Health
Why Do People Get Sick? Unraveling the Mystery and Protecting Heart Health

Last Updated on May 18, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
Why Do People Get Sick? Unraveling the Mystery and Protecting Heart Health
The human body is a complex and remarkable system, but it is not invincible. Throughout our lives, we encounter various illnesses and diseases that can impact our overall well-being.
Understanding why people get sick is crucial for taking proactive steps to maintain good health and protect vital organs like the heart.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the underlying causes of sickness, explore the intricate workings of the human body, and highlight essential strategies to safeguard heart health.
So, let’s embark on this journey of unraveling the mystery behind illness and discovering ways to nurture a healthy heart.
The Basics of Human Health
Before we dive into the reasons behind sickness, let’s establish a foundation of understanding about human health. Our bodies consist of numerous interconnected systems, each playing a vital role in maintaining overall well-being.
These systems include the cardiovascular system, respiratory system, immune system, and more. Achieving optimal health requires a delicate balance among these systems, as well as external factors like diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices.
Common Causes of Illness
Despite the remarkable resilience of the human body, certain factors can disrupt its equilibrium, leading to illness. Let’s explore some of the most prevalent causes of sickness:
Infectious Agents: A Constant Battle
Infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites pose a constant threat to our well-being. These microscopic invaders can enter our bodies through various means, including direct contact, airborne transmission, contaminated food or water, and insect bites. Once inside, they can multiply and interfere with normal bodily functions, causing a wide range of illnesses.
Lifestyle Factors and Chronic Diseases
While infectious agents are often immediate triggers of illness, lifestyle factors play a significant role in the development of chronic diseases.
Poor dietary choices, sedentary habits, tobacco use, excessive alcohol consumption, and chronic stress can all contribute to conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, obesity, and certain types of cancer. These lifestyle-related illnesses require long-term management and can significantly impact heart health.
Genetic Predisposition and Inherited Disorders
In some cases, people are more susceptible to certain illnesses due to genetic predisposition. Inherited disorders can affect various bodily systems, including the cardiovascular system, leading to conditions such as congenital heart defects or genetic heart diseases.
Understanding one’s genetic background can help identify potential risks and enable proactive measures to mitigate their impact.
The Intricate Connection: Heart Health and Overall Well-being
Now, let’s shift our focus to the heart, a vital organ responsible for pumping oxygenated blood throughout the body. The health of our heart is intricately connected to our overall well-being. When the heart is compromised, it can have far-reaching effects on our health. Conversely, adopting heart-healthy habits can contribute to improved overall wellness. Here are some crucial aspects to consider:
Diet and Heart Health
A well-balanced diet plays a pivotal role in maintaining heart health. Consuming nutrient-rich foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage cholesterol levels, regulate blood pressure, and reduce the risk of heart disease. Avoiding processed foods, excessive salt, added sugars, and trans fats is equally important.
Physical Activity and Cardiovascular Fitness
Regular physical activity is essential for cardiovascular fitness and overall well-being. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling helps strengthen the heart muscle, improve circulation, and maintain a healthy weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, along with strength training exercises
Stress Management and Emotional Well-being
Stress can take a toll on both our mental and physical health, including the well-being of our hearts. Chronic stress contributes to increased blood pressure, inflammation, and unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating or excessive alcohol consumption.
Implementing stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, regular relaxation, and engaging in activities we enjoy can help protect our hearts and overall well-being.
Regular Health Check-ups and Screenings
Preventive healthcare is crucial for identifying potential health issues before they become major concerns. Regular health check-ups, including blood pressure monitoring, cholesterol screenings, and cardiac evaluations, can provide valuable insights into our heart health.
Early detection of risk factors or abnormalities allows for timely interventions and lifestyle modifications to prevent the progression of heart-related diseases.
If you’re one of those people who catch colds and flu from their coworkers and colleagues, you might think you’re cursed.
Or you might assume that your immune system is crappy, and just resign yourself to spending the entire cold and flu season in bed. But there’s more to why you get sick than just a weak immune system. Here are some common reasons for catching illnesses:
Stress weakens the immune system
Researchers have long wondered whether psychological stress affects the immune system. The association between stress and a reduced immune defense has been established, but the mechanisms behind this link remain largely undefined.
