Healthcare
Treatment Options for Cancer in Older Adults: A Comprehensive Guide
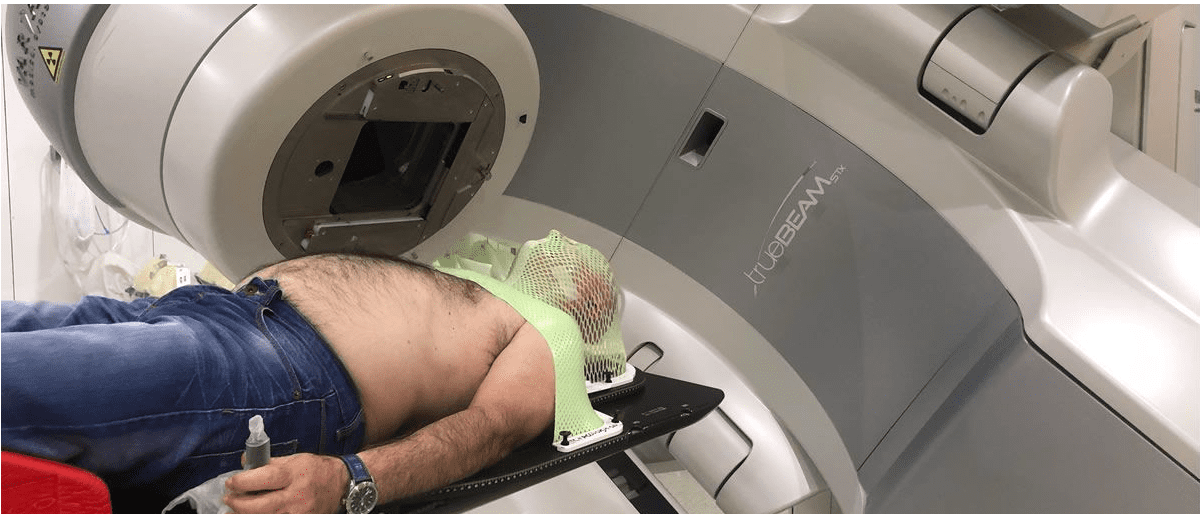
Treatment Options for Cancer in Older Adults
When it comes to cancer treatment, older adults often face unique challenges. Age-related factors such as overall health, existing medical conditions, and the potential impact of treatment on daily life need to be carefully considered.
In this article, we will explore the various treatment options available for cancer in older adults and provide valuable insights to help patients and their loved ones make informed decisions.
1. Surgery
Surgery is a common treatment option for many types of cancer, including those affecting older adults. It involves removing the tumor and surrounding tissues to eliminate cancer cells. Surgeons may also remove nearby lymph nodes to check for the spread of cancer.
The decision to undergo surgery depends on several factors, including the type and stage of cancer, overall health, and the patient’s ability to recover.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation beams to destroy cancer cells. It is often recommended as a primary treatment for localized tumors or as an adjuvant therapy after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells.
Older adults may undergo external beam radiation therapy, where radiation is delivered from outside the body, or brachytherapy, where radioactive sources are placed directly into or near the tumor.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or prevent their growth. It can be administered orally, through injections, or intravenously.
While chemotherapy is known for its side effects, advances in medical science have led to the development of targeted therapies that specifically attack cancer cells, minimizing the impact on healthy cells.
The choice of chemotherapy drugs and dosage may vary depending on the type of cancer and the patient’s overall health.
4. Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a revolutionary treatment approach that harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It works by stimulating the immune system or by introducing substances that enhance its natural ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
Immunotherapy has shown promising results in treating various types of cancer, including those affecting older adults. However, not all patients may be eligible for this type of treatment, and it is essential to consult with an oncologist to determine its suitability.
5. Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a precision medicine approach that specifically targets the genetic mutations or proteins present in cancer cells. By focusing on these specific targets, targeted therapy drugs can disrupt the growth and spread of cancer cells while minimizing damage to healthy cells.
This treatment option has shown considerable success in treating certain types of cancer, such as breast, lung, and colorectal cancer.
6. Palliative Care
Palliative care aims to improve the quality of life for patients with advanced or terminal cancer. It focuses on managing symptoms, providing pain relief, and addressing emotional and psychological needs.
Palliative care can be provided alongside curative treatments or as the primary approach for patients who may not be eligible for aggressive therapies. It is an essential component of comprehensive cancer care for older adults.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can older adults undergo surgery for cancer treatment?
