Health
Preventing COVID-19 During Pregnancy: Essential Precautions for Expecting Mothers
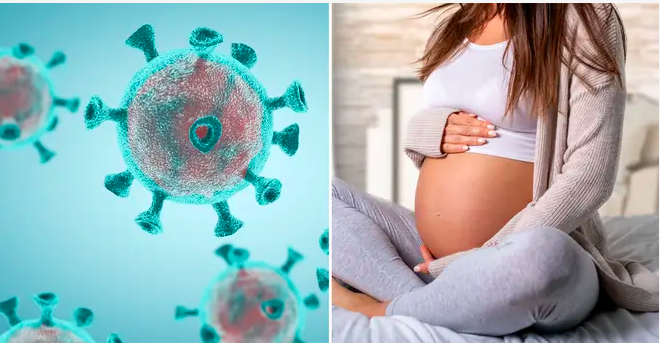
Preventing COVID-19 During Pregnancy: Essential Precautions for Expecting Mothers
As the world continues to grapple with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, it is crucial for everyone, including pregnant women, to take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their unborn babies.
Pregnancy is a delicate phase, and expectant mothers need to be extra cautious to minimize the risk of contracting the virus. In this article, we will discuss the essential precautions that pregnant women should take to prevent COVID-19 and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
First and foremost, it is important for pregnant women to practice good hand hygiene. This means washing hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds. If soap and water are not readily available, using hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol can be an effective alternative.
It is also advisable to avoid touching the face, especially the eyes, nose, and mouth, as this can be a common way for the virus to enter the body.
In addition to hand hygiene, pregnant women should also practice social distancing. This means maintaining a distance of at least six feet from others, especially those who are sick or showing symptoms of COVID-19.
It is important to avoid crowded places and gatherings where the risk of exposure to the virus is higher. If it is necessary to go out in public, wearing a mask can provide an extra layer of protection.
Furthermore, pregnant women should be mindful of their overall health and well-being during this time. It is important to eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep to support a strong immune system.
Additionally, staying hydrated and managing stress levels can also contribute to a healthy pregnancy. Taking prenatal vitamins as prescribed by a healthcare provider is also crucial to ensure that both the mother and baby are getting the necessary nutrients.
Regular prenatal care is essential for pregnant women, even during the pandemic. It is important to attend all scheduled appointments with healthcare providers and follow their recommendations.
Telehealth appointments may be an option for certain check-ups, but in-person visits are necessary for certain tests and procedures. Healthcare providers will also be able to guide any specific concerns or questions related to COVID-19 and pregnancy.
In conclusion, pregnant women need to take extra precautions to prevent COVID-19 and ensure a healthy pregnancy. Practicing good hand hygiene, maintaining social distancing, and taking care of overall health are essential steps in minimizing the risk of contracting the virus.
Regular prenatal care and following healthcare provider’s recommendations are also crucial during this time. By taking these precautions, expectant mothers can protect themselves and their unborn babies from COVID-19 and have a safe and healthy pregnancy.
Understanding the Risks for Pregnant Women
Pregnant women are generally considered to be at a higher risk of developing severe complications from respiratory infections. This is because pregnancy can alter the immune system and make expectant mothers more susceptible to respiratory viruses like COVID-19.
Additionally, pregnant women with underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or obesity may face an even greater risk.
It is important to note that while the overall risk of severe illness or complications from COVID-19 is low for pregnant women, taking preventive measures is crucial to safeguard both maternal and fetal health.
One of the main concerns for pregnant women is the potential impact of COVID-19 on the developing fetus. Research suggests that the virus can cross the placenta and infect the fetus, leading to adverse outcomes such as preterm birth, fetal distress, or even stillbirth. However, it is important to note that these cases are relatively rare, and most babies born to mothers with COVID-19 are healthy.
Another risk factor for pregnant women is the potential exacerbation of underlying health conditions. Conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and obesity can increase the risk of severe illness from COVID-19 in general.
However, when combined with pregnancy, these conditions may further elevate the risk. Pregnant women with these underlying health conditions should take extra precautions to minimize their exposure to the virus and seek medical advice promptly if they develop any symptoms.
Furthermore, pregnant women are more likely to experience severe symptoms if they contract COVID-19. Respiratory infections can put additional strain on the body during pregnancy, leading to complications such as pneumonia or respiratory failure.
This is why pregnant women must practice strict preventive measures, including wearing masks, practicing good hand hygiene, and maintaining social distancing.
While the risk of severe illness or complications from COVID-19 is low for pregnant women overall, it is important to remember that every pregnancy is unique. Factors such as gestational age, overall health, and access to healthcare can all influence the outcomes for pregnant women with COVID-19.
Therefore, it is essential for expectant mothers to stay informed, follow the guidance of healthcare professionals, and prioritize their health and the health of their unborn child.
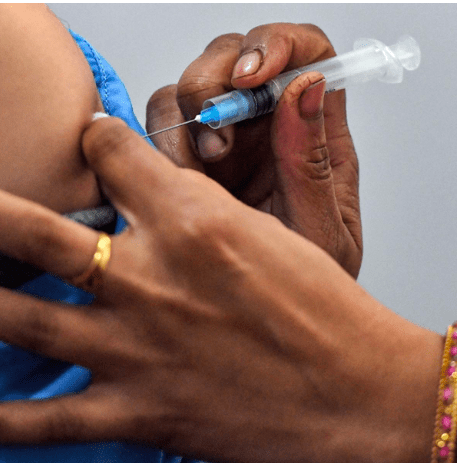
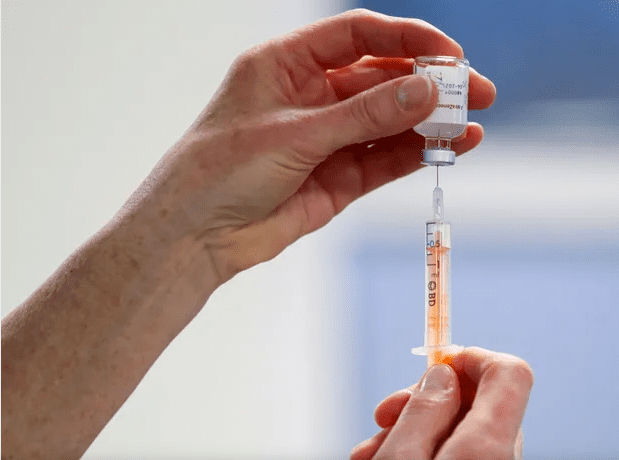
Get Vaccinated: Vaccination against COVID-19 is an important step in protecting both pregnant women and their unborn babies. It is recommended that pregnant women consult with their healthcare providers to discuss the benefits and risks of vaccination and make an informed decision based on their individual circumstances.
Take Extra Precautions in High-Risk Situations: Pregnant women who work in healthcare settings or have close contact with individuals who are at a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 should take extra precautions. This may include wearing additional personal protective equipment, following strict infection control measures, and minimizing exposure as much as possible.
Ensure a Clean and Sanitized Environment: Pregnant women should ensure that their living spaces are clean and properly sanitized. Regularly disinfect frequently touched surfaces such as doorknobs, light switches, and countertops. Good ventilation is also important to improve air circulation.
Seek Medical Help if Experiencing Symptoms: If a pregnant woman experiences symptoms such as fever, cough, difficulty breathing, or loss of taste or smell, it is important to seek medical help promptly. Healthcare providers can provide guidance and determine if further testing or treatment is necessary.