A recent study led by Inserm research director Sophie Ugolini suggests that the relationship is mostly mediated by a particular receptor on cell surfaces: the b2-adrenergic receptor.
The study suggests that these receptors may be responsible for the association between stress and a weakened immune system.
Previous studies have shown that prolonged psychological stress causes changes in the immune system. It decreases immunity, makes people more vulnerable to disease, and speeds up aging.
In a 2004 research meta-analysis, researchers found that chronic stress weakens the immune system on a cellular and hormonal level. These findings are consistent with previous findings showing that people under prolonged stress are more susceptible to disease.
Researchers continue to investigate the mechanisms behind the connection between prolonged stress and lowered immune function.
Chronic stress
If you feel overwhelmed by work and other demands on your time, you may be suffering from chronic stress. Stress can take a toll on your health, making you prone to illness.
To manage chronic stress, you may need to seek professional help, or simply learn how to relax and cope with stressful situations.
Listed below are some helpful techniques that can help you cope with chronic stress. These techniques can help you overcome the effects of stress on your health and work performance.
Acute stress triggers the body to release certain hormones. These hormones increase the heartbeat, make muscles tense, and alert the brain. These responses are necessary for survival and help you cope with a stressful situation, but chronic stress can lead to various health conditions.
Chronic stress is one of the most dangerous types of stress because it impairs the body’s normal functions and makes you more susceptible to illnesses.
Sleep deprivation
If you are suffering from chronic sleep deprivation, you may be more susceptible to illness than you think. Not getting enough sleep can have many health consequences, including the risk of developing chronic health problems.
Fortunately, there are several things you can do to fix this problem. If you don’t get enough sleep, you should consult your doctor. There are also ways to combat this problem, including reducing caffeine in your daytime routine.
Not only does sleep deprivation affect your health, but it can also have long-term effects on your mood, energy level, and performance. Your immune system is negatively affected, and your reflexes are affected. Your memory and learning abilities may suffer.
Your heart may also be affected. It can also affect your sexual drive and affect your ability to deal with stress. You may also experience more heartburn and other problems with your esophagus if you are not getting enough sleep.
Long-term stress
There are several possible reasons that long-term stress makes us sick. In addition to contributing to physical ailments, chronic stress can affect our mental health. Stress triggers our body to go into “fight-or-flight” mode, which is designed to protect us in potentially dangerous situations.
This response increases blood pressure and heart rate and causes a range of other symptoms. When the perceived threat subsides, our body’s functions return to normal.
Research shows that prolonged stress has a negative impact on the immune system. In a 1991 study, researchers assessed the connection between psychological stress and immune response.
In the study, 394 healthy adults were exposed to five different respiratory viruses and were monitored for their symptoms. Participants with higher underlying stress levels had a greater risk of becoming ill.
Many studies have since confirmed this link. Moreover, stress is associated with an increased risk of the common cold, asthma, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Infections can spread from person to person
Infections can be passed from person to person by contact with certain types of food, water, and other surfaces. In addition to human contact, some germs can also spread to animals and pets.
In addition, to direct contact, infectious diseases can be spread indirectly through sexual activity or contact with certain types of environmental materials. In some cases, infections can develop from the microbes on the body of the person infected.
Some infections are transmitted directly, such as gonorrhea and rubella. These infections can also be transmitted indirectly through skin contact or by transferring blood from one person to another.
Cytomegalovirus, for example, is transmitted through a break in skin or needlestick injury. In addition, it can also be transferred through fecal-oral contact and contaminated surfaces. In other cases, an individual may contract the infection without being aware of it.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about illness, heart health, and overall well-being:
Can stress really impact my heart health?
Absolutely, stress can have a significant impact on your heart health. When you experience stress, your body releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can increase your heart rate and blood pressure. These physiological responses are part of the body’s natural “fight or flight” response to stress.
However, if stress becomes chronic and prolonged, it can have detrimental effects on your cardiovascular system. Elevated blood pressure over an extended period puts strain on your heart, increasing the risk of developing heart disease.
Stress can also contribute to the formation of arterial plaque, which can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the narrowing and hardening of the arteries.
Furthermore, stress can influence your behavior and lifestyle choices. Many people resort to unhealthy coping mechanisms when under stress, such as overeating, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or a sedentary lifestyle. These behaviors can further increase the risk of heart disease.