Yes, surgery is a viable treatment option for many older adults with cancer. The decision depends on various factors, including overall health and the type and stage of cancer.
2. Are there any alternative treatments for cancer in older adults?
While alternative treatments may complement conventional cancer treatments, it is important to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure their safety and efficacy.
3. Do older adults experience more side effects from cancer treatment?
Older adults may be more susceptible to certain side effects due to age-related changes in the body. However, advancements in treatment options have minimized the impact on healthy cells.
4. How can palliative care benefit older adults with cancer?
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with advanced or terminal cancer. It provides symptom management, pain relief, and emotional support.
5. Can older adults undergo immunotherapy?
Immunotherapy may be a suitable treatment option for some older adults with cancer. However, eligibility depends on various factors, including overall health and the specific type of cancer.
6. What are the risks associated with radiation therapy?
Radiation therapy carries certain risks, including temporary skin changes, fatigue, and potential long-term effects. However, healthcare professionals carefully consider these risks before recommending treatment.
7. How can I support an older adult undergoing cancer treatment?
Offering emotional support, assisting with daily tasks, and accompanying them to medical appointments can make a significant difference in an older adult’s cancer treatment journey.
Remember, every individual’s cancer treatment journey is unique, and it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance.
Conclusion
When it comes to cancer treatment in older adults, there is no one-size-fits-all approach. Each patient’s situation is unique, and treatment decisions should be based on a thorough assessment of their overall health, cancer type, and individual preferences.
Older adults and their loved ones must work closely with a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including oncologists, surgeons, and supportive care specialists, to determine the most suitable treatment options.

Healthcare
The Importance of Health Care Associated Infections: Impact on Patients and Healthcare Systems

The Importance of Health Care Associated Infections
Health care associated infections (HCAIs) are a significant concern in the medical field. These infections occur when patients acquire infections while receiving medical treatment or care. HCAIs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or other pathogens, and they can lead to severe complications and even death if not properly managed. In this article, we will explore the impact of HCAIs on patients and healthcare systems, as well as the measures that can be taken to prevent and control these infections.
The Impact of HCAIs on Patients
HCAIs pose a serious threat to patients’ health and well-being. When patients acquire infections during their hospital stay or medical procedures, it can significantly prolong their recovery time and increase their risk of complications. These infections can also lead to increased healthcare costs, as patients may require additional treatments and interventions to manage the infection.
Furthermore, HCAIs can have a detrimental effect on patients’ quality of life. Patients who acquire infections may experience pain, discomfort, and emotional distress. They may also face challenges in returning to their normal daily activities and may require extended periods of rehabilitation and support.
The Impact of HCAIs on Healthcare Systems
In addition to the impact on patients, HCAIs also place a considerable burden on healthcare systems. These infections can lead to increased hospital stays, which can result in overcrowding and limited resources. The treatment of HCAIs requires additional healthcare personnel, equipment, and supplies, further straining healthcare facilities.
Moreover, HCAIs can contribute to the development of antimicrobial resistance. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics in the treatment of these infections can lead to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, making it more challenging to effectively treat infections in the future. This poses a significant public health concern and highlights the importance of implementing effective infection prevention and control measures.
Prevention and Control of HCAIs
Preventing and controlling HCAIs requires a comprehensive approach that involves healthcare professionals, patients, and the healthcare system as a whole. Here are some key strategies that can be implemented to reduce the risk of HCAIs:
1. Hand Hygiene
Proper hand hygiene is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of infections. Healthcare workers should wash their hands thoroughly with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand sanitizers before and after patient contact. Patients and visitors should also practice good hand hygiene to minimize the risk of transmission.
2. Infection Control Practices
Healthcare facilities should implement strict infection control practices, including the appropriate use of personal protective equipment (PPE), proper cleaning and disinfection of patient care areas, and adherence to standard precautions. These measures help prevent the transmission of pathogens and reduce the risk of HCAIs.
3. Antimicrobial Stewardship
Antimicrobial stewardship programs aim to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics to prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance. Healthcare professionals should prescribe antibiotics judiciously, considering the type of infection, the causative organism, and the patient’s individual circumstances. This helps prevent the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria and preserves the effectiveness of antibiotics.
4. Patient Education
Educating patients about HCAIs and the importance of infection prevention can empower them to take an active role in their own healthcare. Patients should be informed about hand hygiene, proper wound care, and the signs and symptoms of infection. By actively participating in their care, patients can help reduce the risk of HCAIs.
