
In this article, we will delve into seven intriguing facts about magnesium that may surprise you and help you appreciate its importance in your daily life.
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a naturally occurring mineral found in various foods and is vital for human health.
It is the fourth most abundant mineral in the body and is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions.
Magnesium contributes to nerve function, muscle contraction, blood sugar control, and blood pressure regulation.
It can be obtained from various dietary sources, including leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes.
1. Magnesium is Involved in Energy Production
Did you know that magnesium is essential for converting food into energy? This mineral plays a critical role in the activation of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the energy currency of our cells.
Without sufficient magnesium, your body struggles to produce energy effectively, which can lead to feelings of fatigue and weakness.
How Does It Work?
ATP production occurs in the mitochondria, often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell.
Magnesium helps activate enzymes involved in this energy production process, ensuring that your body has enough energy to perform daily activities.
2. A Key Player in Bone Health
Magnesium is vital for maintaining strong and healthy bones. Approximately 60% of the magnesium in your body is stored in your bones.
It contributes to bone density and strength by regulating calcium levels in the body, which is crucial for bone formation.
The Calcium Connection
Calcium is often touted as the primary mineral for bone health, but magnesium plays an equally important role.
An imbalance of these two minerals can lead to bone-related issues such as osteoporosis.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake is essential for maintaining optimal bone health.
3. Supports Heart Health
Magnesium is a crucial mineral for cardiovascular health. It helps maintain normal heart rhythms and can reduce the risk of heart disease.
Adequate magnesium levels are associated with lower blood pressure and reduced risk of heart attacks.
Regulation of Blood Pressure
Magnesium helps relax blood vessels, which can lead to lower blood pressure.
Studies have shown that individuals with higher magnesium intake tend to have better cardiovascular health. Including magnesium-rich foods in your diet can be an effective strategy for supporting heart health.
4. Magnesium and Mental Health
Emerging research suggests a strong link between magnesium levels and mental health.
Magnesium plays a role in regulating neurotransmitters, which are essential for mood stabilization.
Low magnesium levels have been associated with an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
Cognitive Function
Magnesium may also enhance cognitive function. Studies have indicated that adequate magnesium intake can improve memory and learning abilities.
This mineral is essential for brain health, making it vital for overall mental well-being.
5. Magnesium Deficiency is Common
Despite its importance, magnesium deficiency is surprisingly common.
Factors such as poor diet, chronic stress, and certain medical conditions can lead to low magnesium levels.
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include muscle cramps, fatigue, and irritability.
Risk Factors for Deficiency
Certain populations are at a higher risk for magnesium deficiency, including the elderly, those with gastrointestinal diseases, and individuals who consume a diet low in whole foods.
It’s essential to recognize the signs of deficiency and consider increasing your magnesium intake through diet or supplements if necessary.
6. Natural Relaxant
Magnesium is often referred to as a natural relaxant due to its calming effects on the nervous system.
It helps regulate cortisol levels (the stress hormone) and promotes relaxation, making it beneficial for those dealing with anxiety and stress.
Improving Sleep Quality
In addition to its relaxing properties, magnesium can improve sleep quality.
Many people find that magnesium supplements help them fall asleep faster and stay asleep longer, making it a popular choice for those struggling with insomnia.
7. Magnesium in Sports Performance
Athletes and active individuals often benefit from magnesium’s role in muscle function and recovery.
Magnesium helps prevent muscle cramps and can aid in post-exercise recovery by reducing inflammation and promoting relaxation.
Enhancing Athletic Performance
Research has shown that adequate magnesium levels can enhance athletic performance.
It is involved in muscle contraction and relaxation, making it essential for peak performance during exercise.
Conclusion
Magnesium is a powerhouse mineral that plays an essential role in various bodily functions. From supporting energy production to promoting heart health and mental well-being, its importance cannot be overstated.
Ensuring adequate magnesium intake through a balanced diet rich in whole foods can significantly enhance your overall health and quality of life.
If you suspect you may be deficient in magnesium, consider consulting with a healthcare provider to assess your levels and discuss dietary changes or supplements that may be beneficial.
FAQs about Magnesium
1. What are the best dietary sources of magnesium?
The best sources of magnesium include leafy green vegetables (like spinach), nuts (especially almonds and cashews), seeds (such as pumpkin seeds), whole grains (like brown rice and quinoa), and legumes (like beans and lentils).
2. How much magnesium do I need daily?
The recommended daily intake of magnesium varies by age and gender. Generally, adult men should aim for about 400-420 mg per day, while adult women should aim for about 310-320 mg.
3. Can I take magnesium supplements?
Yes, magnesium supplements are available and can be beneficial, especially for individuals who may not get enough from their diet. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement regimen.
4. What are the symptoms of magnesium deficiency?
Symptoms of magnesium deficiency can include muscle cramps, fatigue, weakness, irritability, and irregular heart rhythms. If you experience these symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
5. Is it possible to get too much magnesium?
Yes, while magnesium from food sources is generally safe, excessive supplementation can lead to toxicity, causing symptoms like diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Always consult a healthcare provider before increasing your magnesium intake significantly.
References:
Health
Whooping Cough: Understanding Its Resurgence and Prevention
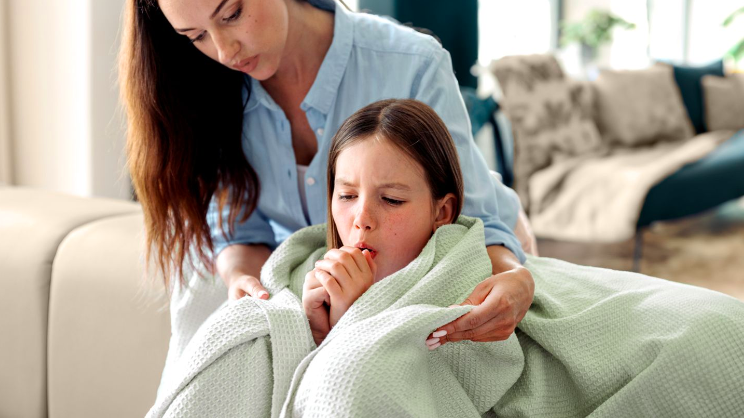

Health
The Power of Beans: Why This Superfood is a Nutritional Treasure
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know