To protect your heart health, it’s crucial to manage and reduce stress levels. Engaging in relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga can help promote a sense of calm and lower your blood pressure.
Regular physical activity and exercise release endorphins, which are natural mood boosters and can help reduce stress. It’s also important to prioritize self-care, engage in activities you enjoy, and maintain a strong support system of family and friends.
If you find that stress is significantly impacting your daily life and well-being, it’s advisable to seek support from a healthcare professional or therapist who can provide guidance and strategies to manage stress effectively.
Remember, taking care of your mental and emotional health is just as important as caring for your physical well-being, and both are interconnected when it comes to maintaining a healthy heart.
How does genetics influence the development of heart diseases?
- Inherited Conditions: Some heart diseases are directly inherited from parents. These conditions are caused by specific gene mutations that affect the structure or function of the heart. Examples include familial hypercholesterolemia, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and familial dilated cardiomyopathy. If a close family member has been diagnosed with one of these conditions, there may be an increased risk of developing the same condition due to shared genetic factors.
- Genetic Markers and Risk Factors: Genetic variations, known as genetic markers, can impact an individual’s risk of developing heart disease. Researchers have identified certain gene variants associated with an increased risk of conditions like coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, and atrial fibrillation. These genetic markers interact with environmental factors, such as diet and lifestyle, to influence disease development.
- Gene-Environment Interactions: Genetics and the environment interact in complex ways when it comes to heart disease. While genetic factors can increase susceptibility to certain conditions, environmental factors, such as diet, physical activity, smoking, and stress, also play a significant role.
- The interplay between genetics and lifestyle choices can determine the actual manifestation and severity of heart diseases. For example, an individual with a genetic predisposition to high blood pressure may be more likely to develop the condition if they lead a sedentary lifestyle and have a poor diet.
- Pharmacogenetics: Genetic variations can influence an individual’s response to medications used to treat heart diseases. Certain genetic markers can impact how the body metabolizes and responds to specific drugs.
- Pharmacogenetic testing can help identify genetic variations that may influence medication effectiveness or potential adverse reactions. This personalized approach allows healthcare providers to prescribe medications tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, optimizing treatment outcomes.
It’s important to note that while genetics can contribute to the development of heart diseases, they are not the sole determining factor. Lifestyle choices, including diet, exercise, and smoking habits, play a significant role in managing and preventing heart diseases, even in individuals with genetic predispositions.
Understanding one’s genetic risk factors can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health, adopt appropriate preventive measures, and work closely with healthcare professionals to manage their heart health effectively.
Is it possible to reverse the effects of an unhealthy diet on the heart?
- Adopting a Heart-Healthy Diet: Start by transitioning to a heart-healthy eating plan, such as the Mediterranean diet or the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. These diets emphasize whole, unprocessed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as fish and poultry), nuts, and seeds. Limit the intake of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars.
- Reducing Salt Intake: High sodium intake is linked to increased blood pressure, which is a risk factor for heart disease. Limiting the consumption of processed and packaged foods, which are often high in sodium, and opting for fresh, homemade meals seasoned with herbs and spices can help lower your overall salt intake.
- Managing Cholesterol Levels: To reduce the effects of an unhealthy diet on cholesterol levels, focus on consuming foods that can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and raise HDL (good) cholesterol levels. Incorporate sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Increase your intake of soluble fiber found in oats, legumes, fruits, and vegetables, as it can help lower LDL cholesterol.
- Increasing Antioxidant-Rich Foods: Antioxidants play a vital role in protecting the heart from oxidative stress and inflammation. Include foods rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, citrus fruits, and dark chocolate, in your diet.
- Moderating Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact heart health. If you choose to drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For men, this means up to two drinks per day, and for women, up to one drink per day.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for heart health. By making positive dietary changes, including portion control, consuming nutrient-dense foods, and incorporating regular physical activity, you can manage your weight effectively and reduce the risk of heart disease.
While adopting a healthy diet is beneficial, it’s important to note that it cannot completely reverse the effects of long-term unhealthy eating habits. The earlier you make positive changes, the better chance you have of improving your heart health.