Conclusion
Health care associated infections are a significant concern that affects both patients and healthcare systems. The prevention and control of HCAIs require a collaborative effort from healthcare professionals, patients, and the healthcare system as a whole. By implementing effective infection prevention and control measures, such as hand hygiene, infection control practices, antimicrobial stewardship, and patient education, the risk of HCAIs can be minimized. It is crucial for healthcare facilities to prioritize the safety and well-being of patients by actively addressing the prevention and control of HCAIs.
Healthcare
Options for Obtaining Health Insurance Without a Job
The Importance of Health Insurance
Health insurance is an essential aspect of our lives, providing financial protection and access to quality healthcare services. Whether you are employed or currently without a job, having health insurance coverage is crucial for safeguarding your well-being and ensuring that you can receive the necessary medical care when needed.
Options for Obtaining Health Insurance Without a Job
While many individuals rely on employer-sponsored health insurance, there are alternative options available for those who are currently unemployed. It is important to explore these avenues to ensure that you have adequate coverage during this transitional period.
1. Medicaid
Medicaid is a government-funded program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility requirements vary by state, but generally, if your income falls below a certain threshold, you may qualify for Medicaid coverage. It is important to research and understand the specific guidelines in your state to determine if you are eligible for this program.
2. Affordable Care Act (ACA) Marketplace
The Affordable Care Act, also known as Obamacare, established a marketplace where individuals can purchase health insurance plans. These plans are designed to be affordable and offer comprehensive coverage. Depending on your income level, you may also be eligible for subsidies that can help reduce the cost of your monthly premiums.
3. COBRA Coverage
If you recently lost your job and had health insurance through your employer, you may be eligible for COBRA coverage. COBRA allows you to continue the same health insurance plan you had while employed, but you will be responsible for paying the full premium,
including the portion that was previously covered by your employer. While COBRA can be more expensive than other options, it provides continuity of coverage and allows you to maintain the same network of healthcare providers.
4. Spouse or Parent’s Health Insurance
If you are married or under the age of 26, you may be eligible to be covered under your spouse or parent’s health insurance plan. This can be a cost-effective option, especially if your spouse or parent has access to employer-sponsored coverage. However, it is important to carefully review the terms and conditions of the plan to ensure that it meets your healthcare needs.
5. Short-Term Health Insurance
Short-term health insurance plans are designed to provide temporary coverage during periods of transition, such as unemployment. These plans typically offer limited benefits and are not as comprehensive as traditional health insurance plans. However, they can provide some level of protection and peace of mind until you secure a more permanent solution
on.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can I apply for Medicaid if I am unemployed?
Yes, Medicaid is designed to provide health insurance coverage to low-income individuals and families, including those who are unemployed. Eligibility requirements vary by state, so it is important to research the guidelines in your specific state.
2. How can I determine if I qualify for subsidies through the ACA Marketplace?
The ACA Marketplace offers subsidies to individuals and families with income levels that fall within a certain range. You can use the online marketplace or consult with a healthcare navigator to determine if you qualify for subsidies based on your income.
3. What happens if I don’t have health insurance?
Without health insurance, you may be responsible for paying the full cost of medical services out of pocket. This can be financially burdensome and may limit your access to necessary healthcare. Additionally, without insurance, you may face penalties when filing your taxes, as the Affordable Care Act requires individuals to have health insurance or pay a fee.
4. Can I enroll in COBRA coverage if I quit my job?
If you voluntarily quit your job, you may still be eligible for COBRA coverage. However, it is important to note that you will be responsible for paying the full premium, including the portion that was previously covered by your employer.
5. Are short-term health insurance plans a good option?
Short-term health insurance plans can provide temporary coverage during periods of transition, such as unemployment. However, they typically offer limited benefits and are not as comprehensive as traditional health insurance plans. It is important to carefully evaluate the terms and conditions of the plan to determine if it meets your healthcare needs.
6. Can I be covered under my spouse or parent’s health insurance plan?
If you are married or under the age of 26, you may be eligible to be covered under your spouse or parent’s health insurance plan. This can be a cost-effective option, especially if your spouse or parent has access to employer-sponsored coverage. Review the terms and conditions of the plan to ensure it meets your healthcare needs.