Communicate with Healthcare Providers: Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial during this time. Pregnant women should inform their healthcare providers about any potential exposure to COVID-19 or any changes in their health status. This will help healthcare providers in providing appropriate care and guidance.
Take Care of Mental Health: The pandemic and its associated stressors can take a toll on mental health. Pregnant women should prioritize self-care and seek support if needed. This may include reaching out to mental health professionals, joining support groups, or talking to trusted friends and family members.
Encourage Supportive Relationships: Building a strong support system is important during pregnancy, especially during challenging times. Pregnant women should seek support from their partners, family members, and friends. Virtual connections can also be valuable in maintaining social connections while practicing physical distancing.
By following these precautions, pregnant women can minimize the risk of COVID-19 and ensure the health and well-being of themselves and their unborn babies.
What to Do If You Suspect COVID-19
If a pregnant woman experiences symptoms such as fever, cough, difficulty breathing, or loss of taste or smell, it is important to seek medical advice promptly. Contacting the healthcare provider and following their instructions is crucial to receive appropriate care and guidance.
It is advisable to call ahead before visiting a healthcare facility to inform them about the symptoms and seek advice on the next steps. Healthcare professionals will provide guidance on whether testing is necessary and the appropriate measures to be taken.
In addition to seeking medical advice, there are several steps a pregnant woman can take if she suspects she may have COVID-19. First and foremost, it is important to self-isolate immediately to prevent the potential spread of the virus to others. This means staying at home and avoiding contact with family members, friends, and colleagues.
During self-isolation, it is essential to monitor symptoms closely and keep a record of any changes or developments. This information will be valuable when discussing the situation with healthcare professionals.
It is also important to maintain good hygiene practices, such as washing hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, using hand sanitizer when soap is not available, and avoiding touching the face.
While self-isolating, it is crucial to take care of one’s physical and mental well-being. This can be achieved by getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and eating a balanced diet.
Engaging in activities that promote relaxation and reduce stress, such as practicing mindfulness or engaging in hobbies, can also be beneficial.
If the symptoms worsen or become severe, it is important to contact the healthcare provider immediately for further guidance.
They may recommend hospitalization or additional treatment options depending on the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s medical history.
It is worth noting that pregnant women may be at a higher risk of developing severe illness from COVID-19 compared to the general population.
Therefore, it is crucial to take all necessary precautions and follow the advice of healthcare professionals to ensure the best possible outcome for both the mother and the baby.
Are there any specific symptoms of COVID-19 that pregnant women should watch out for?
While the symptoms of COVID-19 are similar for pregnant women and the general population, there are a few specific symptoms that pregnant women should be aware of.
These include shortness of breath, persistent chest pain, confusion, and difficulty waking up. If pregnant women experience any of these symptoms, they should seek medical attention immediately.
What precautions should pregnant women take to protect themselves from COVID-19?
Pregnant women should follow the same precautions as the general population to protect themselves from COVID-19. This includes practicing good hand hygiene by washing hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, using hand sanitizer when soap and water are not available, wearing a mask in public settings where social distancing is not possible, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and practicing social distancing by maintaining a distance of at least 6 feet from others.
Should pregnant women avoid routine prenatal care visits during the pandemic?
No, pregnant women should continue to attend their routine prenatal care visits during the pandemic. These visits are important for monitoring the health and development of both the mother and the baby.
Healthcare providers have implemented safety measures to reduce the risk of COVID-19 transmission during these visits, such as limiting the number of individuals in waiting rooms, implementing social distancing measures, and conducting virtual appointments when appropriate.
Are pregnant women at a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 compared to the general population?
There is currently no evidence to suggest that pregnant women are at a higher risk of contracting COVID-19 compared to the general population. However, pregnant women are considered to be at a higher risk of developing severe illness or complications if they do contract the virus, especially if they have underlying health conditions.
Can pregnant women transmit COVID-19 to their partners or other family members?
Yes, pregnant women who are infected with COVID-19 can transmit the virus to their partners or other family members. It is important for pregnant women to take precautions to prevent the spread of the virus, such as wearing a mask, practicing good hand hygiene, and maintaining social distancing.
Should pregnant women avoid travel during the pandemic?
Pregnant women should carefully consider the risks before traveling during the pandemic. The decision to travel should be based on factors such as the destination, the mode of transportation, the prevalence of COVID-19 in the area, and the individual’s health status. Pregnant women should consult with their healthcare providers to assess the risks and make an informed decision.
What support is available for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic?
Various support services are available for pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic. These include telehealth appointments for prenatal care, online support groups and forums, virtual childbirth classes, and access to mental health resources.
Healthcare providers and organizations have adapted their services to ensure that pregnant women receive the necessary support and care during these challenging times.
Health
Can Anxiety Cause Chest Pain While Breathing?