Additionally, it’s important to combine dietary changes with other lifestyle modifications such as regular exercise, stress management, and avoiding tobacco use for optimal heart health. Consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and support in improving your diet and overall cardiovascular well-being.
What role does sleep play in maintaining heart health?
- Blood Pressure Regulation: During sleep, your blood pressure naturally decreases, allowing your heart and blood vessels to rest and recover. Consistently poor sleep or insufficient sleep can lead to elevated blood pressure, which increases the risk of developing heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions.
- Healthy Heart Rhythm: Sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy heart rhythm. Disruptions in sleep patterns, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, can lead to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias). Prolonged or untreated arrhythmias can have detrimental effects on heart function and increase the risk of heart-related complications.
- Inflammation and Immune Function: Adequate sleep is crucial for reducing inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. Additionally, sleep supports a healthy immune system, which helps protect against infections and other health issues that can impact heart health.
- Metabolic Health: Sleep plays a role in regulating various hormones that influence metabolism, including insulin, ghrelin, and leptin. Poor sleep can disrupt the balance of these hormones, leading to insulin resistance, increased appetite, and weight gain. These factors contribute to the development of conditions like obesity and type 2 diabetes, which are risk factors for heart disease.
- Stress Management: Quality sleep is essential for managing stress levels. Chronic sleep deprivation or poor sleep quality can contribute to increased stress hormones, such as cortisol, which can raise blood pressure and negatively impact heart health. On the other hand, sufficient sleep promotes relaxation and helps reduce stress levels, supporting optimal heart health.
To prioritize sleep for better heart health, aim for 7 to 9 hours of quality sleep each night. Establish a consistent sleep schedule, create a conducive sleep environment (cool, dark, and quiet), and practice good sleep hygiene habits, such as avoiding caffeine and electronic devices before bedtime. If you suspect a sleep disorder or are experiencing symptoms like excessive daytime sleepiness or loud snoring, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Remember, taking care of your sleep is not only beneficial for your overall well-being but also plays a vital role in maintaining a healthy heart.
Are all infectious agents equally harmful to the heart?
- Bacterial Infections: Certain bacterial infections can directly affect the heart and lead to conditions such as endocarditis, myocarditis, or pericarditis. Endocarditis is an infection of the inner lining of the heart chambers or heart valves. Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, while pericarditis is the inflammation of the outer lining surrounding the heart. Examples of bacteria that can cause these infections include Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Chlamydia.
- Viral Infections: Viral infections can also impact the heart. Some viruses, such as enteroviruses, adenoviruses, and the influenza virus, can cause myocarditis, leading to inflammation and damage to the heart muscle. Additionally, certain viral infections, like COVID-19, have been associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular complications, including myocarditis and blood clot formation.
- Parasitic Infections: While less common, parasitic infections can affect the heart as well. For example, Chagas disease, caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi, can lead to chronic inflammation of the heart muscle, potentially resulting in heart failure or arrhythmias.
- Fungal Infections: Fungal infections are relatively rare causes of heart-related complications. However, certain fungal infections, such as aspergillosis or histoplasmosis, can occasionally affect the heart, leading to conditions like endocarditis or myocarditis.
It’s important to note that the severity of the cardiac impact can vary among individuals. Factors such as the strength of the immune system, pre-existing heart conditions, and the specific characteristics of the infectious agent all contribute to the overall risk and severity of cardiac complications.
Prompt diagnosis and appropriate treatment of infectious agents are vital in preventing or minimizing potential harm to the heart. Timely medical intervention, including antimicrobial medications, antiviral therapies, or specific treatments targeted at the underlying cause, can help manage the infection and mitigate the risk of heart-related complications.
If you suspect an infection or experience symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or unexplained fatigue, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. A healthcare professional can assess your symptoms, perform appropriate diagnostic tests, and provide the necessary treatment to address the infection and protect your heart health.
The human body is a marvel of complexity, and understanding why people get sick is a crucial step toward protecting our health, particularly our hearts. Various factors, including infectious agents, lifestyle choices, and genetic predisposition, can influence our susceptibility to illness.
Taking proactive measures, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and undergoing regular health check-ups, can significantly contribute to maintaining optimal heart health and overall well-being.