7. How can I find more information about health insurance options?
For more information about health insurance options, you can visit the official websites of Medicaid, the ACA Marketplace, or consult with a licensed insurance agent. They can provide personalized guidance based on your specific situation and help you navigate the enrollment process.
Conclusion
While being without a job can be a challenging time, it is essential to prioritize your health and well-being. Exploring options for obtaining health insurance coverage, such as Medicaid, the ACA Marketplace, COBRA, spouse or parent’s insurance, or short-term plans, can help ensure that you have access to the medical care you need. Remember to carefully evaluate each option based on your circumstances and healthcare needs to make an informed decision.
Healthcare
The Importance of Health Insurance in Nigeria

The Importance of Health Insurance in Nigeria
Health insurance is a crucial aspect of financial planning and overall well-being. In Nigeria, having the right health insurance coverage is essential to ensure access to quality healthcare services and protect against unexpected medical expenses.
In this article, we will explore the different types of health insurance available in Nigeria and help you determine the best coverage for your needs.
Understanding the Nigerian Healthcare System
The Nigerian healthcare system consists of both public and private healthcare providers. While the public healthcare system is intended to provide affordable healthcare services to the general population, it often falls short in terms of quality and accessibility. Private healthcare facilities, on the other hand, offer higher quality services but at a higher cost.
Given the limitations of the public healthcare system, having health insurance becomes even more important. Health insurance provides financial protection and allows individuals to access private healthcare facilities without incurring significant out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of Health Insurance in Nigeria
There are several types of health insurance options available in Nigeria.
These include:
- Individual Health Insurance: This type of insurance covers an individual and their immediate family members. It provides coverage for medical expenses, hospitalization, and sometimes preventive care.
- Family Health Insurance: Family health insurance covers the entire family under a single policy. It offers similar coverage as individual health insurance but extends to all family members.
- Group Health Insurance: Group health insurance is typically offered by employers to their employees. It provides coverage for all employees and their dependents, offering a cost-effective solution for healthcare coverage.
- Government Health Insurance: The Nigerian government has implemented various health insurance schemes to provide affordable healthcare to its citizens. These include the National Health Insurance Scheme (NHIS) and the State Health Insurance Scheme (SHIS).
Choosing the Right Health Insurance
When selecting a health insurance plan, there are several factors to consider:
- Coverage: Assess the coverage provided by each plan, including hospitalization, medication, consultations, and specialized treatments.
- Network of Providers: Check if the insurance plan has a wide network of healthcare providers, ensuring you have access to quality healthcare facilities and specialists.
- Cost: Compare the premiums, deductibles, and co-payment requirements of different plans to find one that fits your budget.
- Additional Benefits: Some health insurance plans offer additional benefits such as maternity coverage, dental care, and wellness programs. Consider these extras when making your decision.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is health insurance mandatory in Nigeria?
No, health insurance is not mandatory in Nigeria. However, having health insurance is highly recommended to protect yourself and your family from unexpected medical expenses.
2. Can I use my health insurance anywhere in Nigeria?
Most health insurance plans have a network of healthcare providers where you can receive cashless treatment. It’s important to check the network of providers before choosing a plan to ensure you have access to quality healthcare facilities.
3. How do I file a claim with my health insurance provider?
To file a claim, you will need to submit the necessary documents, such as medical bills and receipts, to your health insurance provider. They will guide you through the process and reimburse you for the covered expenses.
4. Can I add my parents to my health insurance plan?
Yes, depending on the insurance provider, you may be able to add your parents as dependents to your health insurance plan. However, this may come with additional costs.
5. What happens if I don’t have health insurance?
If you don’t have health insurance, you will be responsible for paying for your medical expenses out of pocket. This can be financially burdensome, especially in the case of major illnesses or emergencies.
6. Can I switch health insurance plans?
Yes, you can switch health insurance plans. However, it’s important to carefully review the terms and conditions of the new plan and ensure it meets your healthcare needs.
7. How often should I review my health insurance coverage?
It is recommended to review your health insurance coverage annually or whenever there are significant changes in your healthcare needs or family structure. This will ensure you have the most suitable coverage for your current situation.
Conclusion
Health insurance is a vital component of financial planning and healthcare access in Nigeria. It provides individuals and families with the necessary financial protection and peace of mind when it comes to medical expenses. By understanding the different types of health insurance available and considering factors such as coverage, network of providers, and cost, you can make an informed decision and select the best health insurance plan for your needs.
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health3 months ago
Health3 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know