Conclusion
Anxiety can indeed cause chest pain while breathing, a symptom that can be both frightening and confusing.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms and triggers, along with adopting effective coping strategies, can help manage and alleviate this distressing symptom.
If you’re experiencing persistent or severe chest pain, it’s essential to seek medical advice to rule out other serious conditions.
Health
What Causes Chest Pain While Breathing?

Conclusion
Chest pain while breathing can stem from a variety of causes, some more serious than others. Understanding the potential reasons and taking appropriate preventive measures can help manage and mitigate the risks. Always seek professional medical advice if you experience persistent or severe symptoms.
Health
Can I Drink Other Beverages Instead of Water to Stay Hydrated?

Conclusion
While water is the most effective and simplest way to stay hydrated, alternative beverages can also contribute to your fluid intake. Herbal teas, coconut water, infused water, and even milk can be excellent options. However, be mindful of the sugar and calorie content in some of these alternatives.
Incorporating a variety of beverages can make hydration more enjoyable and sustainable. Always listen to your body’s needs and maintain a balanced approach to stay well-hydrated.
-

 Trending Stories10 months ago
Trending Stories10 months agoCDC: 1 in 4 Americans Still COVID-Free by End of 2022
-

 Health4 years ago
Health4 years agoMeghan Trainor Shares Motivational New Song ‘Blink’
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHow Long Does Monkey Pox Last Before It Surfaces in the Body?
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoWhat Causes Swollen Body? Understanding Edema and its Triggers
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoNutrition and the Importance of a Fitness Program – 3 Things to Know
-

 Health3 years ago
Health3 years ago5 Weird Reasons Why Pimples Disappear After Marriage
-

 Health2 years ago
Health2 years agoHealth Benefits Of Pawpaw Seed? 7 Things To Know
-
![How important is food in your life - Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips] 125 how important is food in your life - meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [ 7 tips ]](https://nursevicky.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Screen-Shot-2021-11-04-at-7.47.57-AM.png)
![How important is food in your life - Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips] 126 how important is food in your life - meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [ 7 tips ]](https://nursevicky.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Screen-Shot-2021-11-04-at-7.47.57-AM.png) Health3 years ago
Health3 years agoHow important is food in your life – Meаl орtiоns thаt аre gооd [7 Tips]