Health
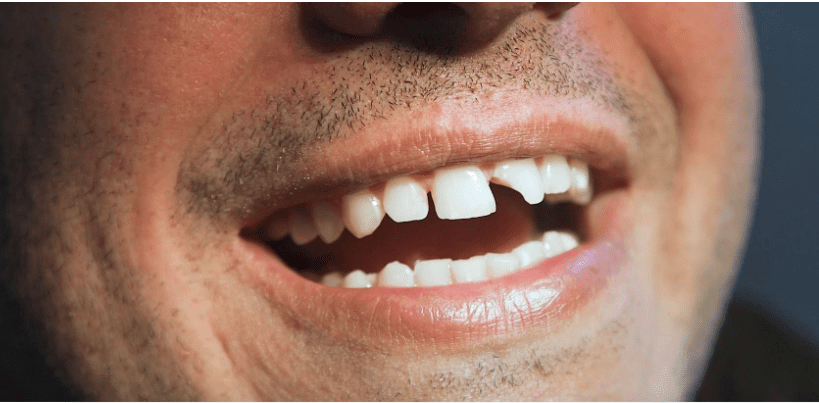
Why Are Teeth Breaking? 5 Things You Need To Know
Last Updated on June 27, 2023 by Nurse Vicky
Why Are Teeth Breaking? 5 Things You Need To Know
Teeth breaking or tooth fracture is a common dental problem. It might seem like a sudden and unexpected mishap, but more often than not, it is the result of a long-standing, unseen issue.
This guide delves into the reasons why teeth break, its effects, and how to prevent them. We’ll also examine several solutions for teeth-breaking problems and essential dental hygiene practices for overall oral health.
Understanding Teeth Breaking
The Basics
A tooth may break due to several reasons, including trauma, grinding, or biting on something hard. In many cases, a tooth may break because of decay that weakens the tooth structure.
Effects on Oral Health
When teeth break, it can lead to significant dental health problems. Apart from discomfort and pain, broken teeth can lead to infections if not treated promptly, ultimately affecting your overall oral health.
Top Five Reasons for Teeth Breaking
To help you understand the phenomenon better, let’s explore the top five reasons why teeth break.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a common culprit behind teeth breaking. Decay weakens the tooth, making it susceptible to fractures. Regular dental checkups can help detect and treat tooth decay early.
Teeth Grinding
Teeth grinding, or bruxism is another major factor contributing to teeth breaking. Over time, the constant grinding wears down the tooth enamel, increasing the risk of a break.
Poor Nutrition
A diet low in essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D can lead to weaker teeth and thus increase the chance of teeth breaking.
Trauma
Accidents falls, or sports-related incidents can lead to broken teeth. In these cases, emergency dental care is essential to prevent further complications.
Aging
As we age, our teeth naturally wear down, and their strength decreases. This can make them more susceptible to breaking.
Effects of Teeth Breaking
Broken teeth can result in a variety of complications. Let’s explore the effects of this common dental issue.
Pain and Discomfort
One of the immediate consequences of a broken tooth is pain and discomfort. Depending on the extent of the break, the pain can range from mild to severe.
Difficulty in Eating
A broken tooth can cause difficulty in eating, limiting your food choices and affecting your nutrition.
Cosmetic Issues
A broken tooth, especially if it’s in the front, can affect your smile and overall appearance, leading to self-esteem issues.
Risk of Infection
If not treated promptly, a broken tooth can expose the inner layers of your tooth to bacteria, leading to infections and potential tooth loss.
Preventing Teeth Breaking
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some ways to prevent teeth from breaking.
Maintain Good Oral Hygiene
Regular brushing and flossing can help prevent tooth decay, a significant factor in teeth breaking.
Wear a Mouthguard
If you’re involved in sports or suffer from bruxism, consider wearing a mouthguard to protect your teeth from trauma or excessive pressure.
Regular Dental Checkups
Regular dental checkups can detect early signs of tooth decay or damage, allowing for timely intervention.
Maintain a Balanced Diet
A diet rich in essential nutrients like calcium and vitamin D can help maintain strong and healthy teeth.
Treating Broken Teeth
Treatment for a broken tooth depends on the severity of the break. Here are a few common solutions.
Dental Filling or Bonding
For minor tooth fractures, your dentist might recommend dental fillings or bonding. This procedure involves using a tooth-colored
If a larger piece of your tooth breaks off, or there is significant decay, your dentist may grind or file part of the remaining tooth and cover it with a crown, or tooth-shaped cap, to protect the tooth and improve its appearance.
Root Canal Therapy
When a break or crack extends into the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be necessary. This procedure involves removing the damaged pulp, cleaning and disinfecting the pulp chamber, and then filling it with a rubber-like material.