By unraveling the mystery behind sickness and prioritizing heart health, we can empower ourselves to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Remember, this article provides valuable insights into the topic of illness and heart health. However, it is essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and guidance based on your specific circumstances. Together, let’s prioritize our health and protect our hearts for a brighter, healthier future.
Health
Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?

Hair Gummies: A Trend Worth Your Time or Just Another Health Fad?
In recent years, hair gummies have taken the health and beauty world by storm, boasting promises of luscious locks and a speedy route to hair health.
But with an array of products flooding the market, it’s essential to separate fact from fiction.
Are these colorful, chewy supplements a miracle solution for your hair troubles, or are they simply a trendy snack with little efficacy?
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the science behind hair gummies, their ingredients, potential benefits, and the questions surrounding their effectiveness.
Understanding Hair Health
The Basics of Hair Growth
To fully grasp the impact of hair gummies, it’s vital to understand how hair grows.
Each strand of hair goes through three main phases:
- Anagen Phase: This is the active growth phase, which can last several years. The length of this phase varies among individuals.
- Catagen Phase: A transitional phase lasting a few weeks, where hair growth slows, and the hair follicle shrinks.
- Telogen Phase: The resting phase, lasting a few months before the hair falls out, making way for new growth.
Hair health is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormones, diet, and overall health.
As such, a balanced approach to hair care, encompassing nutrition, proper hair care routines, and avoiding damaging practices, is essential.
Common Causes of Hair Issues
Hair loss or poor hair health can arise from numerous factors:
- Nutritional Deficiencies: A lack of essential vitamins and minerals can hinder hair growth.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like pregnancy, menopause, and thyroid disorders can significantly affect hair health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can trigger hair loss through a condition known as telogen effluvium.
- Medical Conditions: Certain diseases and medications can also contribute to hair loss.
What Are Hair Gummies?
Hair gummies are dietary supplements designed to promote hair health.
They are usually made with a combination of vitamins, minerals, and sometimes botanical extracts, often marketed as a convenient and tasty alternative to traditional vitamin pills.
Key Ingredients in Hair Gummies
While formulations vary, here are some common ingredients found in hair gummies:
- Biotin: A B-vitamin known for its role in hair and nail health. Biotin deficiencies can lead to brittle hair and hair loss.
- Vitamins A, C, and E: Antioxidants that help protect hair from oxidative stress, promoting a healthy scalp and hair growth.
- Folic Acid: Important for cell growth and regeneration, folic acid is believed to support healthy hair follicles.
- Zinc: Plays a role in hair tissue growth and repair, making it a crucial mineral for maintaining healthy hair.
- Collagen: An essential protein for skin elasticity that may also benefit hair strength and growth.
Do Hair Gummies Really Work?
The Science Behind Hair Gummies
While the ingredients in hair gummies are known to contribute to hair health, the question remains:
Do they work as effectively as claimed?
Here’s what the research suggests:
- Biotin: Studies have shown that biotin can improve hair thickness in those with deficiencies, but most people get sufficient biotin from their diet. Supplementing with biotin may not yield significant benefits for individuals who are not deficient.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Research indicates that vitamins A, C, D, E, and minerals like zinc and iron play a role in maintaining healthy hair. However, simply taking these vitamins in gummy form doesn’t guarantee results unless there’s a deficiency present.
- Collagen: Some studies suggest that collagen supplements can improve hair and skin health by providing amino acids essential for protein synthesis. However, more research is needed to establish direct benefits for hair growth.
User Experiences and Anecdotes
While anecdotal evidence often highlights positive experiences with hair gummies, it’s important to approach these testimonials with caution. Individual results may vary, and factors such as diet, overall health, and genetics play significant roles in hair health.
Potential Benefits of Hair Gummies
While not a miracle solution, hair gummies may offer certain benefits:
- Convenient Form: For those who struggle with swallowing pills, gummies provide a palatable alternative.
- Added Nutrients: If you have a deficiency in specific vitamins or minerals, hair gummies can supplement your diet effectively.
- Increased Awareness of Nutrition: Taking supplements can prompt individuals to pay more attention to their overall nutritional intake.
- Improved Hair Appearance: Users may notice shinier and healthier-looking hair due to the vitamins and antioxidants present in these products.
Are There Risks?
While hair gummies are generally safe, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
- Overconsumption: Gummies are often flavored and sweetened, which may lead to overconsumption and potential digestive issues.
- Sugar Content: Many gummies contain added sugars, which can contribute to other health problems if consumed excessively.
- Interactions with Other Supplements: If you’re taking other vitamins or supplements, it’s essential to ensure you’re not exceeding recommended doses, particularly for fat-soluble vitamins like A and E, which can accumulate in the body.
What Experts Say
Dermatologists and nutritionists often emphasize a balanced diet over reliance on supplements.
They suggest that whole foods—rich in vitamins, minerals, and healthy fats—are the best source for hair health.
Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, and eggs can provide essential nutrients without the added sugars and potential downsides of gummies.
Conclusion:
Fad or Fact?
In conclusion, hair gummies may not be the ultimate solution for hair health, but they can serve as a helpful supplement for those with specific nutritional deficiencies.
They are convenient and may improve the overall appearance of hair for some users. However, it’s crucial to approach them with realistic expectations and prioritize a balanced diet rich in whole foods.
If you’re considering adding hair gummies to your routine, consult with a healthcare provider or nutritionist to ensure you’re making an informed decision that aligns with your health goals.
FAQs
1. Can hair gummies replace a balanced diet?
No, hair gummies are supplements and should not replace a balanced diet. They can help fill nutritional gaps but should be taken alongside a healthy eating plan.
2. How long does it take to see results from hair gummies?
Results vary, but users may start noticing improvements in hair texture and appearance after 4-12 weeks of consistent use.
3. Are hair gummies safe for everyone?
Most hair gummies are safe for general use; however, individuals with specific health conditions or allergies should consult a healthcare professional before taking them.
4. Can I take hair gummies with other supplements?
Yes, but be cautious of total vitamin and mineral intake to avoid exceeding recommended daily allowances. Consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
5. Are there any side effects of hair gummies?
Some users may experience digestive issues, allergic reactions, or headaches due to high sugar content or specific ingredients. It’s best to start with a small dose to assess tolerance.
References:
Health
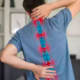
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
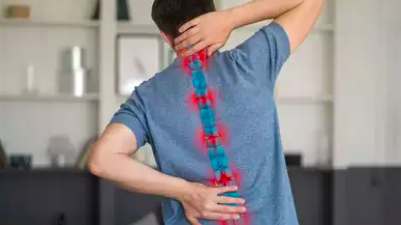
Understanding the Spine: Common Conditions and Effective Solutions
The spine is an essential structure in the human body, acting as a central pillar that supports our posture, facilitates movement, and protects the spinal cord.
Despite its importance, many individuals experience various spine-related conditions that can impact their quality of life.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore common spinal conditions, their causes, symptoms, and effective methods to address them.
What is the Spine?
The spine, also known as the vertebral column, is composed of 33 vertebrae arranged in a flexible yet sturdy structure.
It serves several critical functions:
- Support: The spine supports the head and allows for an upright posture.
- Protection: It encases and protects the spinal cord, a crucial component of the central nervous system.
- Mobility: The spine allows for a wide range of movements, including bending, twisting, and turning.
- Weight Distribution: It helps distribute weight and absorbs shock during activities like walking or running.
Understanding the structure and function of the spine is vital for recognizing and addressing the conditions that can affect it.
Common Spinal Conditions
Several conditions can adversely impact the spine, leading to pain, discomfort, and reduced mobility. Here are some of the most common spinal conditions:
1. Herniated Discs
A herniated disc occurs when the soft inner material of a spinal disc bulges out through a tear in the outer layer. This can compress nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or legs.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Heavy lifting or sudden movements
- Trauma or injury
Symptoms:
- Localized back pain
- Radiating pain to the limbs
- Numbness or tingling
Treatment:
- Physical therapy
- Pain management through medications
- In severe cases, surgery may be required.
2. Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal, which can lead to pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This condition often occurs in the cervical (neck) or lumbar (lower back) regions.
Causes:
- Age-related changes in the spine
- Osteoarthritis
- Herniated discs
Symptoms:
- Pain or cramping in the legs
- Weakness or numbness
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Medications for pain relief
- In some cases, surgical decompression may be necessary.
3. Scoliosis
Scoliosis is an abnormal curvature of the spine, often appearing in childhood or adolescence. While many cases are mild, severe scoliosis can lead to complications.
Causes:
- Idiopathic (unknown cause)
- Congenital (present at birth)
- Neuromuscular conditions
Symptoms:
- Uneven shoulders or hips
- Visible curvature of the spine
- Back pain
Treatment:
- Monitoring and observation for mild cases
- Bracing for growing children
- Surgery for severe curvatures.
4. Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. This is particularly concerning for the vertebrae, which can lead to compression fractures.
Causes:
- Aging
- Hormonal changes
- Lack of calcium and vitamin D
Symptoms:
- Height loss
- Back pain due to fractures
- A stooped posture
Treatment:
- Medications to strengthen bones
- Nutritional supplements (calcium and vitamin D)
- Weight-bearing exercises to improve bone density.
5. Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease refers to the wear and tear of spinal discs over time, leading to pain and reduced flexibility.
Causes:
- Age-related degeneration
- Repetitive stress on the spine
- Genetics
Symptoms:
- Chronic back pain
- Pain that worsens with movement
- Possible radiating pain in the limbs
Treatment:
- Physical therapy and exercise
- Pain management strategies
- Surgical options for severe cases.
Preventing Spinal Conditions
While some spinal conditions are unavoidable due to genetics or aging, many can be prevented or mitigated through healthy lifestyle choices.
Here are some preventative measures:
1. Maintain Good Posture
Proper posture helps reduce strain on the spine. When sitting, keep your back straight, shoulders relaxed, and feet flat on the ground. When standing, distribute your weight evenly on both feet.
2. Stay Active
Regular physical activity strengthens the muscles that support the spine and improves flexibility. Aim for a balanced routine that includes strength training, aerobic exercise, and stretching.
3. Ergonomic Work Environment
If you spend long hours at a desk, ensure your workspace is ergonomically designed. Adjust your chair, desk height, and computer monitor to reduce strain on your back and neck.
4. Healthy Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the spine and helps prevent conditions like degenerative disc disease and spinal stenosis.
5. Avoid Smoking
Smoking impairs blood flow and can lead to spinal degeneration. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and reduce the risk of spinal issues.
Effective Treatments for Spinal Conditions
If you experience spine-related pain or discomfort, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Here are some common treatment options:
1. Physical Therapy
Physical therapists develop personalized exercise programs to strengthen the back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain. They may also use techniques like ultrasound or electrical stimulation to manage discomfort.
2. Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help manage mild to moderate pain. Prescription medications may be necessary for more severe pain or inflammation.
3. Injections
Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis. These are typically used when other treatments have failed.
4. Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. Common surgical procedures include discectomy (removal of herniated disc material), spinal fusion, and laminectomy (removal of part of the vertebra).
5. Alternative Therapies
Complementary treatments like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and massage therapy may provide relief for some individuals. Always consult with a healthcare professional before trying alternative therapies.
Conclusion
Understanding the spine and its common conditions is crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and preventing potential issues.
By recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment, individuals can address spinal conditions effectively.
Implementing preventative measures, such as maintaining good posture and staying active, can significantly reduce the risk of developing spine-related issues.
Prioritize your spinal health, consult with professionals when necessary, and take proactive steps to ensure a healthy and pain-free back.
FAQs
1. What are the common symptoms of spinal conditions?
Common symptoms include localized back pain, radiating pain in the limbs, numbness, tingling sensations, and difficulty with movement.
2. How can I improve my posture while working?
To improve your posture at work, adjust your chair and desk height, use a supportive chair, and ensure your computer screen is at eye level.
3. Can physical therapy help with spinal conditions?
Yes, physical therapy can help strengthen back muscles, improve flexibility, and alleviate pain associated with various spinal conditions.
4. When should I see a doctor for back pain?
If you experience persistent back pain that does not improve with rest, is accompanied by numbness or weakness, or interferes with daily activities, it’s essential to see a doctor.
5. Are there lifestyle changes I can make to prevent spinal issues?
Yes, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, practicing good posture, and avoiding smoking can help prevent spinal conditions.
References:
Health
Understanding the Causes of Premature Menopause in Women
-

 Trending Stories1 year ago
Trending Stories1 year agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health5 years ago
Health5 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health6 months ago
Health6 months agoHow Do Pawpaw Seeds Support Cardiovascular Health?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know