Dental Implants
In cases where the tooth cannot be saved, it may need to be extracted. A dental implant can replace the missing tooth. The implant acts as a new tooth root, and a crown is attached to provide a functional and aesthetic replacement for the lost tooth.
FAQs
Why do teeth break?
Teeth can break due to various reasons, including tooth decay, trauma, teeth grinding, poor nutrition, and age-related wear and tear.
What should I do if my tooth breaks?
If your tooth breaks, it’s important to see a dentist as soon as possible. They can determine the extent of the damage and suggest the best course of treatment.
Can a broken tooth heal itself?
Unlike bones, a broken tooth cannot heal itself and needs professional dental care.
How can I prevent my teeth from breaking?
Good oral hygiene, a balanced diet, regular dental checkups, and using a mouthguard while playing sports or if you grind your teeth, can help prevent teeth from breaking.
What are the treatments for a broken tooth?
The treatment depends on the severity of the break. Options include dental fillings, crowns, root canals, and dental implants.
Does a broken tooth always hurt?
Not always. Sometimes a broken tooth may not hurt at all. However, if the break has exposed the nerve inside the tooth, it can be extremely painful.
Can a tooth break due to decay?
Yes, tooth decay can weaken the structure of the tooth, making it susceptible to breakage.
How is a broken front tooth repaired?
Depending on the extent of the damage, a broken front tooth can be repaired using bonding, veneers, or dental crowns.
Can I wait to see a dentist if my tooth breaks?
It’s advisable to see a dentist as soon as possible after a tooth breaks to prevent further complications, such as infection.
Are teeth grinding bad for my teeth?
Yes, teeth grinding can wear down your tooth enamel and lead to tooth sensitivity, tooth breakage, and other dental problems.
Tooth breakage is a common dental issue that can result from various factors such as tooth decay, trauma, bruxism, poor nutrition, and aging. It can lead to pain, discomfort, difficulty in eating, cosmetic issues, and an increased risk of infection.
However, with good oral hygiene practices, a balanced diet, regular dental checkups, and appropriate preventive measures, it’s possible to minimize the risk of tooth breakage.
If a tooth break does occur, treatments such as dental fillings, crowns, root canals, and dental implants can effectively manage the situation. Regular dental care is paramount to keep such problems at bay and maintain a healthy smile
Health
Understanding the Surge in Prostate Cancer: What You Need to Know
Health
How Often Do I Need to Get the Yellow Fever Vaccine?
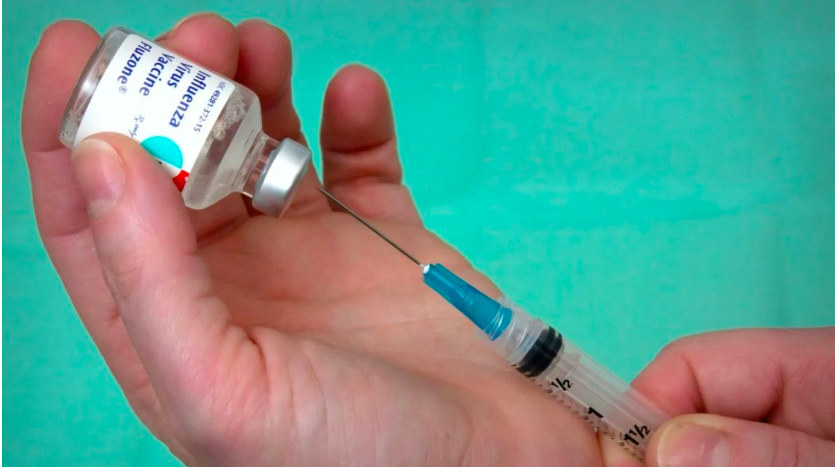
Health
Conquering Yellow Fever: How Long Does the Vaccine’s Shield Last?
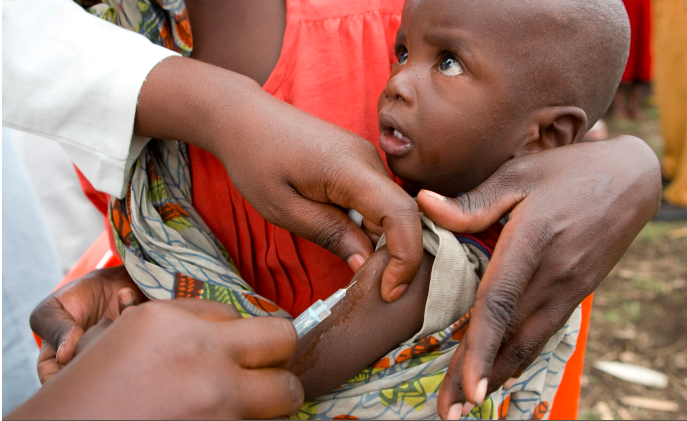
Conquering Yellow Fever: How Long Does the Vaccine’s Shield Last?
Imagine this: you’re backpacking through the lush rainforests of South America, the vibrant sights and sounds filling your senses with wonder. But lurking beneath this beauty is a silent threat – yellow fever.
This mosquito-borne illness can wreak havoc on your travel dreams, and worse, your health. Thankfully, a powerful weapon exists in our arsenal: the yellow fever vaccine.
But a crucial question lingers:
How long does the yellow fever vaccine immunity last?
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the world of yellow fever vaccination, exploring its effectiveness, duration of protection, and factors influencing immunity. We’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about safeguarding your health on your next adventure.
Understanding Yellow Fever: The Pesky Pathogen
Yellow fever is a viral infection transmitted through the bite of infected Aedes mosquitos. These tiny terrors are most active during the day, making daytime protection crucial in endemic areas.
The virus attacks the liver, kidneys, and muscles, causing a range of unpleasant symptoms like fever, nausea, vomiting, and muscle pain. In severe cases, it can lead to bleeding complications and even death.
The Hero in Disguise: The Yellow Fever Vaccine
The yellow fever vaccine is a single-dose marvel of modern medicine. It works by introducing a weakened form of the yellow fever virus to your body. This triggers your immune system to develop antibodies, creating a shield against future exposure.
Here’s the exciting part: the World Health Organization (WHO) considers a single dose of the yellow fever vaccine to provide lifelong immunity [link to WHO yellow fever vaccine page]. That’s right, one shot can potentially protect you for life! However, there are some nuances to consider, which we’ll explore next.
The Immunity Equation: Factors at Play
While lifelong immunity is the ideal scenario, several factors can influence how long the vaccine’s protection lasts:
- Age at Vaccination: Infants vaccinated before 9 months of age might require a booster dose later in life due to a less robust initial immune response.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS, certain cancers, or immunosuppressive medications might require a booster dose for optimal protection.
- Travel History: Travelers visiting areas with high yellow fever activity, particularly those with ongoing outbreaks, might be advised to get a booster dose as a precaution by some countries.
Booster Doses: When Are They Necessary?
While a single dose is generally considered sufficient, there are situations where a booster dose might be recommended.
Here’s a breakdown:
- Individuals vaccinated before 1971: Earlier vaccines might have had slightly lower efficacy. Consulting a healthcare professional for guidance is advisable.
- Travelers to high-risk areas: Some countries with ongoing outbreaks might have stricter entry requirements, mandating a booster dose within a specific timeframe (often 10 years) of the initial vaccination.
- Always check the latest travel advisories for your destination.
- People with weakened immunity: Those with compromised immune systems should consult a healthcare professional to determine if a booster dose is necessary.
Remember: Consulting a healthcare professional or travel clinic before any trip is vital. They can assess your risk factors and advise on the need for a booster dose based on your specific situation and travel itinerary.
Frequently Asked Questions on Yellow Fever Vaccine
Here are some frequently asked questions to address lingering concerns:
Is the yellow fever vaccine safe?
Generally, the yellow fever vaccine is safe for most healthy adults and children. However, as with any medication, there can be mild side effects like headache, muscle aches, or mild fever. Serious side effects are extremely rare. Discussing any concerns with a healthcare professional is always recommended.
How long does it take for the yellow fever vaccine to become effective?
The yellow fever vaccine offers significant protection within 7 to 10 days of vaccination, with immunity reaching near-optimal levels within 30 days.
Can I travel immediately after getting the yellow fever vaccine?
While the vaccine offers some protection within days, it’s best to wait 10 days before traveling to allow your body to develop full immunity.
Are there any alternatives to the yellow fever vaccine?
Unfortunately, there is no alternative to the yellow fever vaccine for preventing the disease.
What should I do if I experience symptoms suggestive of yellow fever after traveling to a high-risk area?
Seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for a good prognosis.
Can I get the yellow fever vaccine if I’m pregnant?
Generally, pregnancy is a contraindication for the yellow fever vaccine. However, in exceptional circumstances, with a high risk of exposure
-

 Trending Stories11 months ago
Trending Stories11 months agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health4 years ago
Health4 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know
-
![How important is food in your life - Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips] 113 how important is food in your life - meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [ 7 tips ]](https://nursevicky.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Screen-Shot-2021-11-04-at-7.47.57-AM.png)
![How important is food in your life - Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips] 114 how important is food in your life - meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [ 7 tips ]](https://nursevicky.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Screen-Shot-2021-11-04-at-7.47.57-AM.png) Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoHow important is food in your life – Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips]